Team:TU Munich/Parts
From 2010.igem.org
FPraetorius (Talk | contribs) (→Submitted Parts) |
(→Screening system: Backbone BBa_K494001) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Backbone <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> is a new backbone which can be utilized not only for evaluation of terminator-based switches but also for testing basically all PoPS devices. In principle, <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> is a modified version of <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo>, which allows more flexibility in regard of the reporter protein and suits very well for testing and screening of switches based on bioLOGIC principles ''in vivo'' and with an ''in vitro'' translation assay. As an internal control, eGFP is integrated into the backbone to evaluate measurement setups and induction quality. eGFP is under the control of an pBAD promoter, therefore the whole pBAD promoter cassette being also located on <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>. In comparison to <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo> a new cloning site was created right after the eGFP protein which allows the insertion of every DNA encoded BioBrick reporter. Reporter proteins may be exchanged to fit the challenge and can be easily exchanged if not well-functioning. | Backbone <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> is a new backbone which can be utilized not only for evaluation of terminator-based switches but also for testing basically all PoPS devices. In principle, <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> is a modified version of <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo>, which allows more flexibility in regard of the reporter protein and suits very well for testing and screening of switches based on bioLOGIC principles ''in vivo'' and with an ''in vitro'' translation assay. As an internal control, eGFP is integrated into the backbone to evaluate measurement setups and induction quality. eGFP is under the control of an pBAD promoter, therefore the whole pBAD promoter cassette being also located on <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>. In comparison to <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo> a new cloning site was created right after the eGFP protein which allows the insertion of every DNA encoded BioBrick reporter. Reporter proteins may be exchanged to fit the challenge and can be easily exchanged if not well-functioning. | ||
{{:Team:TU Munich/Templates/ToggleBoxStart}} | {{:Team:TU Munich/Templates/ToggleBoxStart}} | ||
| - | For efficient usage of this part, several cloning steps must occur. First of all, the second reporter protein needs to be chosen. This can be directly introduced into the backbone using the standard BioBrick restriction enzymes EcoRI and PstI and it was done in the case of <partinfo>BBa_K494002</partinfo>. | + | {| style="background-color:transparent" |
| - | + | |- | |
| + | |[[Image:TUM2010 BBa K494001.png|300px|left | ||
| + | |For efficient usage of this part, several cloning steps must occur. First of all, the second reporter protein needs to be chosen. This can be directly introduced into the backbone using the standard BioBrick restriction enzymes EcoRI and PstI and it was done in the case of <partinfo>BBa_K494002</partinfo>. | ||
| + | |} | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
The improved screening system is optimized for the evaluation of PoPS-based devices in fluorescence measurements. RFP which was known to contain an RNase restriction site was replaced by mCherry which combines good expression yield, short maturation times and an acceptable and well-characterized quantum yield. A unique challenge for the characterization of our switches is the expression of a corresponding signal independent of the input/output measurement. Thus, we moved the BioBrick cloning site resulting in the fluorescent reporter being inside the cloning site and giving the possibility to clone independent parts behind the reporter protein. | The improved screening system is optimized for the evaluation of PoPS-based devices in fluorescence measurements. RFP which was known to contain an RNase restriction site was replaced by mCherry which combines good expression yield, short maturation times and an acceptable and well-characterized quantum yield. A unique challenge for the characterization of our switches is the expression of a corresponding signal independent of the input/output measurement. Thus, we moved the BioBrick cloning site resulting in the fluorescent reporter being inside the cloning site and giving the possibility to clone independent parts behind the reporter protein. | ||
Revision as of 03:26, 28 October 2010
|
|
Submitted Parts<groupparts align="center" width="100%">igem2010 TU_Munich</groupparts>
Malachite Green Binding Aptamer - <partinfo>BBa_K494000</partinfo>
The malachite green binding aptamer has been successfully used in screening systems being both robust and easy to produce. Aptamers provide specifities in the range of antibodies and can be evolved to target small molecules and proteins.[3] PlasmidsIn general we want to provide a new principle of gene regulation which can be further developed, tested and optimized by everybody. Therefore we focus on providing the parts needed for verification and testing of new individual switches. We provide a plasmid backbone which can be used for further cloning, a positive control to test the general functionality and measurements setups and the constructs we characterized for comparison. Screening system: Backbone <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>Backbone <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> is a new backbone which can be utilized not only for evaluation of terminator-based switches but also for testing basically all PoPS devices. In principle, <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> is a modified version of <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo>, which allows more flexibility in regard of the reporter protein and suits very well for testing and screening of switches based on bioLOGIC principles in vivo and with an in vitro translation assay. As an internal control, eGFP is integrated into the backbone to evaluate measurement setups and induction quality. eGFP is under the control of an pBAD promoter, therefore the whole pBAD promoter cassette being also located on <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>. In comparison to <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo> a new cloning site was created right after the eGFP protein which allows the insertion of every DNA encoded BioBrick reporter. Reporter proteins may be exchanged to fit the challenge and can be easily exchanged if not well-functioning.
