|
Chitin is an abundant biopolymer found primarily in the exoskeletons of arthropods, including many insects and crustaceans. It is composed of N-acetylglucosamine monomers (Fig. 1)
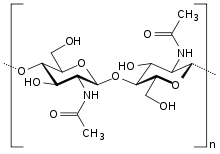 Figure 1 Chitin molecular structure.
- chitin - what is it, how is it used in nature
- The production of chitin in yeast, pathway, mechanism
Chitin Synthase 3 (CHS3) was cloned out of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae (S.C.) cDNA.
CHS3 from S.C. was chosen because the the protein does not require cofactors or activation factors and also because it was determined to be the most active of the Chitin Synthase family.
Chitin Synthase polymerizes N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine, also known as Chitin, with substrate as UDP-N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine.
|  "
"






