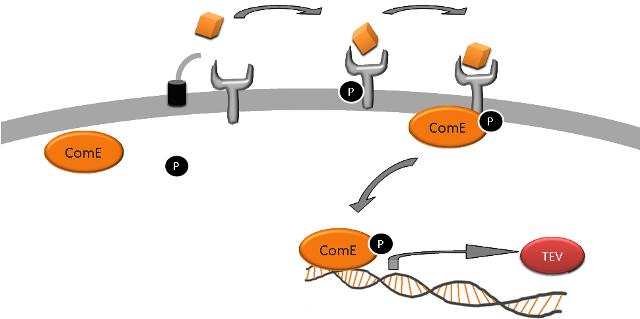
Team:Imperial College London/Modelling/Signalling/Detailed Description
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|- | |- | ||
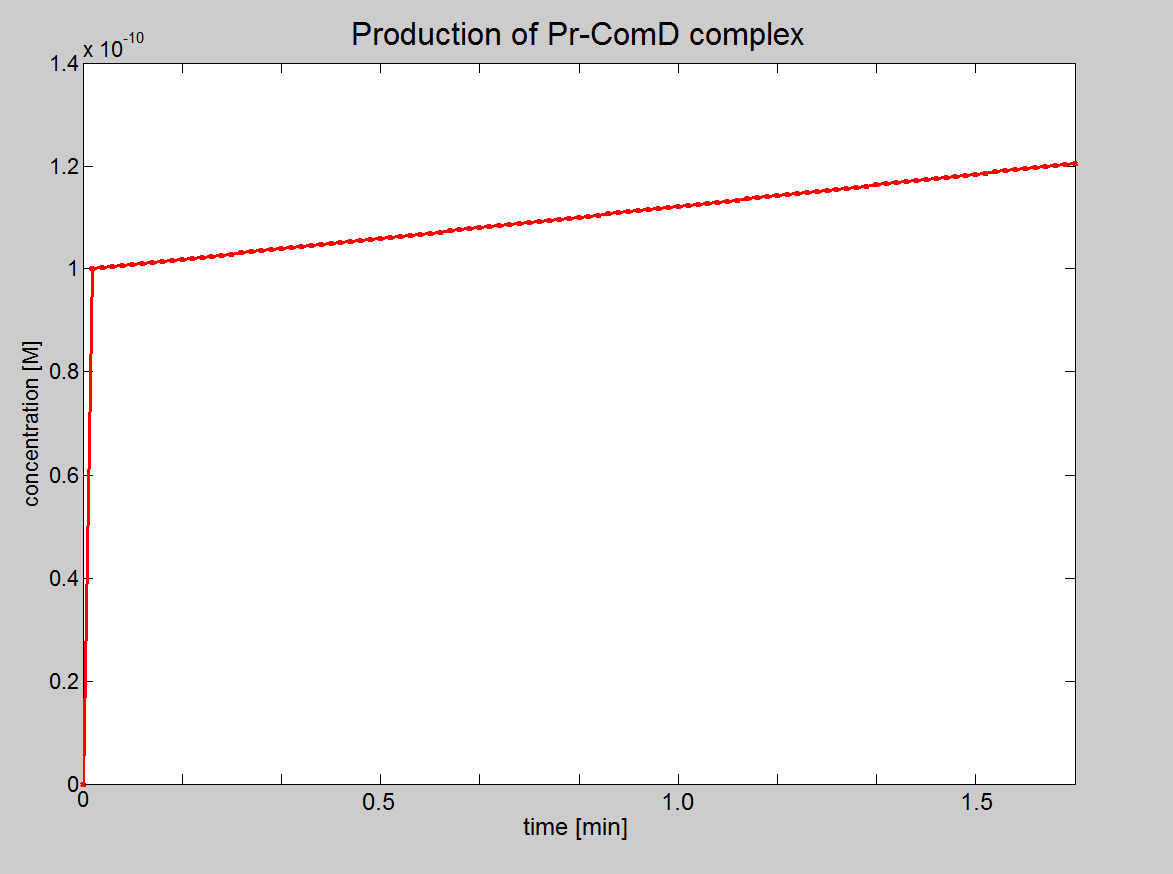
|AIP + ComD <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD | |AIP + ComD <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:IC_Signalling_Results2.png|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Graph showing production of AIP-ComD | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
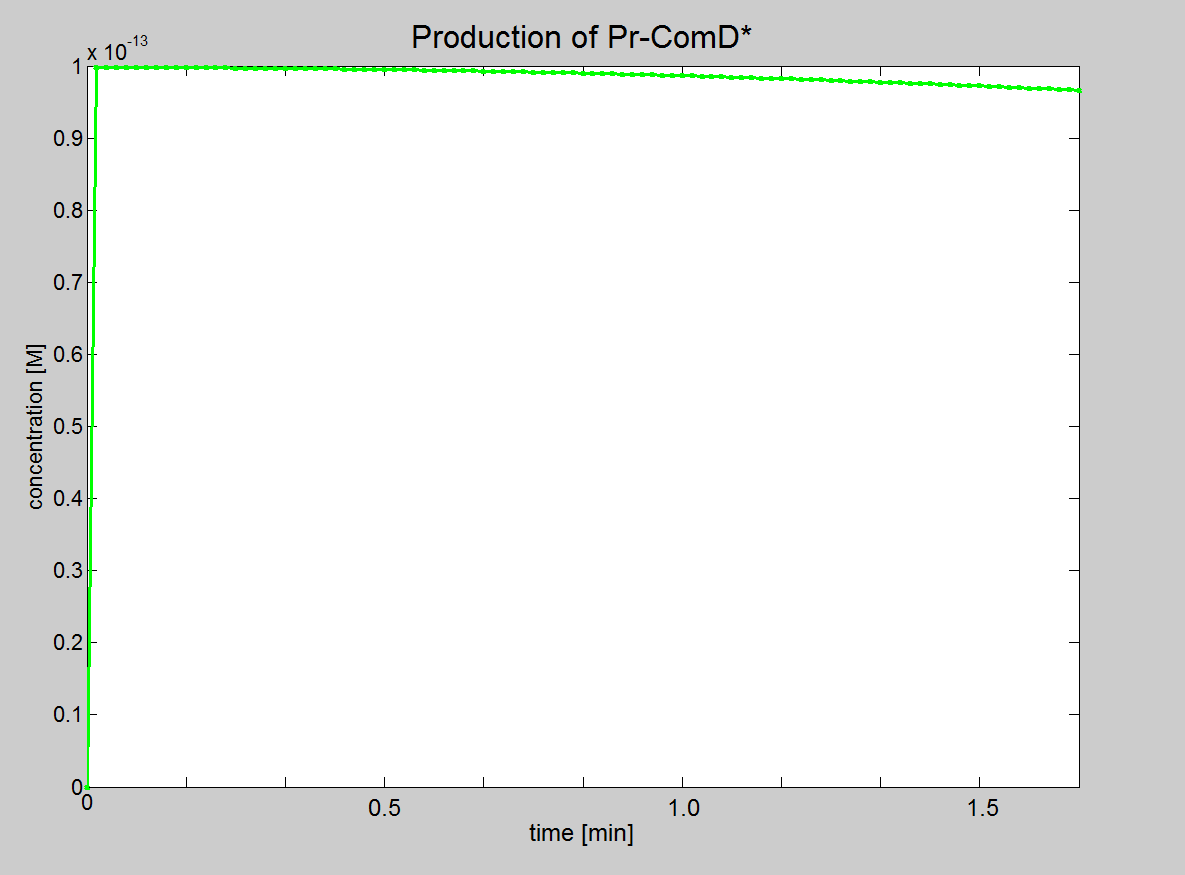
|'''Equation 2:''' Phosphate binds to the AIP-ComD complex to form another complex (AIP-ComD*) | |'''Equation 2:''' Phosphate binds to the AIP-ComD complex to form another complex (AIP-ComD*) | ||
| Line 24: | Line 33: | ||
