Team:Alberta/biobyte2
From 2010.igem.org
Overview
BioBytes 2.0 is the heart of the GENOMIKON kit. We have taken the original BioBytes Assembly System developed from last year's iGEM project and adapted it for a high school setting. The system is designed by the sequential addition of gene elements with alternating ends bla ble bla bla bla...
Traditional Methods
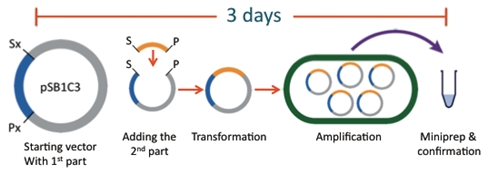
The current assembly standard is the BioBrick method. While the registry of parts and the assembly standard has allowed for efficient construction of plasmids in a laboratory setting, it has numerous limitations prohibiting its use in high schools. For example, common laboratory protocols such as transformation, ligation, and restriction digestion require materials and equipment not available to high schools. Not only does this require expensive reagents and equipment, it also takes days to weeks to assemble acomplicated construct. An experiment of such length far surpasses the average high school student’s attention span and the time a curriculum can spend on a particular subject.
Comparison
The BioBytes Assembly System 2.0 has provided a solution to these issues. The GENOMIKON kit is fast allowing for assembly in an afternoon rather than over the course of several days. The kit does not require expensive equipment which is unavailable to high schools. Bla bla bla bla
Components of the System
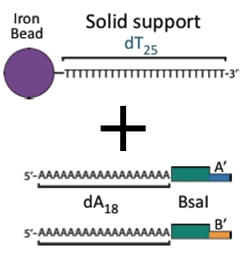
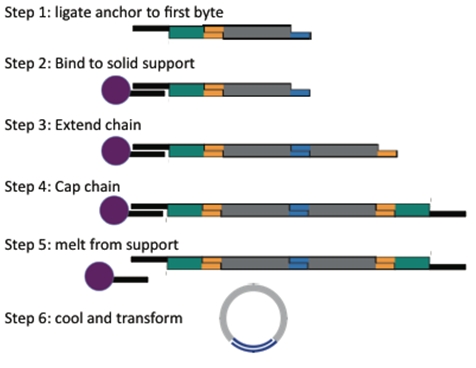
The Assembly Method 2.0 is composed of three main components. An anchor piece attached to a ferro-magnetic bead is used to begin chain initiation. Because of the magnetic nature of these beads, they can be dragged to different points in the tube using a simple magnet. The BioBytes are added to the anchor piece and have alternating end structures allowing them to be added in a sequential order. Finally, a cap is added allowing for circularization of the construct.
Overhangs
Anchor
The Anchor piece begins the process of assembly. It is composed of:
- a poly-A tail
- an AB or BA cut site
- a poly-T linked ferro-magnetic bead
A ferro-magnetic bead attached to a piece of DNA. This piece serves as the initial piece from which we assemble a DNA construct. The bead allows us to manipulate the DNA with magnets making washing and subsequent attachments easier. Magnetic beads purchased from New England Biolabs have covalently attached poly-T tails. We have designed an anchor byte which begins the process of assembly. The anchor byte is comprised of a poly-A tail and one of the two overhangs discussed earlier. Construction begins by ligating a selectable marker to the anchor. This first step allows incomplete constructs to be easily selected against. Incorporation of a BsaI cut site give versatility to the construct, an advantage discussed shortly. Once the selectable marker is ligated to the first byte,we anneal the anchor to the poly-T tails on the magnetic bead. We have created anchors with both varieties of ends so that assemblies can begin with either type of byte. The results of one of our experiments is shown here. Note that the interaction between the anchor and the bead is non-covalent. The anchor along with the construct can be separated from the bead with heat. The lefthand gel shows the process of anchoring a construct. A anchor-byte construct of 1kb is allowed to anneal to the magnetic beads. This is done in excess, and the supernatant is shown in the first lane. A subsequent wash step showed the absence of DNA, indicating that DNA construct is stably bound. The construct can be melted from the scaffold at 70 degrees Celsius. The melted construct can be seen in the last lane.
This schematic shows the alternating addition of bytes starting from the anchor. Parts are added and ligated in an sequential fashion. Cycle time for each step was about 7 minutes. This is much faster than the Biobrick method. In on of our assemblies, we were able to create an octamer, with a total size of 12 kb. As you can see, there are some minor incomplete products.
If you recall, we have incorporated a BsaI cut site into the anchor. This allows for constructs to be created in parallel and then utilized in the standard assembly.
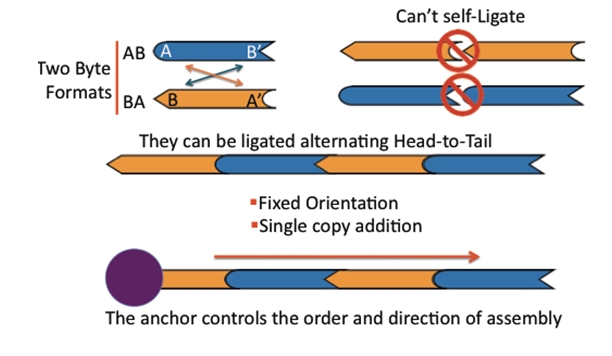
BioBytes
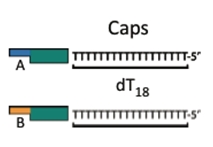
Cap
Byte Construction
Assembly System
BioBytes Vs BioBytes 2.0
The "BioBytes Version 2.0" construction method has been shown to create (insert actual data here) plasmids from up to 8 separate parts in
an afternoon's work. This is a vast improvement.
[[Image:team-alberta-building-tour.jpg|center|frame|BioByte version 2.0 construction.]
BioBytes Components
The method has three main components:
The Anchor
The BioBytes
DNA fragments that can be attached together to build up a larger construct. There are two types of pieces, AB and BA. The A end can join only with another A end and the B end can join only with another B end. As a result pieces can only be joined in a single orientation.
The Cap
A DNA fragment that finishes off a construct and allows for circularization of the construct into a plasmid.
The process of building a plasmid is more elegant and more rapid than the current biobyte system!
The Process
Starting with an anchor, add the first piece and ligate.
Then hold the single piece construct in the tube by placing it on the magnetic rack. Now you can wash away most of the excess of piece 1.
Add the next piece and repeat until you have added all the pieces you want.
Then add the cap.
Now just heat to release the anchor and open up the cap, upon cooling the construct will circularize.
Easy!
Using this process we were able to assemble eight pieces in an afternoon!
 "
"