Team:Baltimore US/Project
From 2010.igem.org
BioMechanic (Talk | contribs) (→Overall project) |
m (→Developing low-cost alternatives to existing enzymes: Taq polymerase Project Details) |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | [[Image:TitleBarBalti US.png | center]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | {| style="background-color:#7998AD;" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" border="0" bordercolor="#fff" width="924px" align="center" | |
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US|<span style="color:white;">Home</span>]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US/Team|<span style="color:white;">Team</span>]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[https://igem.org/Team.cgi?year=2010&team_name=Baltimore_US <span style="color:white;">Official Team Profile</span>] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US/Project|<span style="color:white;">Project</span>]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US/Parts|<span style="color:white;">Submitted Parts</span>]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US/Modeling|<span style="color:white;">Modeling</span>]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US/Notebook|<span style="color:white;">Notebook</span>]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US/MeetingTimes|<span style="color:white;">Meeting/Lab Times</span>]] | ||
| + | !align="center"|[[Team:Baltimore_US/Safety|<span style="color:white;">Safety</span>]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| - | + | {| style= "background-color:#FFFFF;" width="924px" align="center" | |
| - | + | | | |
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | | | ||
| - | + | <!--- The Mission, Experiments ---> | |
| - | + | == DIY-GEM: a path towards low cost high throughput gene synthesis. == | |
| - | + | Synthetic biology research requires more cost effective approaches toward reagents and hardware accessibility. We are developing low-cost alternatives to existing hardware and enzymes in an attempt to expand participation in biological research and development. Our project expands the accessibility of Taq Polymerase by engineering it in a form compatible with BioBrick assembly. This allows use of the over-expressed enzyme from a crude bacterial extract in a PCR reaction at a fraction of the cost of highly purified commercial enzyme. In addition, we have developed inexpensive and easily assembled lab equipment such as a gel electrophoresis apparatus and a PCR thermal cycler. Enabling researchers to synthesize their own enzymes and having access to inexpensive tools will allow for increased participation among the DIY-bio community, stretch increasingly scarce educational funds, and allow rapid scale up of large scale gene synthesis projects." | |
| - | + | ==Developing low-cost alternatives to existing enzymes: ''Taq'' polymerase Project Details== | |
| + | We wished to insert Taq Polymerase into a standard BioBrick vector. If this part should prove useful to other teams as an element of a rational design, we must ensure that no sites for the standard BioBrick restriction enzymes exist within the part itself, otherwise the part would shear upon assembly. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | We examined the Taq [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/155128 sequence]and exported the SEQ into Plasma DNA. [http://research.med.helsinki.fi/plasmadna/ Plasma DNA] is free software from University of Helsinki which provides quick analysis of plasmid sequence information. In particular, we obtained a restriction map which identified potential EcoRI, Xbe1, Sbe1, or Pst1 sites within the coding sequence. Here we encountered our first difficulty. | |
| - | + | ====Problem: a PstI restriction site within the coding sequence==== | |
| - | + | At 1717nt, we discovered a restriction site for Pst1: | |
| - | + | ...CTGCAG... PstI restriction site<br> | |
| - | + | ...GACGTC... Complement<br> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | We attempted to eliminate the restriction site by employing a site-specific mutagenesis by overlap extension protocol (see [http://www.cshlpress.com/default.tpl?cart=1279686078181232350&fromlink=T&linkaction=full&linksortby=oop_title&--eqSKUdatarq=21 Sambrook, Joseph; Russell, David W. ; Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd Edition]). | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | We then used the Gene Designer 2.0 from [https://www.dna20.com/genedesigner2/ DNA2.0] to analyze the open reading frames and examine the codons within the PstI restriction site. We find that the first three code for leucine with CTG; we can substitute the final base pair to yield CTT without sacrificing functional integrity in the manufactured enzyme.<br> | ||
