Team:Newcastle/5 August 2010
From 2010.igem.org
(→Conclusion) |
(→Discussion) |
||
| Line 191: | Line 191: | ||
D=Diameter of cylinder, | D=Diameter of cylinder, | ||
| - | We | + | We calculated the maximum tensile strength of this concrete cylinder to be . |
==Conclusion== | ==Conclusion== | ||
Revision as of 23:07, 25 October 2010

| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Contents |
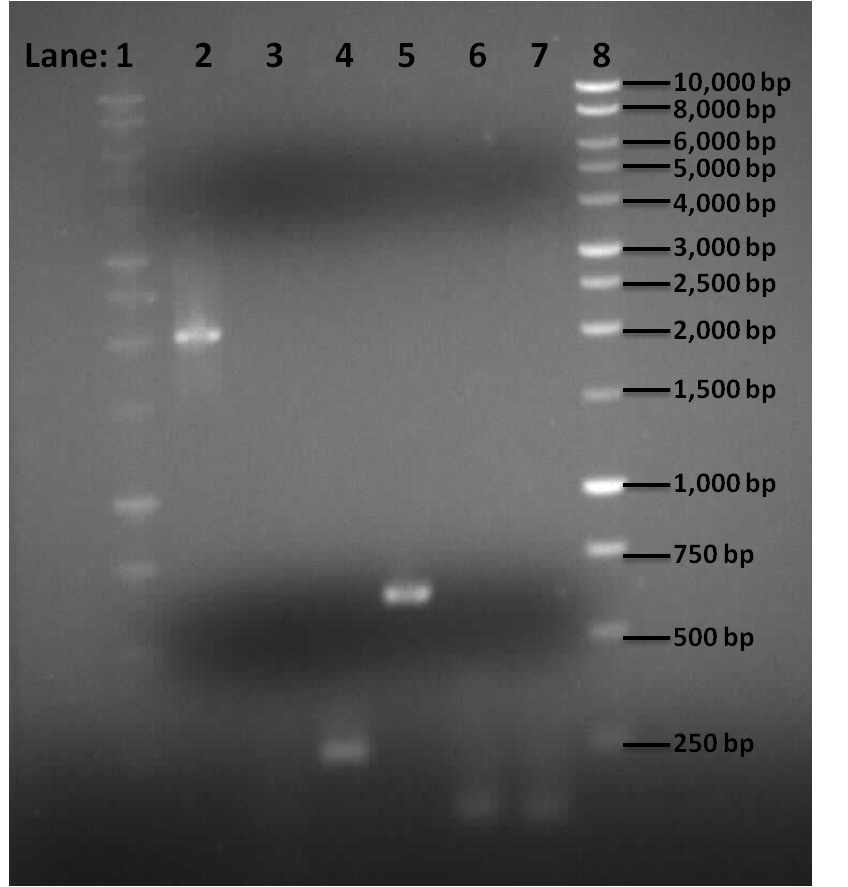
Gel Electrophoresis for the Amplified Fragments of rocF
Aim
The aim of the experiment is to check for the PCR amplified RocF frangments that was performed on 4th August, 2010 by using gel electrophorsis.
Materials and Protocol
Please refer to: Gel electrophoresis.
Result
Figure 1: Gel electrophoresis of the pSB1C3, Pspac_oid promoter, rocF fragments and double terminator.
- Lane 1: 1kb DNA ladder
- Lane 2: BioBrick compatible vector pSB1C3
- Lane 3: Pspac_oid promoter
- Lane 4: 1st fragment of rocF CDS
- Lane 5: 2nd fragment of rocF CDS
- Lane 6: 3rd fragment of rocF CDS
- Lane 7: Double Terminator
- Lane 8: 1kb DNA ladder
| Biobrick compatible vector pSB1C3 | Pspac_oid pormoter | 1st fragment of rocF CDS | 2nd fragment of rocF CDS) | 3rd fragment of rocF CDS | Double Terminator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size of the Fragment (in bp) | 2072 approx. | 106 approx. | 246 approx. | 597 approx. | 125 approx. | 116 approx. |
Table 1: Table represents the size of the fragments represented as bands on the gel in their corresponding lanes.
