Team:Northwestern/Project
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 191: | Line 191: | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | | | + | |- |
| + | |||
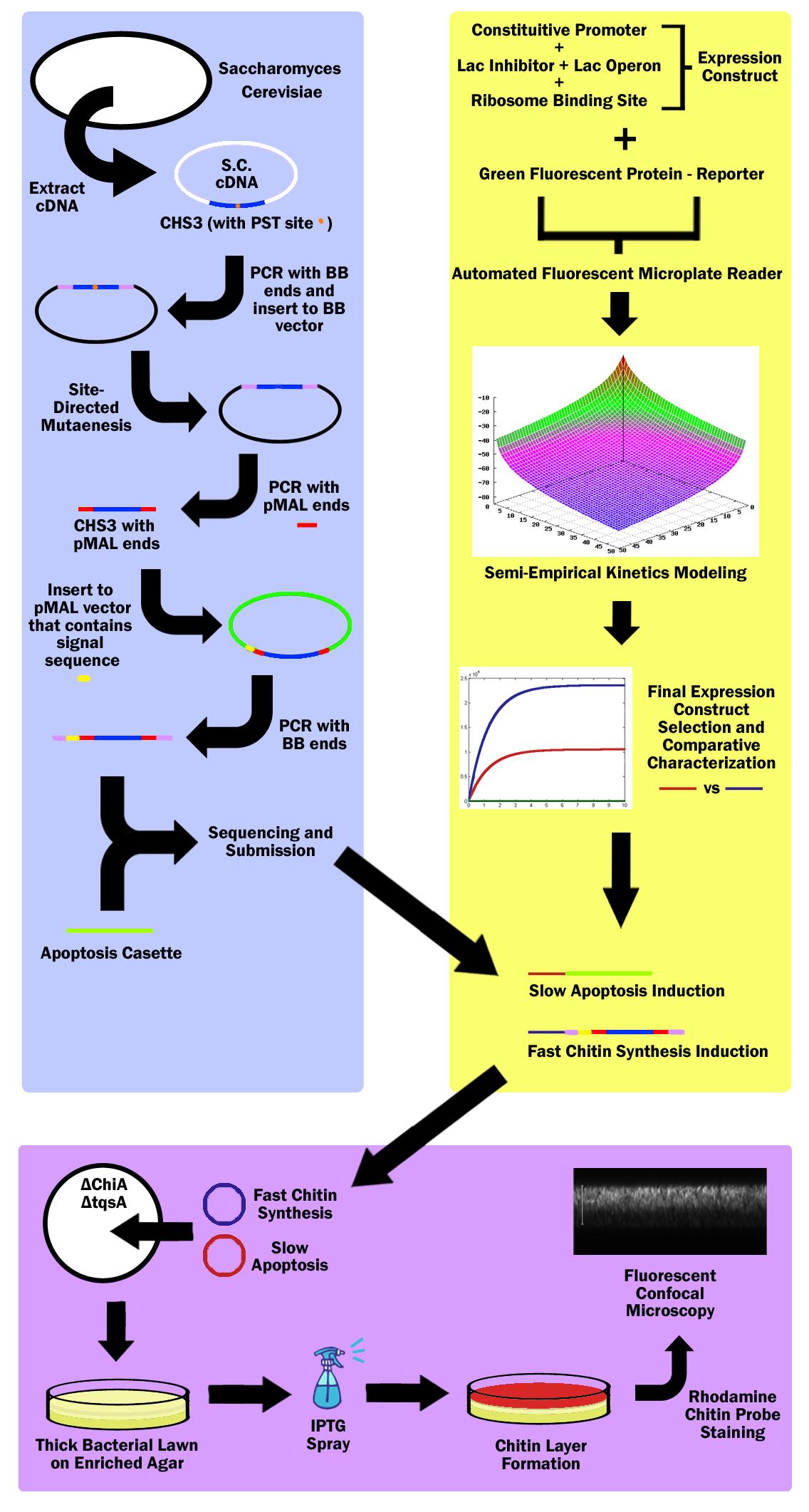
First, the Chitin Synthase 3 (CHS3) gene was subcloned out of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae (Baker’s Yeast) cDNA (complementary DNA – contains no introns, thus can be used in prokaryotes) with biobrick restriction sites (EcoR1, Xbal1 on one end, and Spe1, Pst1 on the other). CHS3 was chosen as it was found to be the major enzyme (knockouts had 80% reduced Chitin) in its family and requires no co-enzyme or activating compounds. Upon running CHS3 through NEB Cutter V2.0, we found a PST1 restriction site which is incompatible with the biobrick standard (EcoR1, Xbal, Spe1, Pst1). To remove this Pst1 site, we inserted CHS3 into a biobrick vector plasmid, and performed site-directed mutagenesis (SDM). | First, the Chitin Synthase 3 (CHS3) gene was subcloned out of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae (Baker’s Yeast) cDNA (complementary DNA – contains no introns, thus can be used in prokaryotes) with biobrick restriction sites (EcoR1, Xbal1 on one end, and Spe1, Pst1 on the other). CHS3 was chosen as it was found to be the major enzyme (knockouts had 80% reduced Chitin) in its family and requires no co-enzyme or activating compounds. Upon running CHS3 through NEB Cutter V2.0, we found a PST1 restriction site which is incompatible with the biobrick standard (EcoR1, Xbal, Spe1, Pst1). To remove this Pst1 site, we inserted CHS3 into a biobrick vector plasmid, and performed site-directed mutagenesis (SDM). | ||
Revision as of 01:59, 23 October 2010
| Home | Brainstorm | Team | Acknowledgements | Project | Human Practices | Parts | Notebook | Calendar | Protocol | Safety | Links | References | Media | Contact |
|---|
 "
"