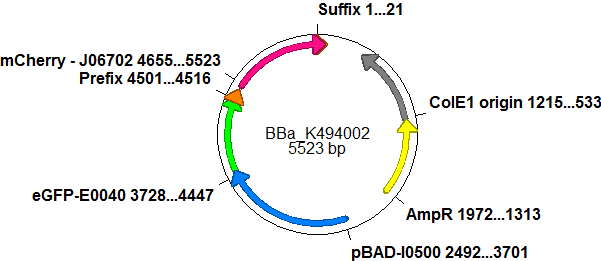
Screening System: Positive Control <partinfo>BBa_K494002</partinfo>BBa_K494002 is the backbone <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> with an mCherry inserted into the standard BioBrick cloning site using EcoRI and PstI. mCherry was further equipped with an arabinose inducible promoter (pBAD) for good expression yield and can be used as a further reference and internal standard to compare measurements and setups. With the mCherry fluorescence in the red, a fast maturation time and a satisfying quantum yield, mCherry is the perfect complement to eGFP if fluroscence is used as an output. mCherry is expressed together with eGFP after induction with arabinose without delaying elements in between both proteins.
Here we present a ready to use composite part consisting of our screening system <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo>mod <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>, the PBad Promotor <partinfo>BBa_I13453</partinfo> and the reporter protein mCherry <partinfo>BBa_J06702</partinfo> including RBS and double Terminator <partinfo>BBa_B0015</partinfo>. This part belongs to the screening system and is intended as positive control. Close Screening System: <partinfo>BBa_K494003</partinfo> - exemplary insert into <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>With the reporter protein inserted, EcoRI and XhoI upstream of the chosen reporter protein and SpeI and PstI downstream the reporter protein are now free for insertion of further proteins. In the case of <partinfo>BBa_K494003</partinfo>, <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> was utilized to evaluate a terminator for both termination efficiency and evaluation of antitermination. To test the termination efficiency, a terminator was inserted upstream of the reporter protein mCherry, in this case a Rho-independent terminator based on the regulative hairpin in front of the his-operon from Salmonella enterica. With this strong terminator right before mCherry, no mCherry fluorescence can be detected anymore while the eGFP fluorescences grows steadily over time. Another example of the same principle is shown in <partinfo>BBa_K494005</partinfo>. A further part can be inserted following the reporter protein using SpeI and PstI, this was done in the case of <partinfo>BBa_K494004</partinfo>.
Here we present a ready to use composite part consisting of our screening system <partinfo>pSB1A10</partinfo>mod <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>, the PBad Promotor BBa_I13453, the His Terminator and the reporter protein mCherry BBa_J06702 including RBS and double Terminator BBa_B0015. This part belongs to the screening system and is intended as negative control.
Close
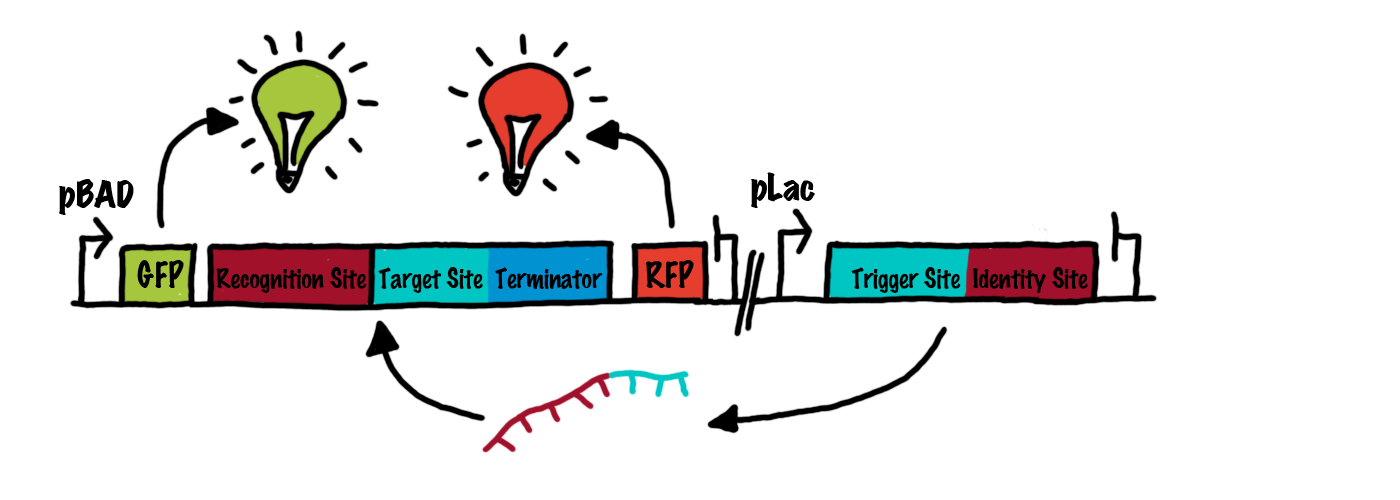
Screening System: <partinfo>BBa_K494004</partinfo> - exemplary insert into <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo>BBa_K494004 was constructed using <partinfo>BBa_K494001</partinfo> as a backbone and the cloning steps described before. Starting from <partinfo>BBa_K494003</partinfo>, a signal sequence was inserted downstream of the reporter protein mCherry. The main goal of our project is to construct and evaluate switchable elements based on terminators, our so called BioLOGICS in response of a short RNA signal strand. Therefore the signal needs to be incorporated in the plasmid. The inserted signal follows an IPTG inducible promoter, for tight regulation of the transcription. In theory every promoter can be used and any other DNA encoded signal or addition sequence can be cloned downstream of the reporter protein. Upon induction with IPTG the signal is transcribed and can in theory bind to the terminator stem loop, leading to antitermination and therefore detectable mCherry fluorescence. Another example of the same principle is shown in <partinfo>BBa_K494006</partinfo>. Again, it is no time is lost due to more than one cloning step, since like in the case of <partinfo>BBa_K494002</partinfo>, a negative control for measurements based on <partinfo>BBa_K494004</partinfo> is given by <partinfo>BBa_K494003</partinfo>.