Discussion
Correct sized bands were observed in lanes 2,4,5,6 and 7. However lane 3 did not contain any band.
Conclusion
PCR reaction was successful for all the fragments apart from Pspac_oid promoter which was represented in lane 3. This could be due to the following prpeblems:
- Primer sequences could be incorrect.
- Melting temperature could be incorrect.
- Plasmid pMutin4 could have degenerated due to long term storage.
Solution for the problem
- Check the primer sequences so as to eliminate any problems associated with the primer sequence.
- Perform PCR reactions for the Pspac_oid fragment with 3 different melting temperatures at 50°C, 51°C and 52°C.
Amplification of the Pspac_oid promoter and RocF fragments by PCR
Aim
The aim of this experiment is to amplify the Pspac_oid promoter fragment from the plasmid pMutin4 for the construction of the rocF BioBrick using 3 different melting temperatures in the Phusion PCR protocol, as well as to rerun the gel electrophoresis of the RocF fragments and the double terminator fragments obtained this morning.
Materials and Protocol
Please refer to PCR for the Phusion PCR protocol. The details for the 3 PCR reactions are mentioned below:
PCR
| Tube | Part to be amplified | DNA fragment consisting the part | Forward primer | Reverse Primer | Melting Temperature (Tm in °C) | Size of the fragment (in bp) | Extension time* (in seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pspacoid Promoter | pMutin4 | P1P1 forward | P2P1 reverse | 51 | 106 approx. | 15 |
| 2 | Pspacoid Promoter | pMutin4 | P1P1 forward | P2P1 reverse | 50 | 106 approx. | 15 |
| 3 | Pspacoid Promoter | pMutin4 | P1P1 forward | P2P1 reverse | 52 | 106 approx. | 15 |
Table 2: Table represents 3 different Phusion PCR reactions for the amplification of Pspac_oid promoter, so that it can be ligated together with other fragments for the construction of rocF with the help of Gibson Cloning method.
- The extension rate of the Phusion polymerase is 1Kb/ 30 seconds. Therefore the extension time of each PCR reaction is different.
- To learn more about the rocF fragments, please refer to the Cloning strategy for rocF.
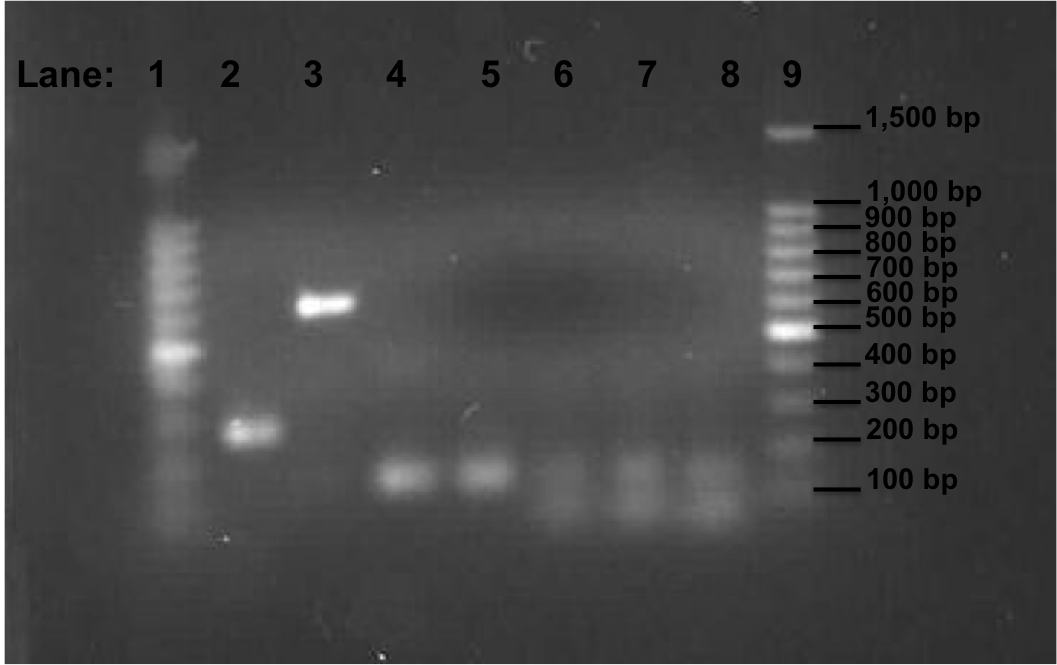
Result
Figure 2: Gel electrophoresis of the pSB1C3, Pspac_oid promoter, rocF fragments and double terminator.
