Team:Heidelberg/Project/miRNA Kit
From 2010.igem.org
(→Results) |
(→Results) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
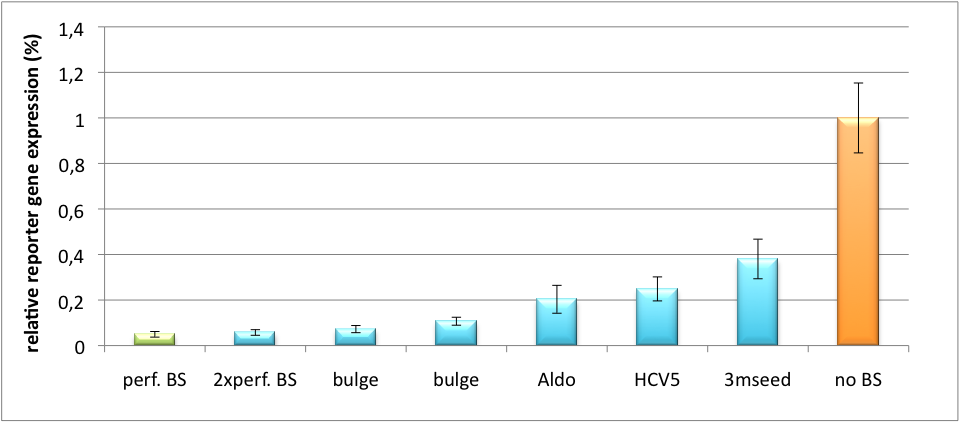
[[Image:PsiCheck.png|thumb|center|600px|'''Figure 3: Tuning of gene expression through different imperfect miR122 binding sites in psiCHECK-2.''' Construct was transfected into HeLa cells together with an plasmid expressing miR122. Control without binding site was used for normalization.]] | [[Image:PsiCheck.png|thumb|center|600px|'''Figure 3: Tuning of gene expression through different imperfect miR122 binding sites in psiCHECK-2.''' Construct was transfected into HeLa cells together with an plasmid expressing miR122. Control without binding site was used for normalization.]] | ||
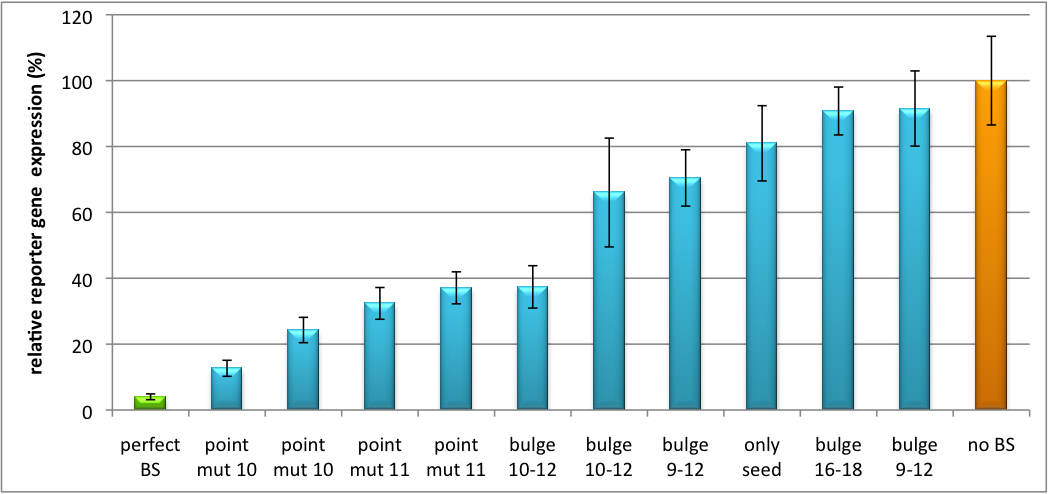
Measurements were done in HeLa cells overexpressing miR122 from plasmid. Besides that, even endogenous miR122 levels were sufficient for off-targeting HuH cells (Fig. 4). A single perfect binding site leads to 95% knockdown, which seems to be maximum, since even a perfect binding site duplicate results in the same reporter gene expression. | Measurements were done in HeLa cells overexpressing miR122 from plasmid. Besides that, even endogenous miR122 levels were sufficient for off-targeting HuH cells (Fig. 4). A single perfect binding site leads to 95% knockdown, which seems to be maximum, since even a perfect binding site duplicate results in the same reporter gene expression. | ||
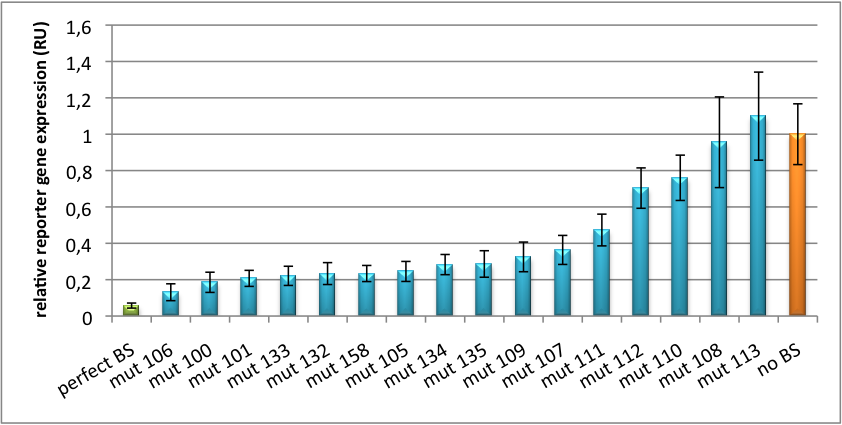
| - | + | [[Image:HuH Offpng.png|thumb|center|500px|'''Figure 4: Knockdown of reporter gene expression due to endogenous miR122 that interferes with binding sites.''' Construct transfected to HuH cells to off-target those.]] | |
| - | [[Image:HuH Offpng.png|thumb|500px|'''Figure 4: Knockdown of reporter gene expression due to endogenous miR122 that interferes with binding sites.''' Construct transfected to HuH cells to off-target those.]] | + | |
<!--After creating a binding site library and testing the miRNA-binding site interaction <i>in vitro</i>, we were able to compute an [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Modeling/miGUI <i>in silico</i> model] based on a machine learning approach to predict knockdown efficiencies. A more detailed description of the different binding sites, we characterized can be found in our [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project/miMeasure measurements] page. | <!--After creating a binding site library and testing the miRNA-binding site interaction <i>in vitro</i>, we were able to compute an [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Modeling/miGUI <i>in silico</i> model] based on a machine learning approach to predict knockdown efficiencies. A more detailed description of the different binding sites, we characterized can be found in our [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Project/miMeasure measurements] page. | ||
Revision as of 10:15, 27 October 2010

|
|
||
 "
"