Team:Newcastle/Initial filamentous
From 2010.igem.org
Revision as of 23:06, 25 October 2010 by RachelBoyd (Talk | contribs)

| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Molecular tweezer tensile strength test.
Filamentous Cells
Filamentous cells genes list
- yneA (Transcribed with yneB, ynzC, is an analogue of sulA in E.coli) * our biobrick is designed to over express this gene reducing cell division possibly by inhibiting FtsZ ring formation or constriction.
- dinR (Homologue of lexA in E.coli transcribed in the opposite direction)
- ftsZ (Involved in the recruitment of other proteins to the divisisome for cytokinesis, strangely over expression results in disruption of Zring formation as well as reduced expression)
- secA (Involved in the secretion of extracellular proteins and the insertion of transmembrane proteins)
- recA (Involved in SOS response removing the repressor DinR (LexA))
- wpr and epr produce extracellular proteases that cleave the signal peptide/transmembrane domain of YneA
- ezr produces a protein which sequesters FtsZ monomer by binding its C terminal domain and also inhibits GTP binding; however overexpression does not result in filamentation.
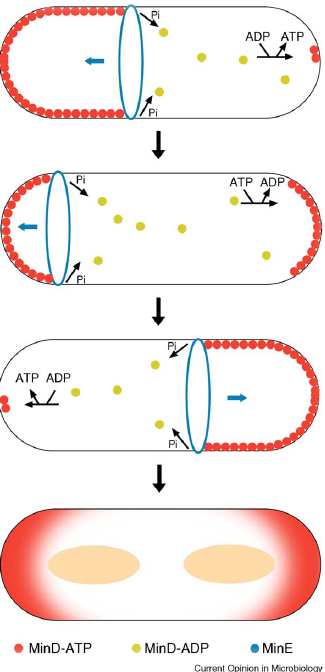
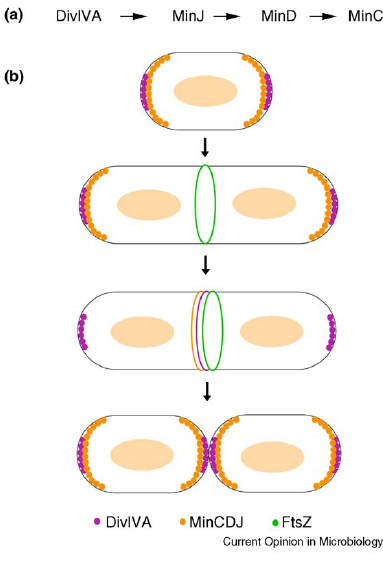
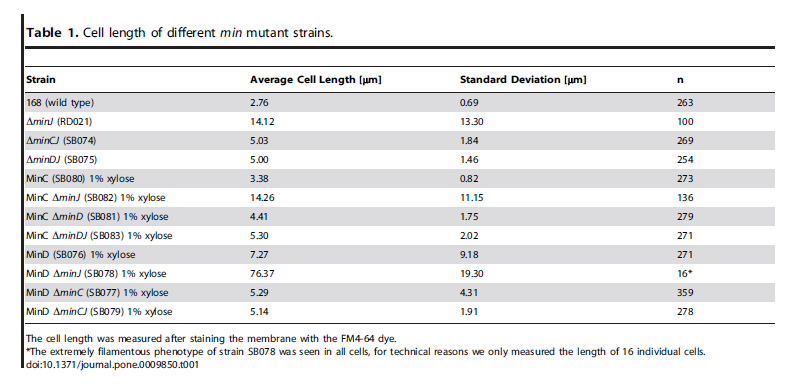
- min C,D ,J and divIVA prevent polar cell division .
- Positive regulators of FtsZ: ftsA, zapA, zipA, ftsL and divIC
- Inhibitors of Daughter cell separation: lytC,D,E,F and cwlS *Chains rather than filaments, yneA is also reported to increase the time spent in chains well into the stationary phase of bacterial growth.
 "
"