- Lane 1: 100bp DNA ladder
- Lane 2: 1st fragment of rocF CDS
- Lane 3: 2nd fragment of rocF CDS
- Lane 4: 3rd fragment of rocF CDS
- Lane 5: Double Terminator
- Lane 6: Pspac_oid promoter (Tm 50°C i.e. Tube 2 of PCR reaction which is mentioned above)
- Lane 7: Pspac_oid promoter (Tm 51°C i.e. Tube 1 of PCR reaction which is mentioned above)
- Lane 8: Pspac_oid promoter (Tm 52°C i.e. Tube 3 of PCR reaction which is mentioned above)
- Lane 9: 100bp DNA ladder
| Pspac_oid pormoter | 1st fragment of rocF CDS | 2nd fragment of rocF CDS) | 3rd fragment of rocF CDS | Double Terminator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size of the Fragment (in bp) | 106 approx. | 246 approx. | 597 approx. | 125 approx. | 116 approx. |
Table 3: Table represents the size of the fragments represented as bands on the gel in their corresponding lanes.
Discussion
Correct bands size was observed in lanes 2,3,4 and 5 but not in lanes 6,7, and 8. The three different melting temperature used during the PCR for the Pspac_oid promoter is not successful.
Conclusion
The amplified frangments of RocF and the double terminator have been successful. However we are still not able to obtain the Pspac_oid promoter even when we have checked the primer sequence and using 3 different melting temperature. This could be due to the folloeing reason:
- Plasmid pMutin4 could have degenerated due to long term storage.
Solution for the problem
- Use a different stock of the plasmid pMutin4 and perform PCR reaction for the amplification of Pspac_oid promoter.
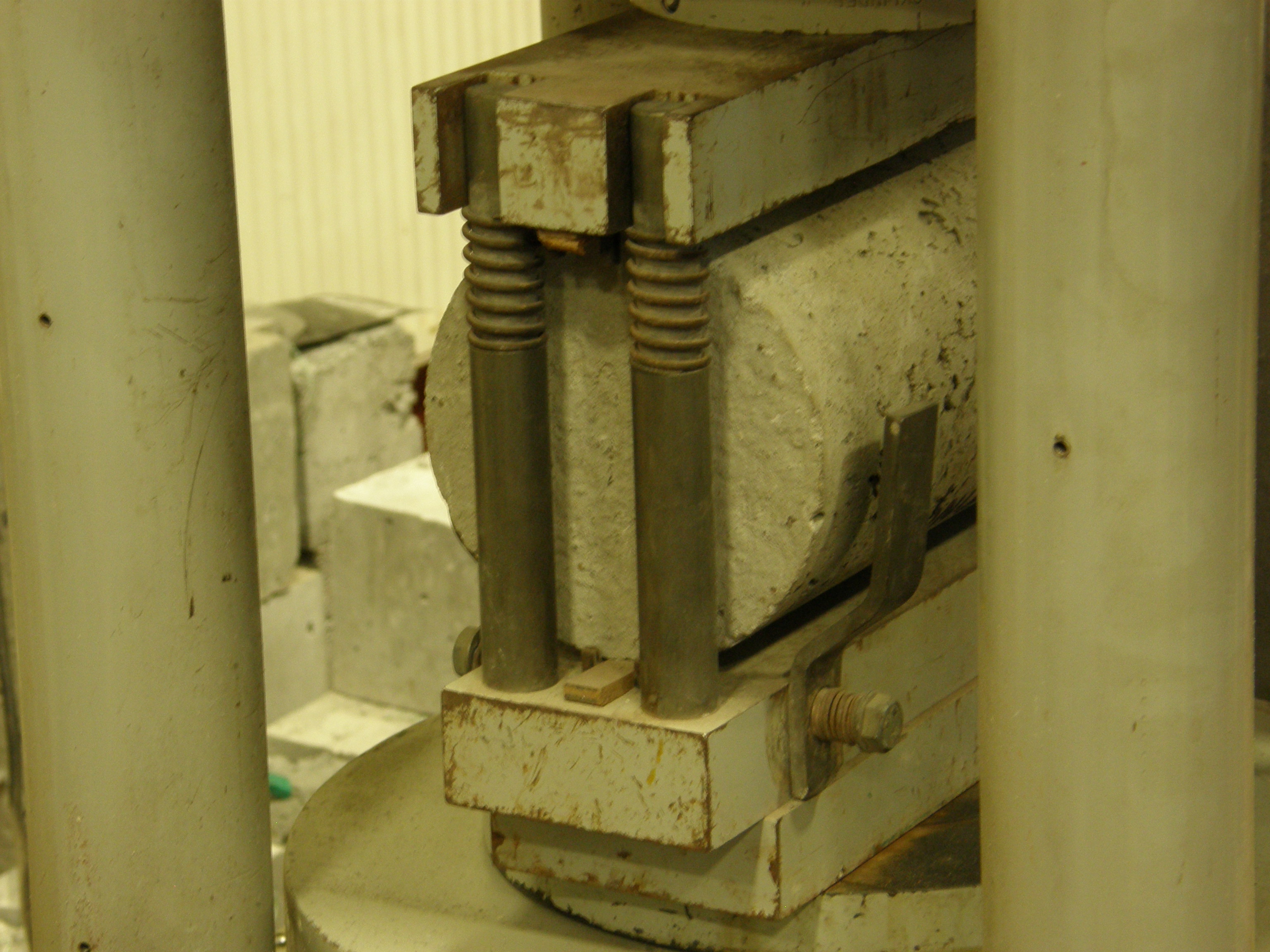
Concrete Tensile Splitting Test
Aim
To obtain samples of cracked concrete for BacillaFilla to fill up the cracks and also to determine the tensile strength of concrete before the cracks are filled up.
Materials
- Concrete cylinder
- Jubilee clips
Procedure
- A concrete cylinder was made beforehand and left for more than 28 days to cure so that a straight line of crack will form down the diameter of the cylinder.
- The cylinder is placed on two diametrically opposed loading generators. Two pieces of plywood are placed between the loading plates and the concrete cylinder to prevent failure in compression.
