Team:Debrecen-Hungary/favorite
From 2010.igem.org
|
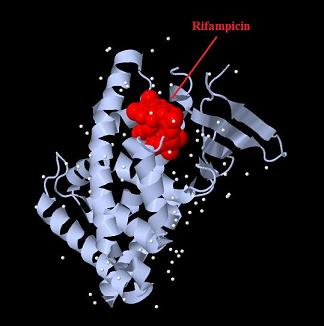
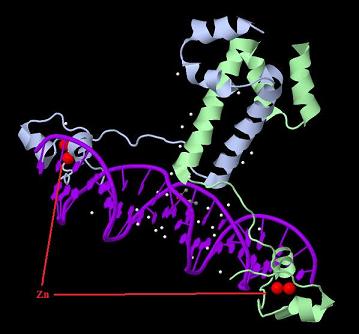
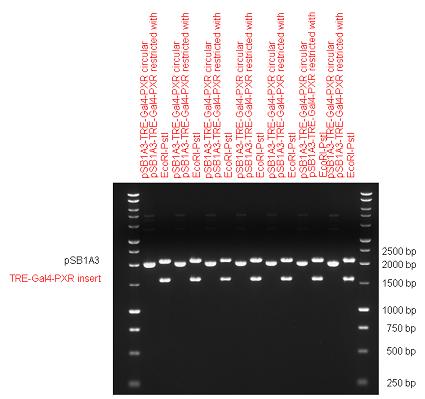
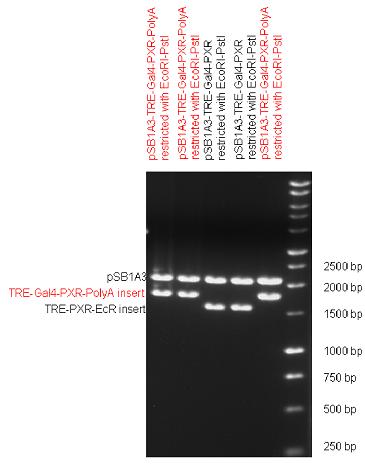
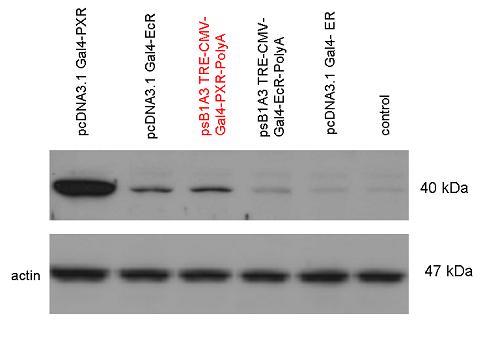
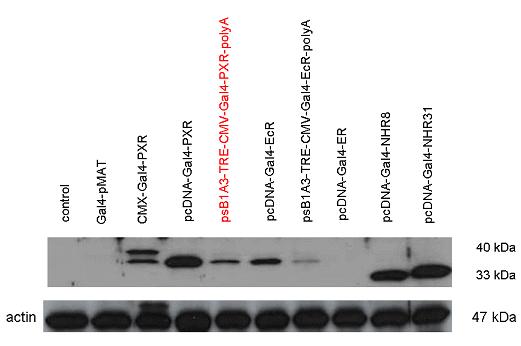
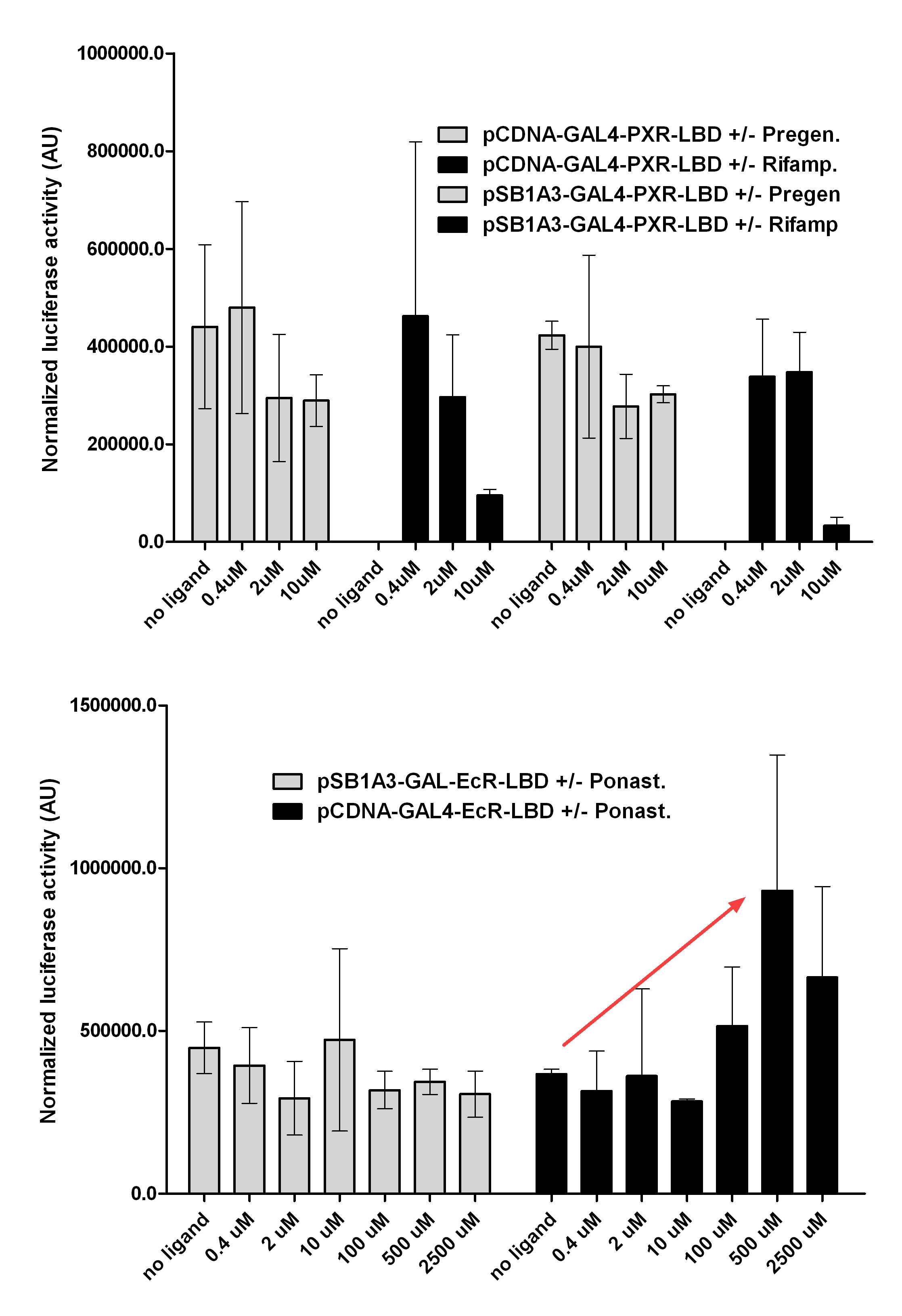
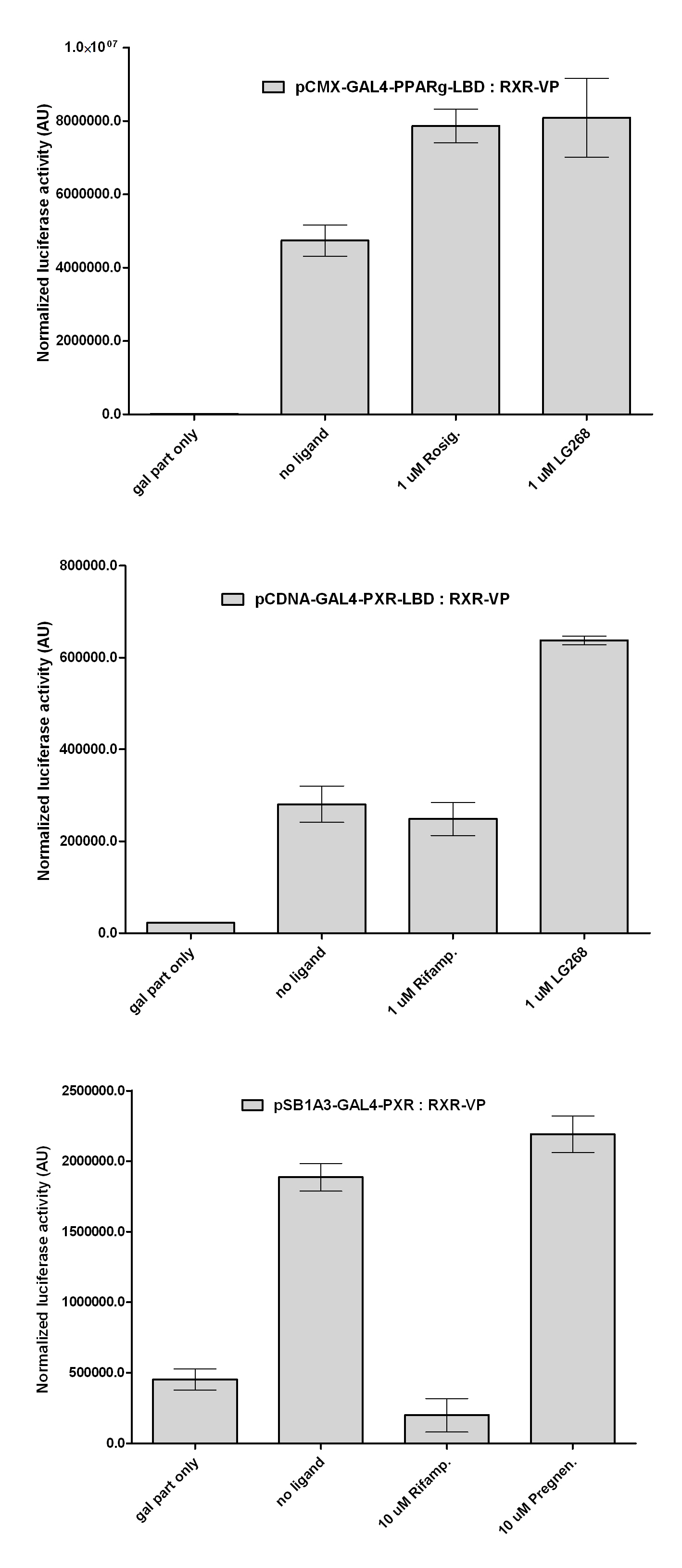
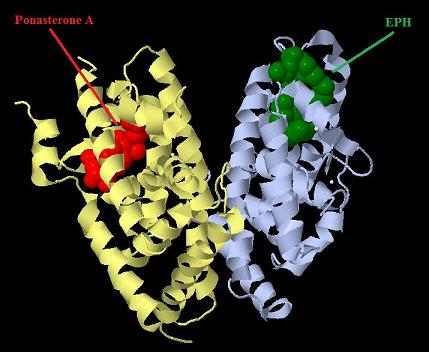
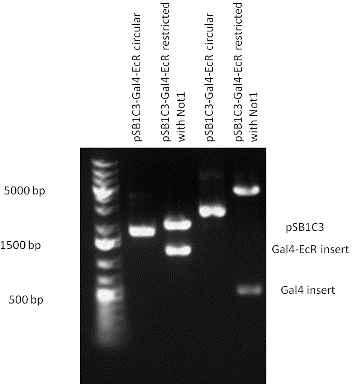
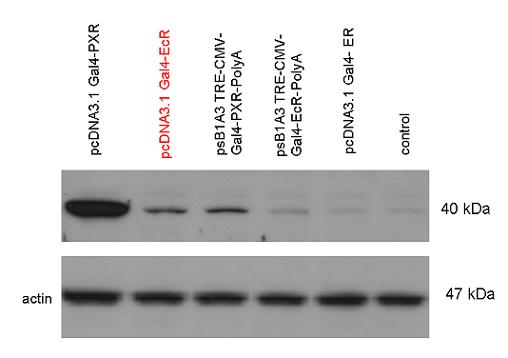
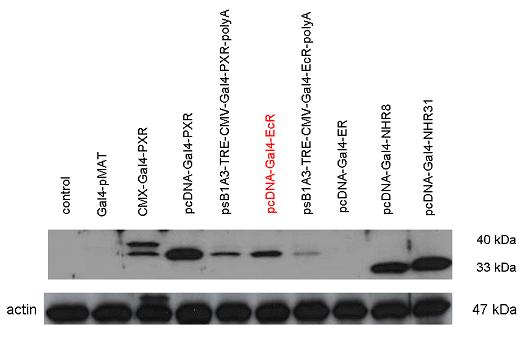
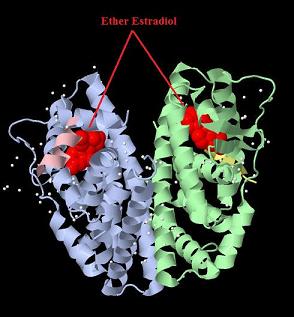
Introduction TextWhich parts are best described and tested [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K364332 TRE-Gal4-PXR-PolyA in PSB1A3 (expression vector)]Expression vector from standard BioBrick parts, expressing Gal4 - human Pregnane X receptor LBD composite part. The Gal4-PXR Chimeric nuclear receptor is an artificial eukaryotic TF made of Gal4 DBD (DNA Binding Domain) and H. sapiens nuclear hormone receptor LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) which can be expressed by this expression vector. The minimal CMV promoter ensures a continuous expression of the chimeric construct, but furthermore it can be expressed in an inducible form using the Tetracyclin-controlled transcriptional activation system. [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K364332 Go to the official parts registry page for this part] PXR LBD PXR is a xenobiotic-activated member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors. PXR is involved in transcriptional induction of hepatic xenobiotic-catabolizing cytochrome 3A enzymes, playing a fundamental role in protecting body tissues from toxic bile acids. PXR is almost exlcusively expressed in the gastrointestinal system (stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, colon and gall bladder) and liver, with lower levels in the kidney and ovary. PXR dysfunction is associated with immune disorders (sclerosing cholangitis, inflammatory bowel disease) and biliary primary cirrhosis. Gal4 DBD This protein is a positive regulator for the gene expression of the galactose-induced genes such as GAL1, GAL2, GAL7, GAL10, and MEL1 which encode for the enzymes used