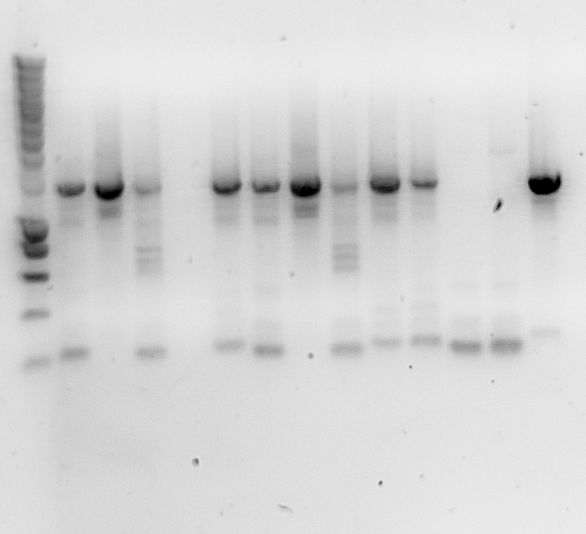Team:TU Delft/16 August 2010 content
From 2010.igem.org
Contents |
Alkane degradation
Unfortunately last week's attempts hadn't yielded any BioBricks making use of the 2-way ligation method. We thus decided to take another stab at the 3-way ligation procedure, according to the BioBrick Assembly Manual of Ginkgo Bioworks. The BioBrick numbers we tried to construct were: 014C, 020C, 405C, 327C and 304C.
Digestion
| # | Sample | Enzyme 1 | Enzyme 2 | Enzyme 3 | Buffer | BSA | Needed fragment |
| 1 | 011A | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - J23100-J61100-alkB2-J61100-rubA3 - S’ |
| 2 | 013K | XbaI | PstI | HindIII | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - J61100-rubA4-J61100-rubR-B0015 - P’ |
| 3 | 017A | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - J23100-J61100-ladA - S’ |
| 4 | 018A | XbaI | PstI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - J61101-ADH - P’ |
| 5 | 402A | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - J23100-J61101-PhPFDα - S’ |
| 6 | 403A | XbaI | PstI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - J61101-PhPFDβ - P’ |
| 7 | pCaiF | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - pCaiF - S’ |
| 8 | B0032 | XbaI | PstI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - B0032 - P’ |
| 9 | B0032 | XbaI | PstI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - B0032 - P’ |
| 10 | pAlkS | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - pAlkS - S’ |
| 11 | pSB1C3 | EcoRI | PstI | None | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ |
The digestions were executed for 15 minutes at 37 degrees, and checked on 1% agarose gel:
Lane description
| # | Description | Expected size (bp) | OK? |
| 1 | Smartladder | Varies | Yes |
| 2 | 011A cut | 1523, 1199, 857 | Yes |
| 3 | 013K cut | 1825, 1592, 1342, 43 | Yes |
| 4 | 017A cut | 1410, 1199, 857 | Yes |
| 5 | 018A cut | 1185, 872, 793, 43 | Yes |
| 6 | 402A cut | 1199, 857, 543 | Yes |
| 7 | 403A cut | 1185, 872, 397, 43 | Yes |
| 8 | pCaiF in pANY cut | 1277, 1143, 74 | Yes |
| 9 | B0032 in pSB1A2 cut | 1185, 872, 35 | Yes |
| 10 | B0032 in pSB1A2 cut | 1185, 872, 35 | Yes |
| 11 | pAlkS cut | 1272, 1138, 106 | Yes |
| 12 | pSB1C3 cut | 2035, 1081 | Yes (However incomplete digestion, see 3116 bp) |
| 15 | BioRad EZ Load Marker | Varies | Yes |
Ligation
Following the digestion the products were ligated for 15 minutes at RT:
| # | BioBrick | Fragment 1 | Fragment 2 | Destination Vector |
| 1 | 014C | ‘E - J23100-X-J61100-alkB2-J61100-rubA3 - S’ | ‘X - J61100-rubA4-J61100-rubR-B0015 - P’ | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ |
| 2 | 020C | ‘E - J23100-X-J61100-ladA - S’ | ‘X - J61101-ADH - P’ | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ |
| 3 | 405C | ‘E - J23100-X-J61101-PhPFDα - S’ | ‘X - J61101-PhPFDβ - P’ | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ |
| 4 | 327C | ‘E - pCaiF - S’ | ‘X - B0032 - P’ | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ |
| 5 | 304C | ‘E - pAlkS - S’ | ‘X - B0032 - P’ | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ |
| 6 | Ligation control | None | None | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ |
