From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
|
|
| Line 11: |
Line 11: |
| | | Wild type ''Bacillus subtillis'' | | | Wild type ''Bacillus subtillis'' |
| | |- | | |- |
| - | |[[Image:Wild type Bacillus subtillis.jpg]] | + | |[[Image:Wild type Bacillus subtillis.jpg|right]] |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |''dinR'' KO | | |''dinR'' KO |
Revision as of 08:42, 13 August 2010

|
|
|
Molecular tweezer tensile strength test.
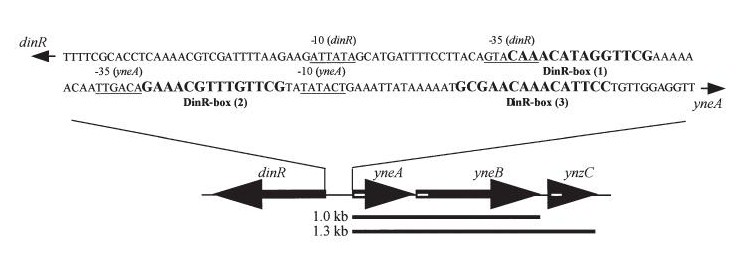
YneA
| SOS response is believe to be a universal bacteria phenomenon first studied in E.coli -LexA, recA
|
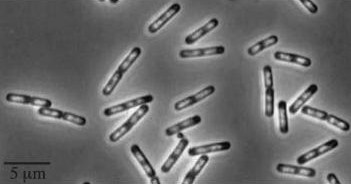
| In Bacillus subtillis (gram positive) dinR protein is homologous to lexA (Repressor of din-damage inducible genes). din genes include uvrA, uvrB, dinB, dinC dinR and recA. DNA damage inhibits cell division.
|
| Wild type Bacillus subtillis
|
|
|
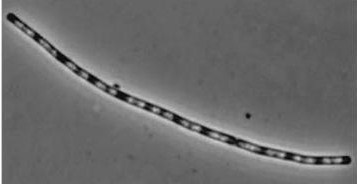
| dinR KO
|
|
|
| dinR KO mutant over expressed the divergent (opposite direction) transcript for YneA, YneB and YnzC. These genes form the SOS regulon (recA independent SOS response)
|
|
| YneA suppressed in wt without SOS induction #
|
| Expression of YneA from IPTG controlled promoter in wt leads to elongation.
|
| Disruption of YneA in SOS response leads to reduced elongation. Altering YneB and YnzC expression does not affect cell morphology.
|
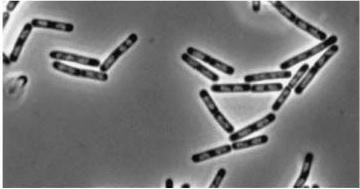
| Double mutant (dinR YneA)
|
|
| YneA protein required to suppress cell division. Not chromosome replication or segregation.
|
| FtsZ is important for bacterial cell division forming a ring structure at the division site by polymerising
assembling other proteins necessary for division at the site.
|
| FtsZ localises to the cell division cycle unless dinR is disrupted or YneA is being induced.
|
| YneA suppresses FtsZ ring formation- no proven direct interaction by two-hybrid.
|
| Filamentous cells less colony formation.
|
| YneA expression via the inactivation of dinR by Rec A is important.
|
| Sequence of YneA: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NC_000964.3?from=1918391&to=1918738&report=graph&content=5
|
Kawai, Y., Moriya, S., & Ogasawara, N. (2003). Identification of a protein, YneA, responsible for cell division suppression during the SOS response in Bacillus subtilis. Molecular microbiology, 47(4), 1113-22. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12581363.
yneA cloning strategy
Media:yneA cloning strategy.pdf

 "
"