to convert galactose to glucose. This protein contains a fungal Zn(2)-Cys(6) binuclear cluster domain. TRE-CMV The Tetracycline Response Element (TRE) is recognized and bound by the Tetracycline repressor (TetR) protein. The TRE consists of 7 repeats separated by spacer sequences and placed upstream of CMV minimal promoter that has basal expession in the abscence of bound TetR. Tetracycline derivatives (e.g. doxycycline) bind TetR and render it incapable of binding to TRE, thereby forcing the expression of target genes. PolyA The PolyA tail of mRNA has multiple adenilates which is important for the nuclear export, translation and stability of mRNA in eukaryotes. This composite artificial transcription factor will activate any reporter or any gene in general that has a UAS (Upper Activating Sequence) 3' of it's promoter. The usual binding sites of reporters, contain multiple UAS elements. In order to have a POPS output, the LBD has to recruit activators in the cell. This can be initiated by ligand binding or by recruiting a protein that has a fused strong activator like the VP activator. With this system NHR (Nuclear Hormone Receptor) ligands or NHR interacting partners can be screened. The NHR: cofactor-VP interaction should be also broken by a potential ligand binding, this is why this setup is also suitable for ligand identification. The benefit of the cofactor-VP interaction test is that the dynamic range of the assay is much higher than the dynamic range of the normal Gal4-NHR ligand activation assay. Design NotesCompatible with RFC-10 and RFC-25. SourceArtificial and human PXR LBD. LigandPXR is activated by a large number of endogenous and exogenous chemicals including steroids, antibiotics, antimycotics, bile acids, hyperforin, a constituent of the herbal antidepressant St. John's Wort, and many other herbal compounds. PXR is activated by a range of compounds that induce CYP3A4, including dexamethasone and rifampicin. ApplicationsReferencesGuhaniyogi J, Brewer G. Regulation of mRNA stability in mammalian cells. Gene. 2001 Mar 7;265(1-2):11-23. D R Gallie. The cap and poly(A) tail function synergistically to regulate mRNA translational efficiency. Genes Dev. 1991 5: 2108-2116 1.Lehmann JM, McKee DD, Watson MA, Willson TM, Moore JT, Kliewer SA (September 1998). "The human orphan nuclear receptor PXR is activated by compounds that regulate CYP3A4 gene expression and cause drug interactions". J. Clin. Invest. 