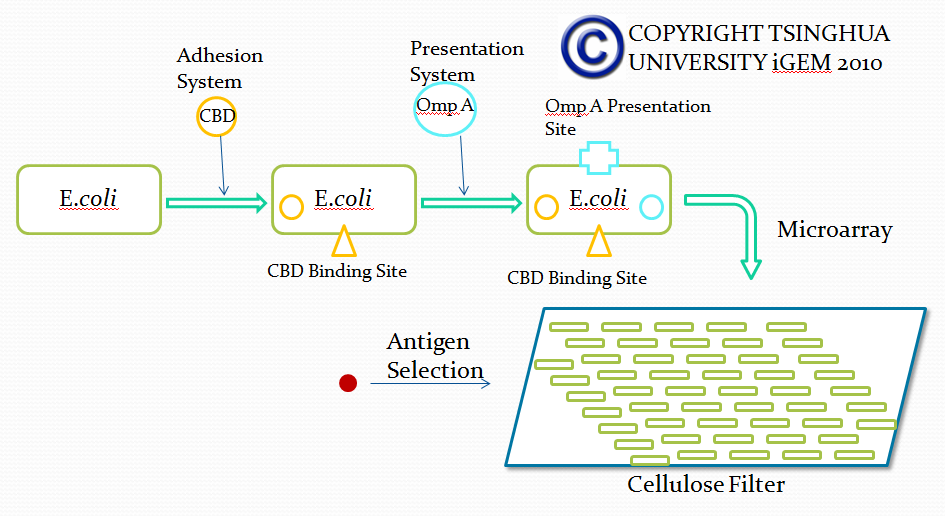
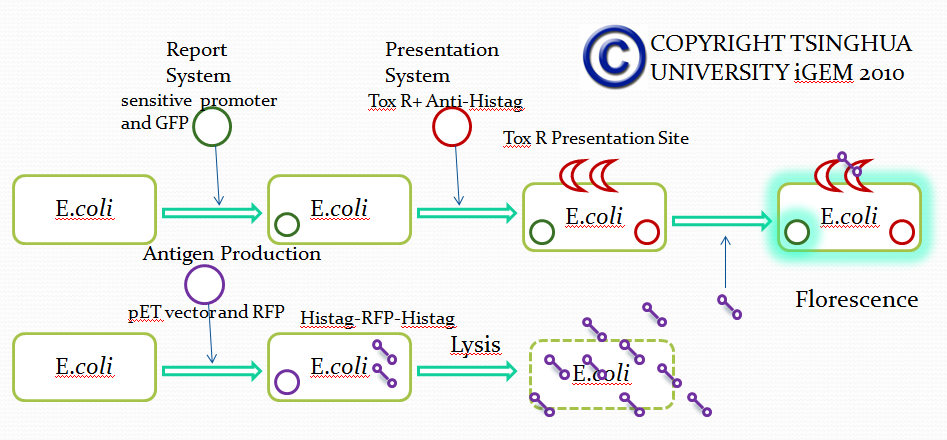
Team:Tsinghua/project/outline
From 2010.igem.org
(→Landing Pad Insertion) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<div class="content_block"> | <div class="content_block"> | ||
| - | + | @ Purpose of this step | |
Landing pad insertion is the first step of our two-step recombination system. | Landing pad insertion is the first step of our two-step recombination system. | ||
We insert a “landing pad” fragment which includes a promoter (placIQ1) and a tetracycline resistance gene (tetA) flanked by I-SceI recognition sites and 20-bp landing pad regions (LP1 and LP2) into Escherichia coli chromosome via att recombination. Then the helper plasmids encoding I-SceI endonuclease and λ-Red and donor plasmid encoding various antibiotic genes flanked by I-SceI recognition sites and same landing pad regions (LP1 and LP2) are transformed, which will be introduced in detail in next part. I-SceI expression is induced via the addition of L-arabinose. I-SceI recognition sites in the donor plasmid and chromosome are cleaved. Integration of the fragment in donor plasmid is facilitated by IPTG-induced λ-Red expression. | We insert a “landing pad” fragment which includes a promoter (placIQ1) and a tetracycline resistance gene (tetA) flanked by I-SceI recognition sites and 20-bp landing pad regions (LP1 and LP2) into Escherichia coli chromosome via att recombination. Then the helper plasmids encoding I-SceI endonuclease and λ-Red and donor plasmid encoding various antibiotic genes flanked by I-SceI recognition sites and same landing pad regions (LP1 and LP2) are transformed, which will be introduced in detail in next part. I-SceI expression is induced via the addition of L-arabinose. I-SceI recognition sites in the donor plasmid and chromosome are cleaved. Integration of the fragment in donor plasmid is facilitated by IPTG-induced λ-Red expression. | ||
This two-step recombination method allows for the insertion of very large fragments into a specific location in Escherichia coli chromosome and in any orientation. | This two-step recombination method allows for the insertion of very large fragments into a specific location in Escherichia coli chromosome and in any orientation. | ||
| - | + | @ Construction of landing pad | |
Landing pad consists of the following parts: a promoter (placIQ1), two landing pad regions, two I-SceI recognition sites and a tetracycline resistance gene (tetA). | Landing pad consists of the following parts: a promoter (placIQ1), two landing pad regions, two I-SceI recognition sites and a tetracycline resistance gene (tetA). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | @ First we obtain two target DNAs – promoter and tetA with PCR. Then We use the overlap extension polymerase chain reaction (or OE-PCR) to link two fragments together. Primer 2 and primer 3 have homologous sequences, so one segment can anneal to the other in certain conditions, in other words, the two segments can overlap into one segment after extension. If necessary, operate PCR again with primer 1 and primer 4 to obtain more products. | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 16 October 2010

Outline
Module I
Abstract
Flow chart
Landing Pad Insertion
@ Purpose of this step Landing pad insertion is the first step of our two-step recombination system. We insert a “landing pad” fragment which includes a promoter (placIQ1) and a tetracycline resistance gene (tetA) flanked by I-SceI recognition sites and 20-bp landing pad regions (LP1 and LP2) into Escherichia coli chromosome via att recombination. Then the helper plasmids encoding I-SceI endonuclease and λ-Red and donor plasmid encoding various antibiotic genes flanked by I-SceI recognition sites and same landing pad regions (LP1 and LP2) are transformed, which will be introduced in detail in next part. I-SceI expression is induced via the addition of L-arabinose. I-SceI recognition sites in the donor plasmid and chromosome are cleaved. Integration of the fragment in donor plasmid is facilitated by IPTG-induced λ-Red expression. This two-step recombination method allows for the insertion of very large fragments into a specific location in Escherichia coli chromosome and in any orientation.
@ Construction of landing pad Landing pad consists of the following parts: a promoter (placIQ1), two landing pad regions, two I-SceI recognition sites and a tetracycline resistance gene (tetA).
@ First we obtain two target DNAs – promoter and tetA with PCR. Then We use the overlap extension polymerase chain reaction (or OE-PCR) to link two fragments together. Primer 2 and primer 3 have homologous sequences, so one segment can anneal to the other in certain conditions, in other words, the two segments can overlap into one segment after extension. If necessary, operate PCR again with primer 1 and primer 4 to obtain more products.
Helper Plasmid(HP) Insertion
Donor Plasmid(DP) Construction
Strategy 1
Strategy 2
Donor Plasmid(DP) Insertion & Recombination Induction
Removal of Helper Plasmid(HP)
Module II
Strategy 1
Strategy 2
Strategy 3
Cooperation with Macquarie Australia
 "
"