Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization
From 2010.igem.org
(→K389015: VirA/G reporter device with luciferase) |
(→K389421, K389422, K389423: Sensitivity Tuner amplified Vir-test system) |
||
| (79 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<style type="text/css"> | <style type="text/css"> | ||
#subnavigation li { | #subnavigation li { | ||
| - | margin-left: | + | margin-left:68px; |
| - | margin-right: | + | margin-right:68px; |
} | } | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<div id="subnavigation"> | <div id="subnavigation"> | ||
<li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results">Results</a></li> | <li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results">Results</a></li> | ||
| - | <li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/ | + | <li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization">Characterization</a></li> |
<li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Used">Used</a></li> | <li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Used">Used</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Submitted">Submitted</a></li> | <li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Submitted">Submitted</a></li> | ||
| - | <li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/ | + | <li><a href="/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Sequencing">Sequencing</a></li> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</body> | </body> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | =<partinfo>K238008</partinfo>: ''virA''= | ||
| + | We wanted to use this part in our project, but could only obtain unexpected/faulty restriction patterns. Finally we chose to sequence the part, hoping to find the cause for the maintained restriction patterns. Unfortunately we could not approve the sequence of <partinfo>BBa_K238008</partinfo> deposited in the parts registry so that we chose to design our own VirA BioBrick. I strongly recommend using our VirA since it has been approved by multiple means, e.g. restriction patterns and sequencing (<partinfo>K389001</partinfo>). | ||
| - | + | =<partinfo>BBa_K238011</partinfo>: ''vir''-promoter= | |
| - | We | + | We wanted to use this part in our project, but could only obtain unexpected/faulty restriction patterns. Finally we chose to sequence the part, hoping to find the cause for the maintained restriction patterns. Unfortunately we could not approve the sequence of <partinfo>BBa_K238011</partinfo> deposited in the parts registry so that we chose to design our own VirA BioBrick. I strongly recommend using our VirA since it has been approved by multiple means, e.g. restriction patterns and sequencing (<partinfo>K389003</partinfo>). |
| - | + | =<partinfo>P1010</partinfo>: ''ccdB''-gene= | |
| - | + | The ''ccdB'' gene targets the gyrase of ''Escherichia coli'' and is lethal for all ''E. coli'' strains without the gyrase mutation gyrA462 ([http://openwetware.org/wiki/CcdB Openwetware]). The ''ccdB'' BioBrick is used for the 3A-assembly as a positive selection marker. | |
| - | The ''ccdB'' gene targets the gyrase of ''Escherichia coli'' and is lethal for all ''E. coli'' strains without the gyrase mutation gyrA462 [ | + | |
We transformed this BioBrick into ''E. coli'' JM109, DH5α, TOP10, XL1-Blue, EC100D and DB3.1. ''E. coli'' JM109, XL1-Blue and DH5α seem to be ''ccdB'' resistant because there were as much colonies after P1010 transformation as observed with DB3.1. The P1010 works as expected in ''E. coli'' TOP10, EC100D (no colonies after transformation) and DB3.1 (many colonies after transformation). | We transformed this BioBrick into ''E. coli'' JM109, DH5α, TOP10, XL1-Blue, EC100D and DB3.1. ''E. coli'' JM109, XL1-Blue and DH5α seem to be ''ccdB'' resistant because there were as much colonies after P1010 transformation as observed with DB3.1. The P1010 works as expected in ''E. coli'' TOP10, EC100D (no colonies after transformation) and DB3.1 (many colonies after transformation). | ||
| - | <center> | + | <center>Table 1: Results of the transformation of the cell-death gene ''ccdB'', BioBrick <partinfo>P1010</partinfo>, into different strains of ''E. coli''. |
| - | Table 1: Results of the transformation of the cell-death gene ''ccdB'', BioBrick <partinfo>P1010</partinfo>, into different strains of ''E. coli''. | + | |
{|cellpadding="10" style="border-collapse: collapse; border-width: 1px; border-style: solid; border-color: #000" | {|cellpadding="10" style="border-collapse: collapse; border-width: 1px; border-style: solid; border-color: #000" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 43: | Line 39: | ||
!style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Resistant to ''ccdB''? | !style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Resistant to ''ccdB''? | ||
!style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Expected result? | !style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Expected result? | ||
