Team:WITS-South Africa/Machine Design
From 2010.igem.org
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Template:WITS-South_Africa_Main_Menu_0910}} | {{Template:WITS-South_Africa_Main_Menu_0910}} | ||
| + | == Machine Design == | ||
| + | ===Ideal Machines=== | ||
| + | ===Intermediate Machines=== | ||
== Machine Construction == | == Machine Construction == | ||
| - | + | == Machine Testing == | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Final Machine 1 - LactoDetect | Final Machine 1 - LactoDetect | ||
Revision as of 12:56, 24 October 2010

Contents |
Machine Design
Ideal Machines
Intermediate Machines
Machine Construction
Machine Testing
Final Machine 1 - LactoDetect
Purpose:
a) To act as the ‘Detector’ Machine within the population and produce the quorum signalling peptide in response to an input signal
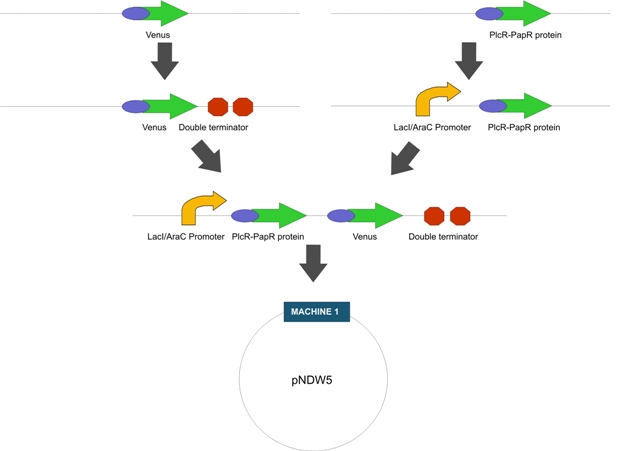
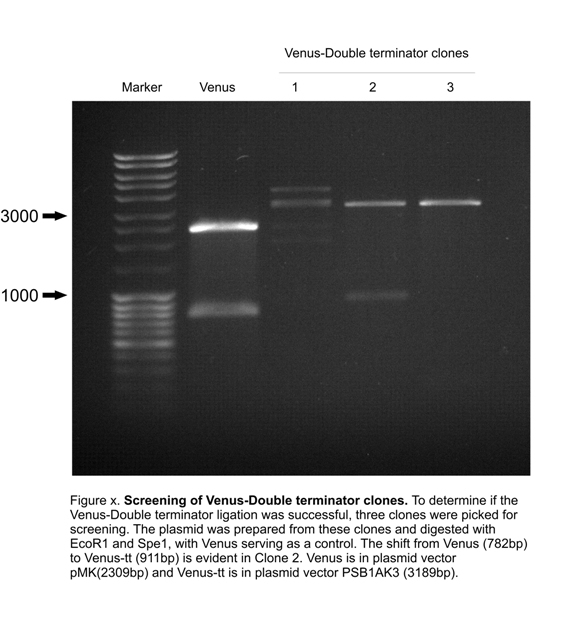
Construction: LactoDetect was contructed via a series of cloning steps using the standard assembly method. These are outlined in Figure 1 below.
Machine 2
Intermediate Machines
Intermediate Machine 2 (Figure 1) Purpose: a) To characterise the strength of the induction of the LacI/AraC promoter by measuring fluorescence after IPTG is added b) To show that the PlcR promoter is activated in L. gasseri by measuring fluorescence after the addition of exogenous PlcR and PapR proteins
Fig1. The proposed intermediate Machine 2
Fig 2. The proposed Final Machine 1
Final Machine 2 (Figure 3) Purpose a) To act as the ‘Reporter’ Machine within the population and respond to infection as previously described
Fig 3. The proposed Final Machine 2
 "
"