| + | ====Primer Design==== | ||
| + | We designed a primer pair in order to induce point-mutagenesis at the Pst1 restriction site, flanking the base pair to be altered by 14 nt: | ||
| + | GTGGAGAAGATCCT(T)CAGTACCGGCGG<br> | ||
| + | CACCTCTTCTAGGA(A)GTCATGGCCGCC<br> | ||
| - | + | While we designed the point-mutagenesis primers, we took the opportunity to design and order the primers for the BioBrick Suffix and Prefix. We followed the examples laid out in the Registry of Standard Parts for designing the oligos needed to make a part. | |
| - | + | Important considerations are melting point and CG concentration, as well as self-dimerizations and hairpins. We analyzed these primers using the [http://www.idtdna.com/analyzer/Applications/OligoAnalyzer/ OligoAnalyzer] from [http://www.idtdna.com/Home/Home.aspx IDT]. When analyzing PolI, only the coding seuence itself was used for sequence inquiry, not the BioBrick Suffix/Prefixes.<br> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | http:// | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | When | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | PCR Reaction | + | ====PolI Coli Primers For Overlap Extension PCR==== |
| + | '''PCR Reaction 1''' <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | Fwd | + | Bb Prefix + PolI (Fwd Complement) : (Forward complement will begin coding at 121 according to BLAST CDS information.)<br> |
GTTTCTTCGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAG-ATGCTGCCCCTCTTTGAGCC<br> | GTTTCTTCGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAG-ATGCTGCCCCTCTTTGAGCC<br> | ||
60.5 c ; 56.5 % GC Concetration<br> | 60.5 c ; 56.5 % GC Concetration<br> | ||
| Line 152: | Line 58: | ||
61.5 c ; 55.6 % GC Concentration<br> | 61.5 c ; 55.6 % GC Concentration<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | PCR | + | '''PCR Reaction - 2'''<br> |
<br> | <br> | ||
TAQ Fm<br> | TAQ Fm<br> | ||
| Line 158: | Line 64: | ||
61.5 c; 55.6 % GC<br> | 61.5 c; 55.6 % GC<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | Bb Suffix + | + | Bb Suffix + PolI (Reverse Complement) : (Reverse complement will end coding at 2619 according to Blast CDS information.<br> |
GTTTCTTCCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTA-TCACTCCTTGGCGGAGAGCC<br> | GTTTCTTCCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTA-TCACTCCTTGGCGGAGAGCC<br> | ||
61.8 c; 65 % GC<br> | 61.8 c; 65 % GC<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | PCR 3<br> | + | '''PCR Reaction - 3'''<br> |
Bb Prefix & Suffix Primers<br> | Bb Prefix & Suffix Primers<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 168: | Line 74: | ||
Run PCR w 1/100 dilutions for PCR (5-10 uL per PCR reaction)<br> | Run PCR w 1/100 dilutions for PCR (5-10 uL per PCR reaction)<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | NEXT<br> | + | '''NEXT'''<br> |
| - | - Create Full Bb Prmr w Plasmid combining new part | + | - Create Full Bb Prmr w Plasmid combining new part using<br> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <partinfo>R0010 - Promoter (LacI) | + | <partinfo>R0010</partinfo> - Promoter (LacI)<br> |
| - | <partinfo>B0034 | + | <partinfo>B0034</partinfo> - Strong RBS<br> |
| - | NEW PART - PolI Bb Format | + | NEW PART - PolI Bb Format<br> |
| - | <partinfo>B0015 - Double Terminator<br> | + | <partinfo>B0015</partinfo> - Double Terminator<br> |
| - | Psb1_?_3 - Plasmid of Interest with Chosen Resistance<br> | + | Psb1_?_3 - Plasmid of Interest with Chosen Resistance : http://partsregistry.org/Plasmid_backbones<br> |
<br> | <br> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 201: | Line 107: | ||
Combine in Ampecillan/Kanamyacin Resistan Plasmid (cut w/EcoRI & PstI)<br> | Combine in Ampecillan/Kanamyacin Resistan Plasmid (cut w/EcoRI & PstI)<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | '''Voila!!!''' Brand New Taq Polymerase Bb Part.<br> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | == Developing low-cost alternatives to existing hardware: Project Details and Results == | ||
| + | An unfortunate fact of reality is that precision lab equipment is very costly. Even simple devices such as an Electrophoresis or PCR have significant cost. To ameliorate this a portion of our project will involve designing biological tools that are easy to build and are economical.<br><br> | ||