|AIP-ComD + Phosphate <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD* | |AIP-ComD + Phosphate <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |<div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:IC_Signalling_Results3.png|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Graph showing production of AIP-ComD* | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |- | ||
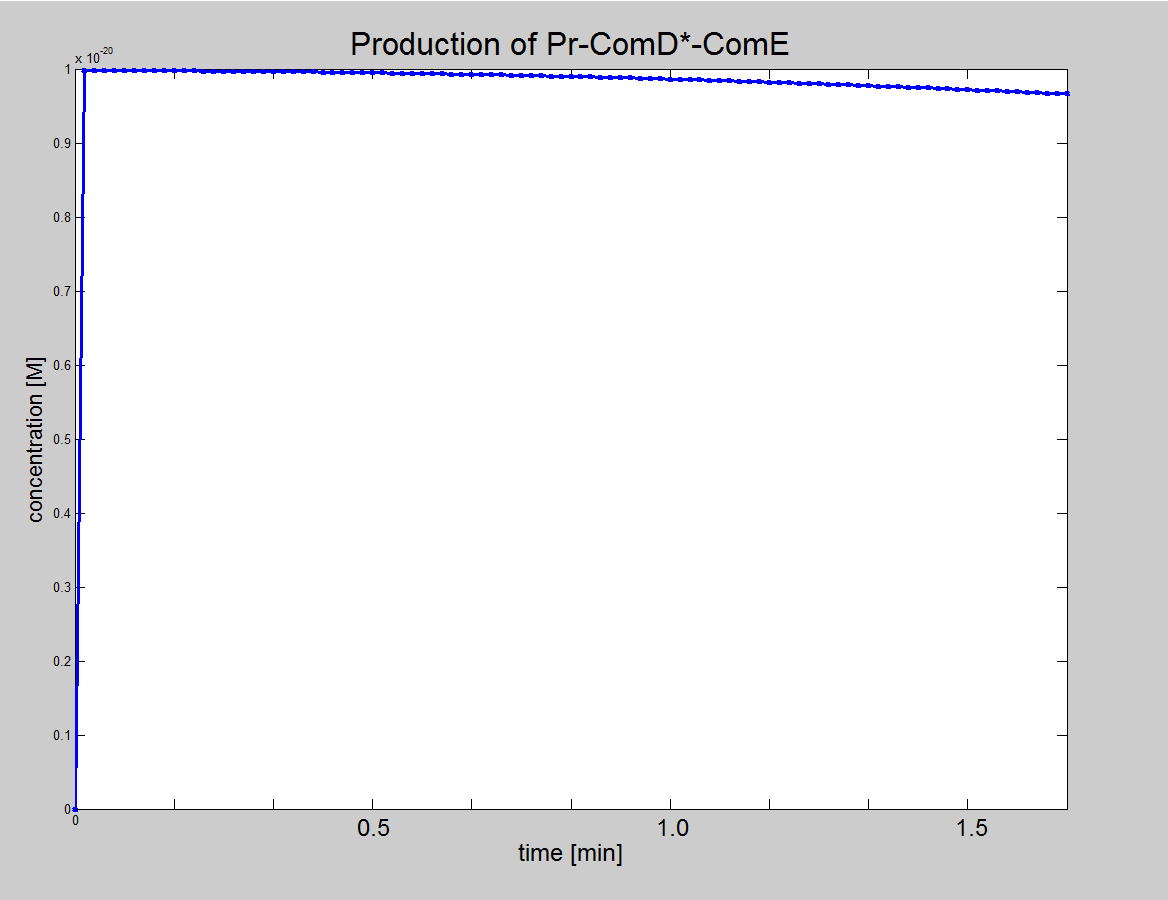
|'''Equation 3:''' ComE binds to the AIP-ComD* recepetor to form another complex (AIP-ComD*-ComE) | |'''Equation 3:''' ComE binds to the AIP-ComD* recepetor to form another complex (AIP-ComD*-ComE) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|AIP-ComD* + ComE <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD*-ComE | |AIP-ComD* + ComE <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD*-ComE | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:IC_Signalling_Results4.png|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Graph showing production of AIP-ComD*-ComE | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
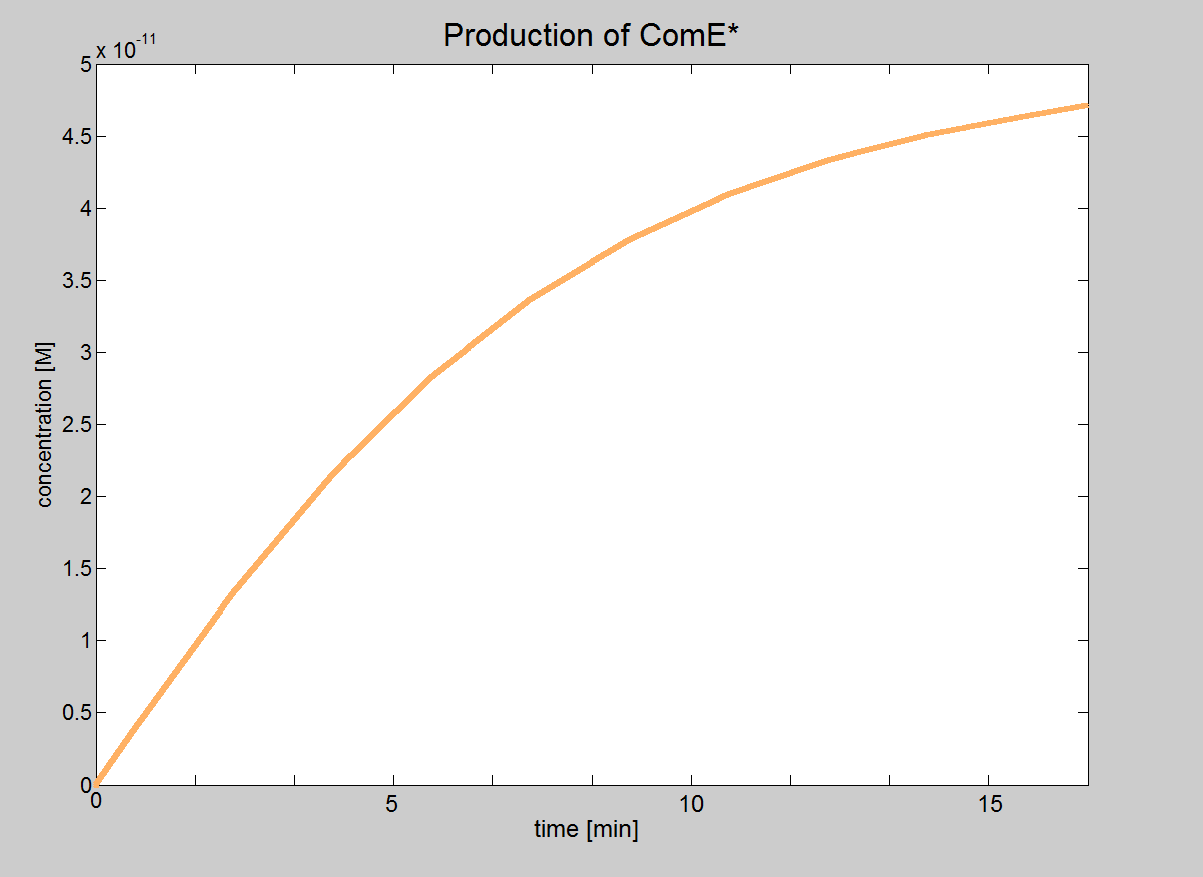
|'''Equation 4:''' Phosphate group on ComD binds to ComE and forms two products: phosphorylated ComE (ComE*) and AIP-ComD | |'''Equation 4:''' Phosphate group on ComD binds to ComE and forms two products: phosphorylated ComE (ComE*) and AIP-ComD | ||
|- | |- | ||
|AIP-ComD*-ComE <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD + ComE* | |AIP-ComD*-ComE <html>↔</html> AIP-ComD + ComE* | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:IC_Signalling_Results1.png|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Graph showing production of ComE* | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Using the Law of Mass Action, we can rewrite these 4 equations: | |Using the Law of Mass Action, we can rewrite these 4 equations: | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 27 October 2010
| Modelling | Overview | Detection Model | Signaling Model | Fast Response Model | Interactions |
| A major part of the project consisted of modelling each module. This enabled us to decide which ideas we should implement. Look at the Fast Response page for a great example of how modelling has made a major impact on our design! | |
| Objectives | Description | Results | Constants | MATLAB Code |
 "
"