Screening System: <partinfo>BBa_K494005</partinfo>BBa_K494005 is constructed following the same principles like <partinfo>BBa_K494003</partinfo>. Instead of the his-operon attenuation sequence, a Rho-independent terminator from E. coli which regulates the transcription of the trp-operon was chosen. The Trp-terminator does not inhibit transcription as efficiently as the His-terminator, mCherry fluorescence is still detectable in the measurements. <partinfo>BBa_K494005</partinfo> was used for further cloning of <partinfo>BBa_K494006</partinfo>. Screening System: <partinfo>BBa_K494006</partinfo>BBa_K494006 again is similiar to <partinfo>BBa_K494004</partinfo>. Like in the case of <partinfo>BBa_K494004</partinfo>, a signal sequence which is constructed to bind into the hairpin-structure of the Trp-Terminator and therefore resolving it, is inserted downstream of the reporter protein. Since the Trp-terminator does not terminate as efficiently, the noise level is higher which must be concerned upon measurement evaluation. Parts Falsification and Verification
Falsification of pSB1A10The Screening Plasmid pSB1A10 is intended for the characterization of an Input/Output for a PoPS based device on the basis of two fluorescent proteins. While the first fluorescent protein, eGFP quantifies the input from an arabinose induced promoter, the second reporter, RFP detects the output. However, our experiments designed for testing switches revealed the part to be non-functional. In the current available form, RFP fluorescence is not induced even when the PoPS device does not interfere with the Polymerase.
Although induction with arabinose worked fine indicated by GFP fluorescence, we could not detect any RFP output. The kinetic measurment on the left shows pSB1A10 postive control with a nonsense sequence inserted into the BioBrick site between the two fluorescent proteins GFP and RFP. Nevertheless induction does not trigger any RFP expression. Therefore no output signal is created in our experimantal setup. This fact renders the part as it is unsuitable for testing PoPS-based devices. We first assumed degradation of RFP-mRNA which is known to have an RNase site might be responsible. But comparison with our new screening system reveals a transcriptional problem to be most likely as replacing RFP did not improve the construct. Though, introducing a second arabinose promoter finally resulted in the desired output signal.
References[1] Grate, D. and C. Wilson, Laser-mediated, site-specific inactivation of RNA transcripts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999. 96(11): p. 6131. [2] Babendure, J.R., S.R. Adams, and R.Y. Tsien, Aptamers switch on fluorescence of triphenylmethane dyes. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2003. 125(48): p. 14716-14717. [3] Rowe, W., M. Platt, and P.J.R. Day, Advances and perspectives in aptamer arrays. Integrative Biology, 2009. 1(1): p. 53-58. [4] Stojanovic, M.N. and D.M. Kolpashchikov, Modular aptameric sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2004. 126(30): p. 9266-9270. [5] Smolke and so on.... [6] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logic_gate#Symbols |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"