102 (5): 1016–23. doi:10.1172/JCI3703. Ana Traven, Branka Jelicic & Mary Sopta. "Yeast Gal4: a transcriptional paradigm revisited". EMBO reports (2006) 7, 496 - 499. [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K364326 Gal4-EcR Chimeric nuclear receptor]Gal4 DBD - Ecdysone receptor LBD Artificial eukaryotic TF made of Gal4 DBD (DNA Binding Domain) and D. Melanogaster nuclear hormone receptor LBD (Ligand Binding Domain). [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K364326 Go to the official parts registry page for this part] EcR LBD The ecdysone receptor is a nuclear receptor found in arthropods, where it controls development and contributes to other processes such as reproduction. The receptor is a non-covalent heterodimer of two proteins, the EcR protein and ultraspiracle protein (USP). It binds to and is activated by ecdysteroids. Pulses of 20-hydroxyecdysone occur during insect development, whereupon this hormone binds to the ecdysone receptor, a ligand-activated transcription factor found in the nuclei of insect cells. This in turn leads to the activation of many other genes, which ultimately causes physiological changes that result in ecdysis (moulting). Gal4 DBD This protein is a positive regulator for the gene expression of the galactose-induced genes such as GAL1, GAL2, GAL7, GAL10, and MEL1 which encode for the enzymes used to convert galactose to glucose. This protein contains a fungal Zn(2)-Cys(6) binuclear cluster domain. This composite artificial transcription factor will activate any reporter or any gene in general that has a UAS (Upper Activating Sequence) 3' of it's promoter. The usual binding sites of reporters, contain multiple UAS elements. In order to have a POPS output, the LBD has to recruit activators in the cell. This can be initiated by ligand binding or by recruiting a protein that has a fused strong activator like the VP activator. With this system NHR (Nuclear Hormone Receptor) ligands or NHR interacting partners can be screened. The NHR: cofactor-VP