| - | !style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Gyrase genotype [ | + | !style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Gyrase genotype <br> ([http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T39-47PNXC3-F3&_user=2459438&_coverDate=01%2F28%2F1994&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000057302&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=2459438&md5=dfcdeab4c210c1f4ec70de318d013c15&searchtype=a Metcalf ''et al.'', 1994]; [http://openwetware.org/wiki/E._coli_genotypes Openwetware]) |
|- | |- | ||
|style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| DB3.1 | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| DB3.1 | ||
| Line 81: | Line 77: | ||
It seems that not only the gyrase mutation gyrA462 is causing a ''ccdB'' resistance. Also the gyrase mutation gyrA96 gives ''E. coli'' a ''ccdB'' resistance. This should be kept in mind when assembling BioBricks with the 3A assembly. | It seems that not only the gyrase mutation gyrA462 is causing a ''ccdB'' resistance. Also the gyrase mutation gyrA96 gives ''E. coli'' a ''ccdB'' resistance. This should be kept in mind when assembling BioBricks with the 3A assembly. | ||
| + | =<partinfo>K389004</partinfo>: Luciferase from pGL4.10[luc2]= | ||
| + | [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389004#mRFP vs. luciferase as reporter gene | For a comparison between mRFP and luciferase as reporter genes click here. ]] | ||
| - | + | Some important parameters determined by the characterization experiments are shown in tab. 2. For more information concerning these experiments click on the corresponding link in tab. 2 or click here: | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <html><div style="font-size:20px; text-align:center; font-weight:bold;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389004">Detailed information...</a></div></html> | |
| - | |||
| - | + | <center>Table 2: Parameters for <partinfo>K389004</partinfo>. | |
| + | {|cellpadding="10" style="border-collapse: collapse; border-width: 1px; border-style: solid; border-color: #000" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Experiment | ||
| + | !style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| Result | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389004#Accumulation of luciferase | Behaviour during cultivation]] | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| | ||
| + | * production is growth dependent | ||
| + | * degradation in stationary growth phase | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389004#Kinetic of luciferin conversion | Kinetic of luciferin conversion]] | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| max. output between 20 - 40 s | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389004#Sensitivity | Limit of detection (LOD)]] | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| 162 RLU ~ 0.3 % of <partinfo>J23103</partinfo> output | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389004#Sensitivity | Limit of quantification (LOQ)]] | ||
| + | |style="border-style: solid; border-width: 1px"| 306 RLU ~ 0.7 % of <partinfo>J23103</partinfo> output | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| - | + | =<partinfo>K389011</partinfo>: VirA screening device= | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | <html><div style="font-size:20px; text-align:center; font-weight:bold;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389011">Detailed information...</a></div></html> | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Bielefeld_LD50_Graph2.jpg|600px|thumb|center|Figure 1: Ratio of surviving colonies of ''E. coli'' EC100D carrying unmutated <partinfo>K389010</partinfo> and <partinfo>K389011</partinfo> plated on PA agar plates with chloramphenicol, ampicillin and different concentrations of kanamycin. Comparison between cells that were induced with acetosyringone with cells that were not induced.]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ]] | + | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | =<partinfo>K389015</partinfo>: VirA/G reporter device with luciferase= | |
| - | + | Some important parameters determined by the characterization experiments are shown in tab. 3. For more information concerning these experiments click on the corresponding link in tab. 3 or click here: | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <html><div style="font-size:20px; text-align:center; font-weight:bold;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389015">Detailed information...</a></div></html> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | <center>Table 3: Parameters for <partinfo>K389015</partinfo>. | |
| + | {|{{Table}} | ||
| + | !Experiment | ||
| + | !Characteristic | ||
| + | !Value | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="4"|[[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389015#Transfer function | Transfer Function]] | ||
| + | |Maximum induction level | ||
| + | |2.2 fold | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Maximum induction level reached | ||
| + | |200 µM acetosyringone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Hill coefficient | ||
| + | |1.09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Switch Point | ||
| + | |31.6 µM acetosyringone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="3"|[[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389015#Growth functions and Luciferase expression for BBa_K389015 | Doubling time / h]] | ||
