Team:Heidelberg/Project/miMeasure
From 2010.igem.org
(→Analysis of Randomized Binding Sites Against Synthetic miRNA) |
Laura Nadine (Talk | contribs) (→Analysis of Randomized Binding Sites Against Synthetic miRNA) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
===Analysis of Randomized Binding Sites Against Synthetic miRNA=== | ===Analysis of Randomized Binding Sites Against Synthetic miRNA=== | ||
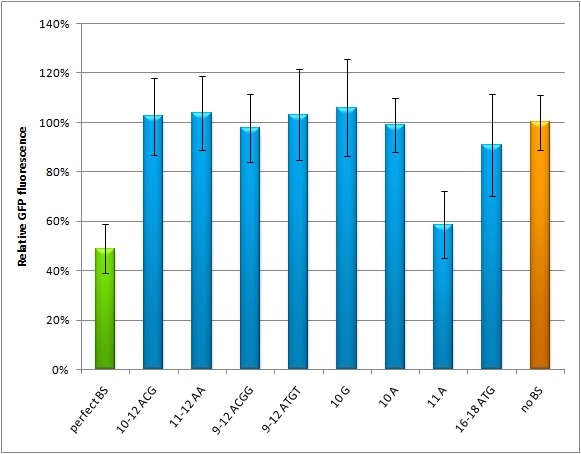
| - | We used microscopy analysis to determine the EGFP expression in relation to EBFP2. EBFP2 serves as a normalization for transfection efficiency. Nine miMeasure constructs with different binding sites were designed. The binding sites are either mutated at one site, or they contain randomly changed sites within a certain range. The construct representing the 100% knock-down carries a perfect binding site, which is complementary to the synthetic miRNA miRsAg. The negative control represents 0% knock-down, since there is no binding site cloned into this miMeasure construct. The GFP/BFP-ratio stand for the level of GFP-expression normalized to on copy per cell. We modified binding sites for the synthetic miRNA by introducing random basepairs surrounding the seed region as described above, thereby changing the knockdown efficiency. In figure 1 we plotted the knockdown percentage of our constructs. | + | We used microscopy analysis to determine the EGFP expression in relation to EBFP2. EBFP2 serves as a normalization for transfection efficiency. Nine miMeasure constructs with different binding sites were designed. The binding sites are either mutated at one site, or they contain randomly changed sites within a certain range. The construct representing the 100% knock-down carries a perfect binding site, which is complementary to the synthetic miRNA miRsAg. The negative control represents 0% knock-down, since there is no binding site cloned into this miMeasure construct. The GFP/BFP-ratio stand for the level of GFP-expression normalized to on copy per cell. We modified binding sites for the synthetic miRNA by introducing random basepairs surrounding the seed region as described above, thereby changing the knockdown efficiency. In figure 1 we plotted the knockdown percentage of our constructs. The miMeasure construct and negative control were [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/Methods#Transfection co-transfected] with either shRNA miRsAg expressed from a CMV promoter on pcDNA5 or an inert synthetic RNA as control in 1:5 ratio, respectively. |
[[Image:M12-M22_HeLa_daten.jpg|thumb|500px|center|'''GFP/BFP ratio normalized by the negative control''' The data are generated by confocal microscopy of Hela cells, which were transfected with different miMeasure constructs M12-M22 including the negative control (miMeasure construct without binding site). The negative control equals to 1.]] | [[Image:M12-M22_HeLa_daten.jpg|thumb|500px|center|'''GFP/BFP ratio normalized by the negative control''' The data are generated by confocal microscopy of Hela cells, which were transfected with different miMeasure constructs M12-M22 including the negative control (miMeasure construct without binding site). The negative control equals to 1.]] | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
| - | Comparing the GFP/BFP-ratio between the constructs, we can see a significant difference of GFP expression in between the negative control and the construct containing the perfect binding site. | + | Comparing the GFP/BFP-ratio between the constructs, we can see a significant difference of GFP expression in between the negative control and the construct containing the perfect binding site. Since the control is not downregulated due to lack of binding sites, we set it as 100% expression on this chart. It can be seen that the perfect binding sites effects the lowest GFP expression, approximately 50%, while other binding sites range in between 55% and 100% of expression. |
| - | + | ||
| - | [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/Methods#Transfection Transfection] with four different conditions were carried out on day two. The ratio of transfection is 1 (M construct) : 4 (stuffer/ miRsAg/ pcDNA5/ shRNA3) with a total amount of 50ng DNA. | + | <!--discussion?The seed region is altered in M22. Since the seed region is considered the most important site for knock-down efficiency, its change diminishes the knock-down capability of the binding site completely. So the GFP expression in this case is as high as the negative control, where no binding site was inserted into the miMeasure plasmid. --> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!--[https://2010.igem.org/Team:Heidelberg/Notebook/Methods#Transfection Transfection] with four different conditions were carried out on day two. The ratio of transfection is 1 (M construct) : 4 (stuffer/ miRsAg/ pcDNA5/ shRNA3) with a total amount of 50ng DNA. | ||
Condition '''a''': cotransfection with stuffer (salmon sperm DNA) | Condition '''a''': cotransfection with stuffer (salmon sperm DNA) | ||
| Line 69: | Line 71: | ||
Condition '''d''': cotransfection with synthetic shRNA3 | Condition '''d''': cotransfection with synthetic shRNA3 | ||
| - | A control consisting of the empty miMeasure plasmid (without binding site) was also cotransfected with the same conditions a, b, c and d. The cells were used for measurements on day three. | + | A control consisting of the empty miMeasure plasmid (without binding site) was also cotransfected with the same conditions a, b, c and d. The cells were used for measurements on day three.--> |
===Analysis of miraPCR generated binding sites against natural miRNA=== | ===Analysis of miraPCR generated binding sites against natural miRNA=== | ||
Revision as of 08:52, 27 October 2010

|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"