Team:Newcastle/End of crack & signalling system
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
RachelBoyd (Talk | contribs) (→Genes required for swarming) |
RachelBoyd (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Team:Newcastle/mainbanner}} | ||
| + | |||
= Subtilin = | = Subtilin = | ||
==2008Brick== | ==2008Brick== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
# ''cheC and D'': chemotaxis protein | # ''cheC and D'': chemotaxis protein | ||
# ''sigD'': transcription factor sigma D, which is required for the expression of genes activated in late phase of flagellum biosynthesis. | # ''sigD'': transcription factor sigma D, which is required for the expression of genes activated in late phase of flagellum biosynthesis. | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | {{Team:Newcastle/footer}} | ||
Revision as of 09:02, 30 July 2010

| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Contents |
Subtilin
2008Brick
- A type 1 antimicrobial peptide [AMP] or lantibiotic produced by B. subtilis
- NB. Lantibiotic = peptide-derived antibiotics with high antimicrobial activity against various Gram-positive bacteria, including pathogenic bacteria such as propionibacteria, staphylococci, clostridia, enterococci and streptococci.
- NB. Subtilin not same as Subtilisin!!!!!
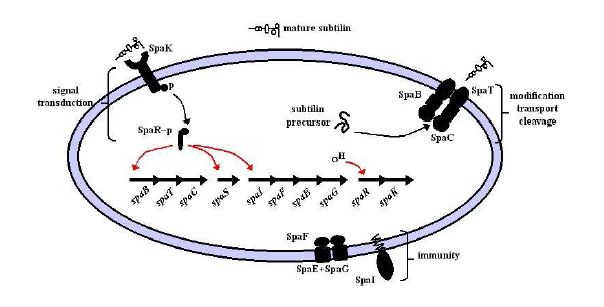
- Production of subtilin involves the spa gene cluster encompassing 10 genes, spaBTCSIFEGRK
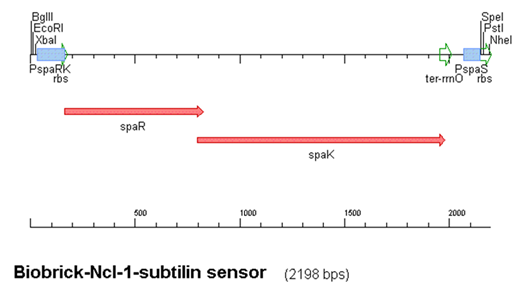
The construct above contains:
- spaRK promotor
- spaR (subtilin peptide antibiotic Regulation) - the 220 amino acid product of this gene usually regulates the downstream production of subtilin antibiotic. It has an N-terminal domain that can be phosphorylated and a C-terminal domian that has DNA binding properties [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T0M-4D4XNMM-4&_user=224739&_coverDate=09%2F01%2F2004&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000014659&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=224739&md5=1f421f180a48e2d68b86da579cc7f920|1]
- spaK (subtilin peptide antibiotic Kinase) - this gene codes for a 325 amino acid histadine kinase peptide that phosphorylates the N-terminus of SpaR [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T0M-4D5KTFV-1&_user=224739&_coverDate=09%2F01%2F2004&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000014659&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=224739&md5=8d450f455463638579798872811ae5c0|2]. This activates the DNA binding ability of the C-terminus of SpaR, which in turn initiates transcription of the downstream gene. In the case of our construct, this gene is gfp.
- rrnO transcriptional terminator
- spaS promotor - a strong promotor inducible by upstream activation of spaRK. It can be placed in front any gene to regulate its activity.
Production and Immunity Bricks
- spaBTCS genes are required for production.
- spaIFEG genes are required for immunity.
- spaB and C are modifiers of the subtilin precursor.
- spaT is a transporter.
- spaS is the gene coding for the subtilin precursor peptide.
- spaI 's gene product sequesters subtilin.
- spaFEG genes code for transporters.
Image from Modeling Subtilin production in Bacillus subtilis Using Stochastic Hybrid Systems. Hu et al.
Genes required for swarming
- comP: Histidine sensor kinase of ComX and PhrC
- comA: Response regulator of Comp
- sfp: Active surfactin synthetase
- srfA,B and C: Surfactin synthetase
- swrA,B and C: Novel gene for swarming and not for swimming
- efp: elongation factor P
- yabR and ymfl: Contribute to proper coordinationamong cells of the swarming population but are not absolutely required for surface migration.
- cheC and D: chemotaxis protein
- sigD: transcription factor sigma D, which is required for the expression of genes activated in late phase of flagellum biosynthesis.
 
|
 "
"