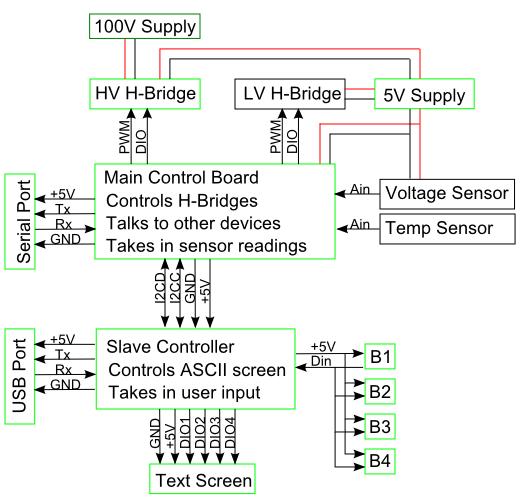
| - | + | [[Image:Baltimore US System.JPG|300px]]<br> | |
| + | Our design incorporates two devices, a PCR and an Electrophoresis. Both are controlled by the same control electronics and power supply. A basic overview of the design can be seen in the diagram above. This design allows precise control from a computer or manual control from the control panel on the control electronics. Additionally multiple Electrophoresis devices can be controlled simultaneously in parallel and any power supply suitable can be used to power the devices. | ||
| - | + | [[Image:EP.jpg|300px]]<br> | |
| + | With regards to equipment, we have successfully constructed a very low-cost Gel Electrophoresis device and are currently working on the control software and control electronics. Additionally, we are working on getting a low-cost PCR thermocycler up and running as well.<br> [[Team:Baltimore_US/Notebook/EPInstructions|Instructions and Design files for building an Electrophoresis device]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:14, 28 October 2010
| Home | Team | Official Team Profile | Project | Submitted Parts | Modeling | Notebook | Meeting/Lab Times | Safety |
|---|
|
DIY-GEM: a path towards low cost high throughput gene synthesis.Synthetic biology research requires more cost effective approaches toward reagents and hardware accessibility. We are developing low-cost alternatives to existing hardware and enzymes in an attempt to expand participation in biological research and development. Our project expands the accessibility of Taq Polymerase by engineering it in a form compatible with BioBrick assembly. This allows use of the over-expressed enzyme from a crude bacterial extract in a PCR reaction at a fraction of the cost of highly purified commercial enzyme. In addition, we have developed inexpensive and easily assembled lab equipment such as a gel electrophoresis apparatus and a PCR thermal cycler. Enabling researchers to synthesize their own enzymes and having access to inexpensive tools will allow for increased participation among the DIY-bio community, stretch increasingly scarce educational funds, and allow rapid scale up of large scale gene synthesis projects." Developing low-cost alternatives to existing enzymes: Taq polymerase Project DetailsWe wished to insert Taq Polymerase into a standard BioBrick vector. If this part should prove useful to other teams as an element of a rational design, we must ensure that no sites for the standard BioBrick restriction enzymes exist within the part itself, otherwise the part would shear upon assembly.
Problem: a PstI restriction site within the coding sequenceAt 1717nt, we discovered a restriction site for Pst1: ...CTGCAG... PstI restriction site We attempted to eliminate the restriction site by employing a site-specific mutagenesis by overlap extension protocol (see [http://www.cshlpress.com/default.tpl?cart=1279686078181232350&fromlink=T&linkaction=full&linksortby=oop_title&--eqSKUdatarq=21 Sambrook, Joseph; Russell, David W. ; Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd Edition]).
Primer DesignWe designed a primer pair in order to induce point-mutagenesis at the Pst1 restriction site, flanking the base pair to be altered by 14 nt: GTGGAGAAGATCCT(T)CAGTACCGGCGG While we designed the point-mutagenesis primers, we took the opportunity to design and order the primers for the BioBrick Suffix and Prefix. We followed the examples laid out in the Registry of Standard Parts for designing the oligos needed to make a part.
Important considerations are melting point and CG concentration, as well as self-dimerizations and hairpins. We analyzed these primers using the [http://www.idtdna.com/analyzer/Applications/OligoAnalyzer/ OligoAnalyzer] from [http://www.idtdna.com/Home/Home.aspx IDT]. When analyzing PolI, only the coding seuence itself was used for sequence inquiry, not the BioBrick Suffix/Prefixes. PolI Coli Primers For Overlap Extension PCRPCR Reaction 1
Developing low-cost alternatives to existing hardware: Project Details and ResultsAn unfortunate fact of reality is that precision lab equipment is very costly. Even simple devices such as an Electrophoresis or PCR have significant cost. To ameliorate this a portion of our project will involve designing biological tools that are easy to build and are economical.
|
 "
"