| + | |without plasmid | ||
| + | |1.98 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |carrying K389015 | ||
| + | |2.24 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |carrying K389015 with 400 µM acetosyringone | ||
| + | |2.67 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="2"|Response time | ||
| + | |Induction: [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389015#Response time | exponential phase]] | ||
| + | |>1 h | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Induction: [[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389015#Data Analysis | begin of cultivation]] | ||
| + | |max. induction at OD<sub>600</sub> = 1 +/- 0.5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="3"|[[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389015#Plasmid conformation analysis | Conformation analysis]] | ||
| + | |ratio ccc monomer / % | ||
| + | |91 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ratio ccc dimer / % | ||
| + | |3.7 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ratio oc forms / % | ||
| + | |5.3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| - | + | =<partinfo>K389016</partinfo>: VirA/G reporter device with mRFP= | |
| - | + | Protocols for [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project/Protocols#Cultivation_for_measuring_mRFP_and_Luciferase_expression Cultivation] and [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project/Protocols#Measuring_of_mRFP Measurement] | |
| - | + | Some important parameters determined by the characterization experiments are shown in tab. 4. For more information concerning these experiments click on the corresponding link in tab. 4 or click here: | |
| - | + | <html><div style="font-size:20px; text-align:center; font-weight:bold;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389016">Detailed information...</a></div></html> | |
| - | |||
| - | 5 | + | <center>Table 4: Parameters for <partinfo>K389016</partinfo>. |
| + | {|{{Table}} | ||
| + | !Experiment | ||
| + | !Characteristic | ||
| + | !Value | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="4"|[[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389016#Transfer function of BBa_K389016 | Transfer Function]] | ||
| + | |Maximum induction level | ||
| + | |2.6 fold | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Maximum induction level reached | ||
| + | |150 µM acetosyringone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Hill coefficient | ||
| + | |1.67 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Switch Point | ||
| + | |26.5 µM acetosyringone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="4"|[[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389016#Growth functions and mRFP expression for BBa_K389016 | Doubling time / h]] | ||
| + | |without plasmid | ||
| + | |1.98 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |carrying K389016 | ||
| + | |2.57 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |carrying K389016 with 150 µM acetosyringone | ||
| + | |2.77 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |carrying K389016 with 1000 µM acetosyringone | ||
| + | |3.01 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="3"|[[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389016#Plasmid conformation analysis | Conformation analysis]] | ||
| + | |ratio ccc monomer / % | ||
| + | |91.2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ratio ccc dimer / % | ||
| + | |3.2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ratio oc forms / % | ||
| + | |5.6 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="5"|[[Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/K389016#Different possible inducers | Inducers]] | ||
| + | |Induction by | ||
| + | |Acetosyringone | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="4"|No Induction by | ||
| + | |Capsaicin | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Dopamine | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Homovanillic acid | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |3-Methoxytyramine | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| - | + | =<partinfo>K389052</partinfo>: Tightly regulated ''lac'' operon with mRFP readout= | |
| + | This construct was plated for plasmid isolation in a ''lacI<sup>q</sup>'' negative ''E. coli'' strain after assembly - and we have never seen such red plates when working with constructs with mRFP downstream of a promoter. This ''lac'' operon definitely shows a very high basal transcription, so it is not tightly repressed. It seems that the ''lacI'' repressor <partinfo>BBa_C0012</partinfo> is not suitable for this purpose due to its LVA degradation tag or it does not work properly. Another indicator for this assumption is the experience page of <partinfo>C0012</partinfo>. | ||
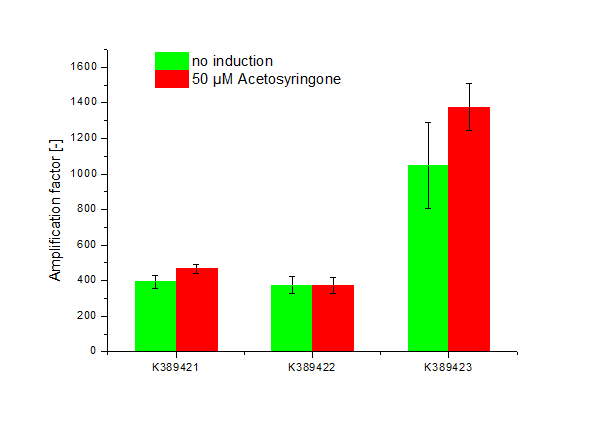
| - | + | =<partinfo>K389421</partinfo>, <partinfo>K389422</partinfo>, <partinfo>K389423</partinfo>: Sensitivity Tuner amplified Vir-test system= | |
| - | |||
| - | + | <html><div style="font-size:20px; text-align:center; font-weight:bold;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/Sen_Tuner">Detailed information...</a></div></html> | |
