Team:Heidelberg/Project/miMeasure
From 2010.igem.org
(→Abstract) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
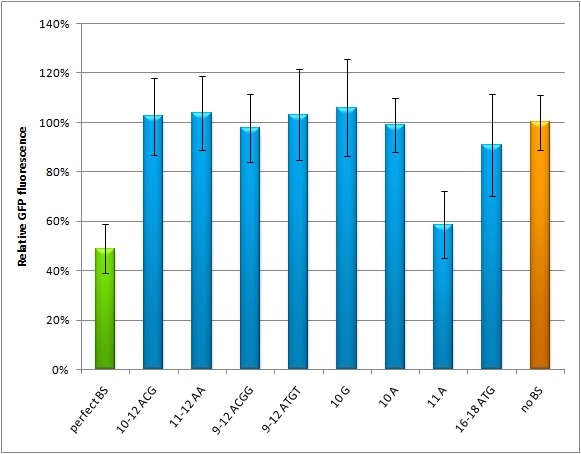
| - | Micro RNAs regulate the translation of their target genes by preferably binding to regions in the 3’ UTR which are called miRNA binding sites (BS)(ref). This miRNA BS consists of a bp seed region at the 5'UTR that is perfectly matched to the miRNA, and surrounding regions that matched partially. The seed region is defined as being the minimal required basepairing at the | + | Micro RNAs regulate the translation of their target genes by preferably binding to regions in the 3’ UTR which are called miRNA binding sites (BS)(ref). This miRNA BS consists of a bp seed region at the 5'UTR that is perfectly matched to the miRNA, and surrounding regions that matched partially. The seed region is defined as being the minimal required basepairing at the 3’ end of the miRNA that can regulate the mRNA. Apart from the seed region, binding can be unspecific, creating bulges between miRNA and mRNA (fig). The position and properties of the bulges seem to play a role in miRNA binding and therefore knockdown efficiency (reviewed in Bartel et al., 2009). |
Since we were going to use synthetic miRNA BS in our genetherapeutic approach, we had to find a way to study their effects in a standardized manner that would be comparable and reproducible. | Since we were going to use synthetic miRNA BS in our genetherapeutic approach, we had to find a way to study their effects in a standardized manner that would be comparable and reproducible. | ||
Revision as of 22:30, 26 October 2010

|
|
||
 "
"