interaction should be also broken by a potential ligand binding, this is why this setup is also suitable for ligand identification. The benefit of the cofactor-VP interaction test is that the dynamic range of the assay is much higher than the dynamic range of the normal Gal4-NHR ligand activation assay. Design NotesArtificial and arthropode EcR SourceCompatible with RFC-10 and RFC-25. LigandEcdysteroids Ecdysteroids are insect moulting and sex hormones which include ecdysone and its homologues such as 20-hydroxyecdysone. Ecdysteroids also occur in other invertebrates where they can play a different role. They also appear in many plants mostly as a protection agents (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivore insects. These phytoecdysteroids have medicinal value and are part of herbal adaptogenic remedies like cordyceps. Physiological functions of EcRPulses of 20-hydroxyecdysone occur during insect development, whereupon this hormone binds to the ecdysone receptor, a ligand-activated transcription factor found in the nuclei of insect cells. This in turn leads to the activation of many other genes, as evidenced by chromosomal puffing at over a hundred sites. Ultimately the activation cascade causes physiological changes that result in ecdysis (moulting). Potential applications of GAL4-EcR LBDBy the addition of lipid ligands(ecdysteroids), the created system activates the expression of any kind of genes fused to UAS (upstream activation seqence)previously. Also can be used as a lipid sensor by activating reporter genes (e.g. Luciferase). ApplicationsReferencesRiddiford LM, Cherbas P, Truman JW (2000). "Ecdysone receptors and their biological actions". Vitam. Horm. 60: 1–73. Henrich VC (2005). "The ecdysteroid receptor". in Sarjeet S. Gill; Gilbert, Lawrence I.; Kostas Iatrou. Comprehensive molecular insect science. Amsterdam: Elsevier. pp. 243–285. Koelle MR, Talbot WS, Segraves WA, Bender MT, Cherbas P, Hogness DS (October 1991). "The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily". Cell 67 (1): 59–77. [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K364327 Gal4-ER Chimeric nuclear receptor]Gal4 DBD - human Estrogen Receptor LBD Artificial eukaryotic TF made of Gal4 DBD (DNA Binding Domain) and H. Sapiens nuclear hormone receptor LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K364327 Go to the official parts registry page for this part] ER LBD ER-α is a 17β-estradiol-activated steroid receptor member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors. It has a variety of central physiological roles, including those involved in maintenance of the reproductive, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal and central nervous systems. ER-α is expressed at low to moderate levels in major physiological systems (central nervous system (CNS), endocrine, metabolic, gastrointestinal, immune, reproductive, cardiovascular, respiratory and structural), with peaks of expression in the pituitary, ovary, uterus and vas deferens. ER-α dysfunction is associated with cancer, cardiovascular system defects, hematological system defects, immune and inflammation diseases, metabolic defects, reproductive defects. Gal4 DBD This protein is a positive regulator for the gene expression of the galactose-induced genes such as GAL1, GAL2, GAL7, GAL10, and MEL1 which encode for the enzymes used to convert galactose to glucose. This protein contains a fungal Zn(2)-Cys(6) binuclear cluster domain. This composite artificial transcription factor will activate any reporter or any gene in general that has a UAS (Upper Activating Sequence) 3' of it's promoter. The usual binding sites of reporters, contain multiple UAS elements. In order to have a POPS output, the LBD has to recruit activators in the cell. This can be initiated by ligand binding or by recruiting a protein that has a fused strong activator like the VP activator. With this system NHR (Nuclear Hormone Receptor) ligands or NHR interacting partners can be screened. The NHR: cofactor-VP interaction should be also broken by a potential ligand binding, this is why this setup is also suitable for ligand identification. The benefit of the cofactor-VP interaction test is that the dynamic range of the assay is much higher than the dynamic range of the normal Gal4-NHR ligand activation assay. Design NotesCompatible with RFC-10 and RFC-25. SourceArtificial and Human ER (of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily). LigandEstrogens Estrogens (AmE), oestrogens (BE), or œstrogens, are a group of steroid compounds, named for their importance in the estrous cycle, and functioning as the primary female sex hormone. Their name comes from estrus/oistros (period of fertility for female mammals) + gen/gonos = to generate. Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates as well as some insects. The presence of these steroids in both vertebrate and insects suggests that estrogenic sex hormones have an ancient history. Estrogens are used as part of some oral contraceptives, in estrogen replacement therapy for postmenopausal women, and in hormone replacement therapy for trans women. Like inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors which in turn modulate the G protein-coupled receptor, GPR30. Physiological function of ERIn the absence of hormone, estrogen receptors are largely located in the cytosol. Hormone binding to the receptor triggers a number of events starting with migration of the receptor from the cytosol into the nucleus, dimerization of the receptor, and subsequent binding of the receptor dimer to specific sequences of DNA. Some of the effects in humans: Createing proliferative endometrium,breast cell stimulation, increased body fat and weight gain, salt and fluid retention, increased risk of blood clots. Possible applications of GAL4-ERBy the addition of lipid ligand, the created system activates the expression of any kind of genes fused to UAS(upstream activation seqence)previously. Also can be used as a lipid sensor by activating reporter genes (e.g. Luciferase). ApplicationsReferencesDahlman-Wright K, Cavailles V, Fuqua SA, Jordan VC, Katzenellenbogen JA, Korach KS, Maggi A, Muramatsu M, Parker MG, Gustafsson JA (2006). "International Union of Pharmacology. LXIV. Estrogen receptors". Pharmacol. Rev. 58 (4): 773–81. doi:10.1124/pr.58.4.8. Levin ER (2005). "Integration of the extranuclear and nuclear actions of estrogen". Mol. Endocrinol. 19 (8): 1951–9. doi:10.1210/me.2004-0390. Leung YK, Mak P, Hassan S, Ho SM (August 2006). "Estrogen receptor (ER)-beta isoforms: a key to understanding ER-beta signaling". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103 (35): 13162–7.

|
 "
"
 Team
Team