| - | ''' | + | [[Image:ST Tuner.png|600px|thumb|center| '''Figure 2: Amplification factor of induced, 50 µM Acetosyringone (red) and not induced (green) modified Sensitivity Tuner <partinfo>K389421</partinfo>, <partinfo>K389422</partinfo> and <partinfo>K389423</partinfo>, Standard deviation shown.''']] |
| - | |||
| - | ''' | + | [[Image:Bielefeld_luc.jpg|600px|thumb|center| '''Figure 3: Vizualitation of induced (from left to right) <partinfo>K389421</partinfo>, <partinfo>K389422</partinfo> and <partinfo>K389423</partinfo> sensitivity tuner amplified vir-system.''']] |
| - | |||
| - | + | =Mutated <partinfo>K389001</partinfo> (exemplary): Results of the directed mutagenesis= | |
| - | |||
| - | ---- | + | <html><div style="font-size:20px; text-align:center; font-weight:bold;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Characterization/Exemplary_results_DM">Detailed information...</a></div></html> |
| - | + | [[Image:Bielefeld_results_screening.jpg|600px|thumb|center| '''Figure 4: Luciferase production rates of the exemplary clone “21” are shown under conditions of induction with acetosyringone (21-A), capsaicin (21-C) and in uninduced state (21-U). The right bar indicates the production rate of the native system without acetosyringone (212-U), all the values in the figure had been normalized to.''']] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | =References= | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | = | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | * | + | *Behrens B, Eppendorf AG, Laborpraxis, Nr.20, Reinste Plasmid-DNA in nur 9 Minuten. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | *http://openwetware.org/wiki/CcdB, CcdB (seen on 10.10.10). | |
| - | + | *http://openwetware.org/wiki/E._coli_genotypes, E. coli genotypes (seen on 10.10.10). | |
| - | + | *Metcalf, WW ''et al.'' (1994) [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T39-47PNXC3-F3&_user=2459438&_coverDate=01%2F28%2F1994&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000057302&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=2459438&md5=dfcdeab4c210c1f4ec70de318d013c15&searchtype=a ''Use of the rep technique for allele replacement to construct new Escherichia coli hosts for maintenance of R6Kλ origin plasmids at different copy numbers''], Gene 138(1):1-7. | |
| - | + | *Stadler J, Lemmens R, Nyhammar T 2004, ''Plasmid DNA purification'', The J. of Gene Medicine,Vol.6, pp.54–S66 | |
Latest revision as of 01:07, 28 October 2010
<partinfo>K238008</partinfo>: virA
We wanted to use this part in our project, but could only obtain unexpected/faulty restriction patterns. Finally we chose to sequence the part, hoping to find the cause for the maintained restriction patterns. Unfortunately we could not approve the sequence of <partinfo>BBa_K238008</partinfo> deposited in the parts registry so that we chose to design our own VirA BioBrick. I strongly recommend using our VirA since it has been approved by multiple means, e.g. restriction patterns and sequencing (<partinfo>K389001</partinfo>).
<partinfo>BBa_K238011</partinfo>: vir-promoter
We wanted to use this part in our project, but could only obtain unexpected/faulty restriction patterns. Finally we chose to sequence the part, hoping to find the cause for the maintained restriction patterns. Unfortunately we could not approve the sequence of <partinfo>BBa_K238011</partinfo> deposited in the parts registry so that we chose to design our own VirA BioBrick. I strongly recommend using our VirA since it has been approved by multiple means, e.g. restriction patterns and sequencing (<partinfo>K389003</partinfo>).
<partinfo>P1010</partinfo>: ccdB-gene
The ccdB gene targets the gyrase of Escherichia coli and is lethal for all E. coli strains without the gyrase mutation gyrA462 ([http://openwetware.org/wiki/CcdB Openwetware]). The ccdB BioBrick is used for the 3A-assembly as a positive selection marker. We transformed this BioBrick into E. coli JM109, DH5α, TOP10, XL1-Blue, EC100D and DB3.1. E. coli JM109, XL1-Blue and DH5α seem to be ccdB resistant because there were as much colonies after P1010 transformation as observed with DB3.1. The P1010 works as expected in E. coli TOP10, EC100D (no colonies after transformation) and DB3.1 (many colonies after transformation).
| E. coli strain | Resistant to ccdB? | Expected result? | Gyrase genotype ([http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T39-47PNXC3-F3&_user=2459438&_coverDate=01%2F28%2F1994&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000057302&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=2459438&md5=dfcdeab4c210c1f4ec70de318d013c15&searchtype=a Metcalf et al., 1994]; [http://openwetware.org/wiki/E._coli_genotypes Openwetware]) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DB3.1 | yes | yes | gyrA462 |
| DH5α | yes | no | gyrA96 |
| EC100D | no | yes | WT |
| JM109 | yes | no | gyrA96 |
| TOP10 | no | yes | WT |
| XL1-Blue | yes | no | gyrA96 |
It seems that not only the gyrase mutation gyrA462 is causing a ccdB resistance. Also the gyrase mutation gyrA96 gives E. coli a ccdB resistance. This should be kept in mind when assembling BioBricks with the 3A assembly.