| 7 | 014C | ‘E - J23100-X-J61100-alkB2-J61100-rubA3 - S’ | ‘X - J61100-rubA4-J61100-rubR-B0015 - P’ | ‘E - pSB1C3 - P’ (Pre-shipped linearized plasmid) |
The ligations were performed in parallel: one batch using the NEB T4 DNA ligase and buffer, the other batch the Fermentas T4 DNA ligase and buffer. We hope to be able to discern the differences in efficiency between the two (if there are any). 1 uL of the ligation mixes was amplified using the universal primers to screen for pSB1C3 plasmids containing the proper ligated insert. The PCR mix was loaded onto 1% agarose gel:
Lane description
| # | Description | Expected size (bp) | OK? |
| 1 | Smartladder | Varies | Yes |
| 2 | Ligation mix 014C (NEB) | No | |
| 3 | Ligation mix 020C (NEB) | No | |
| 4 | Ligation mix 405C (NEB) | No | |
| 5 | Ligation mix 327C (NEB) | No | |
| 6 | Ligation mix 304C (NEB) | No | |
| 7 | Ligation mix 014C (Fermentas) | No | |
| 8 | Ligation mix 020C (Fermentas) | No | |
| 9 | Ligation mix 405C (Fermentas) | No | |
| 10 | Ligation mix 327C (Fermentas) | No | |
| 11 | Ligation mix 304C (Fermentas) | No | |
| 12 | Ligation mix 014C with linearized pSB1C3 (NEB) | No | |
| 13 | Ligation mix 014C with linearized pSB1C3 (Fermentas) | No | |
| 14 | Digestion mix of pSB1C3 | Yes |
Transformation
The ligation products (19 uL) were used to transform 25 uL of commercially competent TOP10 cells (OneShot from Invitrogen) in accordance with the OneShot protocol. In order to test the background the digestion product of pSB1C3 was transformed (digestion control) as well as the ligation controls.
Alkane degradation parallel attempt
We are no longer betting on one horse to ligate the alkane degradation bricks together. So, besides the 3-way ligation mentioned above, we also tried to do a 2 way ligation as well.
Digestion
| # | Sample | Enzyme 1 | Enzyme 2 | Enzyme 3 | Buffer | BSA | Needed fragment |
| 1 | 011A | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - J23100-J61100-alkB2-J61100-rubA3 - S’ |
| 2 | 013K | XbaI | EcoRI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - J61100-rubA4-J61100-rubR-B0015 - E’ | |
| 3 | 017A | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - J23100-J61100-ladA - S’ |
| 4 | 018A | XbaI | EcoRI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - J61101-ADH - E’ | |
| 5 | 402A | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - J23100-J61101-PhPFDα - S’ |
| 6 | 403A | XbaI | EcoRI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - J61101-PhPFDβ - E’ | |
| 7 | pCaiF | EcoRI | SpeI | PvuII | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - pCaiF - S’ |
| 8 | pAlkS | EcoRI | SpeI | AseI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘E - pAlkS - S’ |
| 9 | B0032 | XbaI | EcoRI | NEBuffer 2 | ✓ | ‘X - B0032 - E’ |
The digestions were executed for 1 hour at 37 degrees.
Ligation
Following the digestion the products were ligated over night at 16 C:
| # | BioBrick | Fragment 1 | Vector with Fragment 2 |
| 1 | 014C | ‘E - J23100-X-J61100-alkB2-J61100-rubA3 - S’ | ‘X - J61100-rubA4-J61100-rubR-B0015 - E’ |
| 2 | 020C | ‘E - J23100-X-J61100-ladA - S’ | ‘X - J61101-ADH - E’ |
| 3 | 405C | ‘E - J23100-X-J61101-PhPFDα - S’ | ‘X - J61101-PhPFDβ - E’ |
| 4 | 327C | ‘E - pCaiF - S’ | ‘X - B0032 - E’ |
| 5 | 304C | ‘E - pAlkS - S’ | ‘X - B0032 - E’ |
 "
"