Team:Lethbridge/Results
From 2010.igem.org
Adam.smith4 (Talk | contribs) (→Reference) |
Liszabruder (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
<BLOCKQUOTE> | <BLOCKQUOTE> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | =<font color="white">Placement of Oligoarginine Tail on Proteins</font>= | |
| - | = | + | |
| - | == | + | ==<font color="white">Characterized Parts</font>== |
| - | <font size="+1">< | + | |
| - | <font size="+1">< | + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_K249004"><font color="green" size="+1">K249004</font></a></html> |
| - | <font size="+1">< | + | <br><br> |
| - | <font size="+1">< | + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_K249005"><font color="green" size="+1">K249005</font></a></html> |
| - | == | + | <br><br> |
| + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_K331031"><font color="green" size="+1">K331031</font></a></html> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_K331030"><font color="green" size="+1">K331030</font></a></html> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==<font color="white">Hypothesis</font>== | ||
| + | |||
The placement of an oligoarginine sequence at the N-terminus of a protein will destabilize the protein in vivo. | The placement of an oligoarginine sequence at the N-terminus of a protein will destabilize the protein in vivo. | ||
| - | == | + | |
| - | The long term goal of our team is to utilize an oligoarginine tail to specifically target enzymes into a microcompartment composed of modified lumazine synthase subunits. While conducting background research on the project, we came upon data originally reported by Bachmair <i>et al.</i><sup>1</sup> suggesting that the identity of the amino acid at the N-terminus of a protein is related to its half-life, and mostly notably, that arginine residues at the are destabilizing. This data suggests that by placing an arginine at the N-terminus of a protein to be targeted into a lumazine synthase microcompartment would cause degradation of our protein before it can be moved into the microcompartment. <br> | + | ==<font color="white">Introduction</font>== |
| + | |||
| + | The long term goal of our team is to utilize an oligoarginine tail to specifically target enzymes into a microcompartment composed of modified lumazine synthase subunits. While conducting background research on the project, we came upon data originally reported by Bachmair <i>et al.</i><sup>1</sup> suggesting that the identity of the amino acid at the N-terminus of a protein is related to its half-life, and mostly notably, that arginine residues at the are destabilizing. This data suggests that by placing an arginine at the N-terminus of a protein to be targeted into a lumazine synthase microcompartment would cause degradation of our protein before it can be moved into the microcompartment. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
We chose to investigate the how the placement of an oligoarginine sequence affects the stability of the protein to which it is fused. | We chose to investigate the how the placement of an oligoarginine sequence affects the stability of the protein to which it is fused. | ||
| - | == | + | ==<font color="white">Method</font>== |
| + | |||
In order to further characterize the C-terminal and N-terminal oligoarginine tag (BioBricks <partinfo>BBa_K249005</partinfo> and <partinfo>K249004</partinfo> respectively) and investigate the effect their placement on protein stability, yellow fluorescent proteins (YFP) with the oligoarginine fused to either the C-terminus (<partinfo>BBa_K331023</partinfo>) or N-terminus (<partinfo>BBa_K331022</partinfo>) (and preceded by a ribosomal binding site – <partinfo>B0034</partinfo>) were synthesized. We used our Red/White 3-Antibiotic assembly method to add a tetracycline repressible promoter (<partinfo>BBa_R0010</partinfo>) for constitutive expression of the fusion protein. This addition generated BioBricks <partinfo>BBa_K331031</partinfo> and <partinfo>BBa_K331030</partinfo> for the C-terminal