<partinfo>K389004</partinfo>: Luciferase from pGL4.10[luc2]
For a comparison between mRFP and luciferase as reporter genes click here.
Some important parameters determined by the characterization experiments are shown in tab. 2. For more information concerning these experiments click on the corresponding link in tab. 2 or click here:
| Experiment | Result |
|---|---|
| Behaviour during cultivation |
|
| Kinetic of luciferin conversion | max. output between 20 - 40 s |
| Limit of detection (LOD) | 162 RLU ~ 0.3 % of <partinfo>J23103</partinfo> output |
| Limit of quantification (LOQ) | 306 RLU ~ 0.7 % of <partinfo>J23103</partinfo> output |
<partinfo>K389011</partinfo>: VirA screening device

<partinfo>K389015</partinfo>: VirA/G reporter device with luciferase
Some important parameters determined by the characterization experiments are shown in tab. 3. For more information concerning these experiments click on the corresponding link in tab. 3 or click here:
| Experiment | Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Transfer Function | Maximum induction level | 2.2 fold |
| Maximum induction level reached | 200 µM acetosyringone | |
| Hill coefficient | 1.09 | |
| Switch Point | 31.6 µM acetosyringone | |
| Doubling time / h | without plasmid | 1.98 |
| carrying K389015 | 2.24 | |
| carrying K389015 with 400 µM acetosyringone | 2.67 | |
| Response time | Induction: exponential phase | >1 h |
| Induction: begin of cultivation | max. induction at OD600 = 1 +/- 0.5 | |
| Conformation analysis | ratio ccc monomer / % | 91 |
| ratio ccc dimer / % | 3.7 | |
| ratio oc forms / % | 5.3 |
<partinfo>K389016</partinfo>: VirA/G reporter device with mRFP
Protocols for Cultivation and Measurement
Some important parameters determined by the characterization experiments are shown in tab. 4. For more information concerning these experiments click on the corresponding link in tab. 4 or click here:
| Experiment | Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Transfer Function | Maximum induction level | 2.6 fold |
| Maximum induction level reached | 150 µM acetosyringone | |
| Hill coefficient | 1.67 | |
| Switch Point | 26.5 µM acetosyringone | |
| Doubling time / h | without plasmid | 1.98 |
| carrying K389016 | 2.57 | |
| carrying K389016 with 150 µM acetosyringone | 2.77 | |
| carrying K389016 with 1000 µM acetosyringone | 3.01 | |
| Conformation analysis | ratio ccc monomer / % | 91.2 |
| ratio ccc dimer / % | 3.2 | |
| ratio oc forms / % | 5.6 | |
| Inducers | Induction by | Acetosyringone |
| No Induction by | Capsaicin | |
| Dopamine | ||
| Homovanillic acid | ||
| 3-Methoxytyramine |
<partinfo>K389052</partinfo>: Tightly regulated lac operon with mRFP readout
This construct was plated for plasmid isolation in a lacIq negative E. coli strain after assembly - and we have never seen such red plates when working with constructs with mRFP downstream of a promoter. This lac operon definitely shows a very high basal transcription, so it is not tightly repressed. It seems that the lacI repressor <partinfo>BBa_C0012</partinfo> is not suitable for this purpose due to its LVA degradation tag or it does not work properly. Another indicator for this assumption is the experience page of <partinfo>C0012</partinfo>.
<partinfo>K389421</partinfo>, <partinfo>K389422</partinfo>, <partinfo>K389423</partinfo>: Sensitivity Tuner amplified Vir-test system
Mutated <partinfo>K389001</partinfo> (exemplary): Results of the directed mutagenesis

References
- Behrens B, Eppendorf AG, Laborpraxis, Nr.20, Reinste Plasmid-DNA in nur 9 Minuten.
- http://openwetware.org/wiki/CcdB, CcdB (seen on 10.10.10).
- http://openwetware.org/wiki/E._coli_genotypes, E. coli genotypes (seen on 10.10.10).
- Metcalf, WW et al. (1994) [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T39-47PNXC3-F3&_user=2459438&_coverDate=01%2F28%2F1994&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000057302&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=2459438&md5=dfcdeab4c210c1f4ec70de318d013c15&searchtype=a Use of the rep technique for allele replacement to construct new Escherichia coli hosts for maintenance of R6Kλ origin plasmids at different copy numbers], Gene 138(1):1-7.
- Stadler J, Lemmens R, Nyhammar T 2004, Plasmid DNA purification, The J. of Gene Medicine,Vol.6, pp.54–S66
 "
"