- The generator is then started for loading until the cylinder forms a crack down the diameter. The maximum load is recorded and tensile strength of the concrete cylinder is calculated.
Result
The maximum load that is recorded from the test is 171.3kN.
Discussion
From the formula f=(2P)/(πBD), where f=tensile strength, P=Maximum applied load, B=Depth of cylinder, D=Diameter of cylinder,
We calculated the maximum tensile strength of this concrete cylinder to be .
Conclusion
We now have the original tensile strength of the concrete cylinder, which is . We will test its tensile strength again after the concrete has been filled up by Bacilla Filla.
Amplification of Pspac_oid promoter and lacI from a different stock of pMutin4 by PCR
Aim
The aim of this experiment is to amplify the Pspac_oid promoter fragment and the lacI fragment from a different stock of plasmid pMutin4 using the Phusion PCR.
Materials and Protocol
Please refer to PCR for Phusion PCR protocol. The details for the 2 PCR reactions are mentioned below:
PCR
| Tube | Part to be amplified | DNA fragment consisting the part | Forward primer | Reverse Primer | Melting Temperature (Tm in °C) | Size of the fragment (in bp) | Extension time* (in seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LacI | pMutin4 | P1P1 forward | P2P1 reverse | 54 | 1100 approx. | 15 |
| 2 | Pspacoid Promoter | pMutin4 | P1P1 forward | P2P1 reverse | 50 | 106 approx. | 15 |
Table 4: Table represents 3 different Phusion PCR reactions for the amplification of Pspac_oid promoter from a different source of plasmid pMutin4, so that it can be ligated together with other fragments for the construction of rocF with the help of Gibson Cloning method.
- The extension rate of the Phusion polymerase is 1Kb/ 30 seconds. Therefore the extension time of each PCR reaction is different.
Discussion
Gel electrophoresis was not done for the PCR amplification.
Conclusion
We will be using gel electrophoresis to check the outcome of both the PCR reactions on 6th August, 2010. 
|
 "
"