tagged and N-terminal tagged YFP respectively. | In order to further characterize the C-terminal and N-terminal oligoarginine tag (BioBricks <partinfo>BBa_K249005</partinfo> and <partinfo>K249004</partinfo> respectively) and investigate the effect their placement on protein stability, yellow fluorescent proteins (YFP) with the oligoarginine fused to either the C-terminus (<partinfo>BBa_K331023</partinfo>) or N-terminus (<partinfo>BBa_K331022</partinfo>) (and preceded by a ribosomal binding site – <partinfo>B0034</partinfo>) were synthesized. We used our Red/White 3-Antibiotic assembly method to add a tetracycline repressible promoter (<partinfo>BBa_R0010</partinfo>) for constitutive expression of the fusion protein. This addition generated BioBricks <partinfo>BBa_K331031</partinfo> and <partinfo>BBa_K331030</partinfo> for the C-terminal tagged and N-terminal tagged YFP respectively. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
The BioBrick containing plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α cells. These cells were grown to an OD600 of approximately 0.7, and diluted 1:10 with MilliQ H2O immediately prior to analysis by fluorescent spectroscopy. | The BioBrick containing plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α cells. These cells were grown to an OD600 of approximately 0.7, and diluted 1:10 with MilliQ H2O immediately prior to analysis by fluorescent spectroscopy. | ||
This dilution of cells was excited at 517nm, and the emission spectra was read from 522nm to 650nm. Fluorescence at 524nm (emission maxima of YFP) of control cells (Escherichia coli DH5α), N-terminal tagged, and C-terminal tagged YFP were compared. | This dilution of cells was excited at 517nm, and the emission spectra was read from 522nm to 650nm. Fluorescence at 524nm (emission maxima of YFP) of control cells (Escherichia coli DH5α), N-terminal tagged, and C-terminal tagged YFP were compared. | ||
| - | == | + | ==<font color="white">Results</font>== |
| + | |||
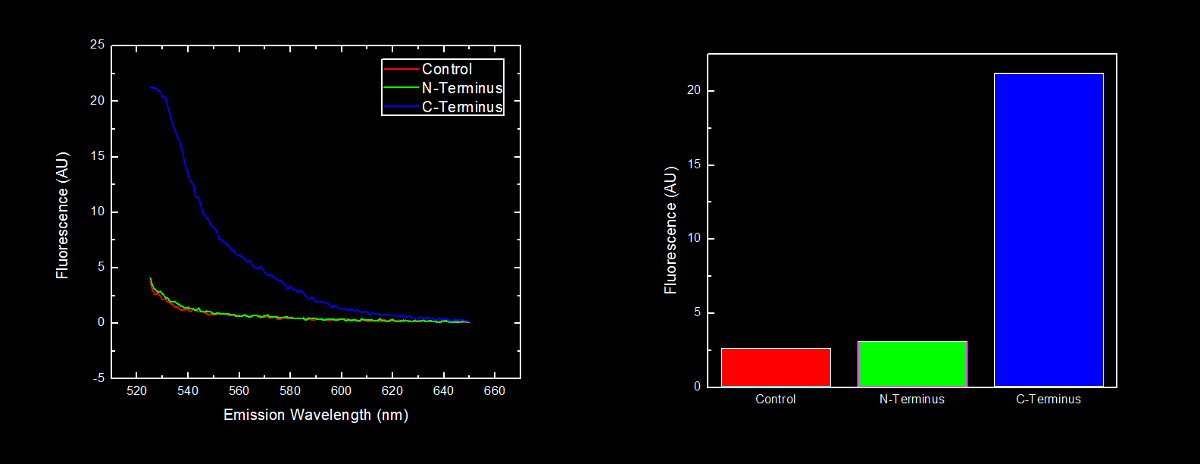
N-terminal tagged YFP did not have substantially more fluorescence than control cells. Cells expressing C-terminal tagged YFP had ten times more fluorescence than control cells and cells expressing N-terminal tagged YFP. | N-terminal tagged YFP did not have substantially more fluorescence than control cells. Cells expressing C-terminal tagged YFP had ten times more fluorescence than control cells and cells expressing N-terminal tagged YFP. | ||
[[image:Lethbridge_NvsC-terminalOligoArgBlackfINAL.png|900px]] | [[image:Lethbridge_NvsC-terminalOligoArgBlackfINAL.png|900px]] | ||
| - | == | + | ==<font color="white">Conclusion</font>== |
| - | Our results are consistent with the data reported by Bachmair <i>et al</i> in that the placement of arginine residues at the N-terminus of our YFP results in no observable fluorescence over control cells. Assuming that transcription of this K331030 and K331031 are equivalent, these data suggest that the N-terminal oligoarginine is reducing the half-life of the protein to which it is fused, ie YFP. | + | |
| + | Our results are consistent with the data reported by Bachmair <i>et al.</i> in that the placement of arginine residues at the N-terminus of our YFP results in no observable fluorescence over control cells. Assuming that transcription of this K331030 and K331031 are equivalent, these data suggest that the N-terminal oligoarginine is reducing the half-life of the protein to which it is fused, ie YFP. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==<font color="white">Reference</font>== | ||
| - | |||
<sup>1</sup>Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. <b>In Vivo Half-Life of a Protein Is a Function of Its Amino-Terminal Residue.</b> <i>Science</i> 234. <b>4773</b> 179-186. | <sup>1</sup>Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. <b>In Vivo Half-Life of a Protein Is a Function of Its Amino-Terminal Residue.</b> <i>Science</i> 234. <b>4773</b> 179-186. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
 "
"