Team:USTC/Project/protein/conclusion
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Evelynzhang (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Template:USTCiGEM2010_header}} | {{Template:USTCiGEM2010_header}} | ||
<div style="padding:0 32px 0 300px;min-height:700px;"> | <div style="padding:0 32px 0 300px;min-height:700px;"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==''' Part Ⅰ: Fusion Proteins to Identify the Localization of BMC '''== | ||
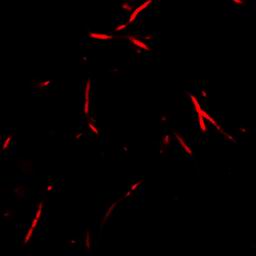
| + | From the following picture(Fig 1), we can identify the structure and Localization of BMC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:USTC2010_Results_of_Fusion_Protein-RFP-A(1).jpg]] | ||
| + | Fig 1: Results of fusion protein --- RFP-A | ||
| + | |||
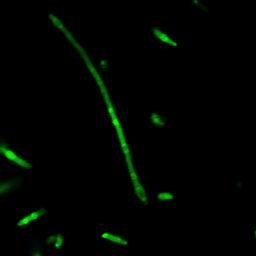
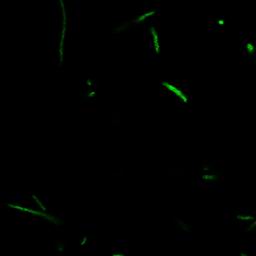
| + | ==''' Part Ⅱ: Fusion Proteins for Transportation into BMC''' == | ||
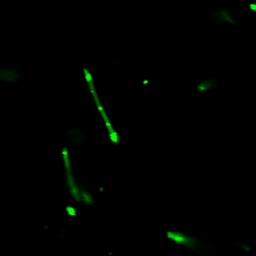
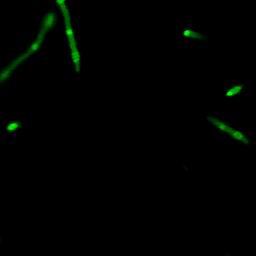
| + | The series of studies presented here demonstrates that a short N-terminal peptide is necessary and sufficient for association of proteins with BMC and likely mediates packaging within the interior of BMC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:USTC2010_Result_of_Fusion_Protein_P_L-GFP(1).jpg]] | ||
| + | [[Image:USTC2010_Result_of_Fusion_Protein_P_L-GFP(2).jpg]] | ||
| + | [[Image:USTC2010_Result_of_Fusion_Protein_P_L-GFP(3).jpg]] | ||
| + | [[Image:USTC2010_Result_of_Fusion_Protein_P_L-GFP(4).jpg]] | ||
| + | Fig 2: Results of fusion protein --- PduP_L-GFP | ||
| + | |||
| + | == '''Part Ⅲ: Fusion Proteins for BMC Purification''' == | ||
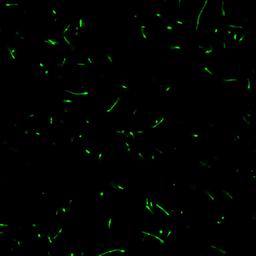
| + | The localization of BMC can be observed in Fig 3, which is expressed by the fusion protein of PduV[1-98] and GFP. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:USTC2010_Results_of_Fusion_Protein_V_S-GFP(1).jpg]] | ||
| + | Fig 3: Results of fusion protein --- PduV_S-GFP | ||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 27 October 2010
Part Ⅰ: Fusion Proteins to Identify the Localization of BMC
From the following picture(Fig 1), we can identify the structure and Localization of BMC.
Fig 1: Results of fusion protein --- RFP-A
Part Ⅱ: Fusion Proteins for Transportation into BMC
The series of studies presented here demonstrates that a short N-terminal peptide is necessary and sufficient for association of proteins with BMC and likely mediates packaging within the interior of BMC.
Fig 2: Results of fusion protein --- PduP_L-GFP
Part Ⅲ: Fusion Proteins for BMC Purification
The localization of BMC can be observed in Fig 3, which is expressed by the fusion protein of PduV[1-98] and GFP.
Fig 3: Results of fusion protein --- PduV_S-GFP "
"