Team:Tokyo Tech/Project/wolf coli
From 2010.igem.org
Contents |
Wolf coli
Overview of new series of OmpC promoters
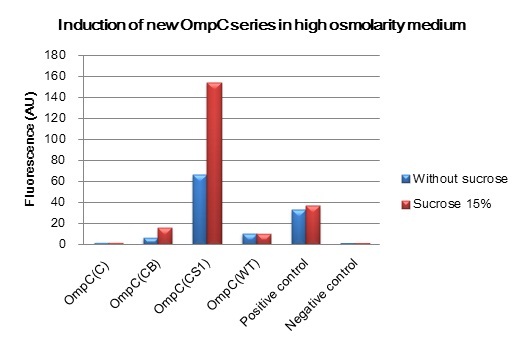
We constructed BioBrick parts of the new series of osmoregulative promoters which are derivatives of the wild type OmpC promoter. The new series of promoters are PompC(C), PompC(CB) and PompC(CS1). In order to measure the strength of each promoter we used GFP as a reporter. We found that expression of GFP in OmpC(CB) and OmpC(CS1) promoters increased in high osmolarity medium comparing with the expression in low osmolarity medium. In contrast, under same conditions, there is no significant difference of GFP expression in OmpC(C) and OmpC(WT) promoters.
New BioBrick Parts
We succeeded in designing 2 news osmoregulative promoters, OmpC(CB) and OmpC(CS1), which can also be utilized in light sensitive system.
Introduction
- What is OmpC promoter?
OmpC promoter, a part of our band detector circuit, plays a crucial role in initiating the transformation of sympathetic coli. into Werewolf coli. in light sensitive system. To accomplish band detector circuit in light sensitive system, varieties of OmpC promoters were designed and characterized in order to find an appropriate strength of the promoter particularly which can be activated by the “full moon light”.
- The new series of OmpC promoters
OmpC(WT) promoter (BBa_R0082) is regulated by phosphorylated OmpR, a response regulator in EnvZ-OmpR two-component system. The EnvZ-OmpR system of E. coli regulates the transcriptional activity of this promoter in response to change in extracellular osmolarity. The OmpC(WT) promoter consists of 3 distinct phosphorylated OmpR recognition sites which are binding site 1, binding site 2 and binding site 3.
Material and Method
- Construction of E. coli strain MG1655
Each new BioBrick part, PompC(C)-GFP, PompC(CB)-GFP and PompC(CS1)-GFP on pSB3K3 was introduced into E. coli strain MG1655. A strain containing pLacq-GFP plasmid (BBa_J54202), a constitutive GFP expressive promoter, and promoterless GFP reporter plasmid (BBa_J54103) was used as a positive control and negative control respectively.
- Medium
Medium A, per liter, contained 7 g of nutrient broth, 1 g of yeast extract, 2 g of glycerol, 3.7 g of K2HPO4, and 1.3 g of KH2PO4. [3]
- Report assay
In order to determine the strength of promoter parts in the reporter plasmid, the change of fluorescence intensities of the reporter stains in the presence and the absence of the inducer were measured. Overnight cultures of reporter strains grown at 37 °C in Medium A containing appropriated antibiotics were diluted at least 1:100 in the medium and incubated at 37 °C as fresh cultures. After their OD590 reached 0.2, the fresh culture was diluted 1 : 3 into 2 ml of pre-warmed medium A. For high osmolarity conditions, the cultures were diluted with sucrose supplemented medium to the final concentration of 15% (wt/vol). [2]
- Sample preparation for GFP measurement
After 4 hours of high ormolarity induction, 0.2 ml of each culture was moved to 2.0 ml eppendorf tube and then centrifuged for 1 min at 4°C, 9000 rpm. The supernatant was discarded from each tube by pipette. In order to adjust each sample to reach approximately same final OD590, appropriate amount of 1×PBS washing solution was added. The cell pellet in each tube was resuspended by vortexing. After all samples for GFP measurement were prepared, 150 l of each sample was applied to 96-well plate and its fluorescence intensity was measured with fluorometer. The fluorescence intensity was calculated by dividing the measured raw fluorescence intensity by the adjusted OD590.
 "
"