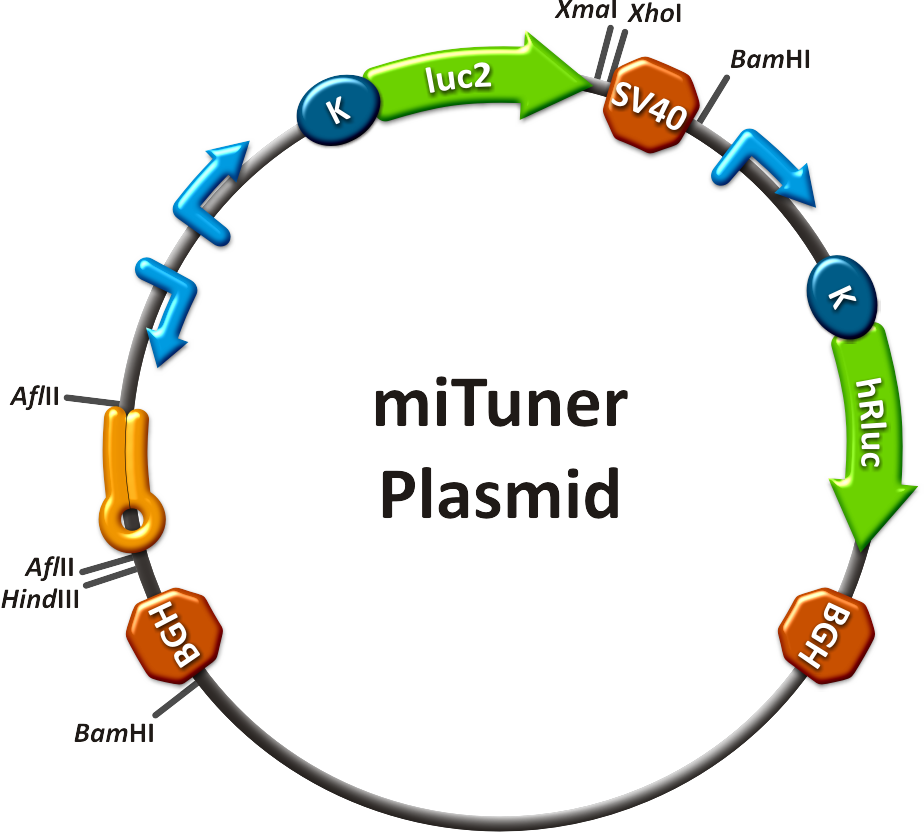
Team:Heidelberg/Project/miRNA Kit
From 2010.igem.org
(→planing) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short endogenous, non-coding RNAs that mediate gene expression in a diversity of organisms {{HDref|Bartel, 2004}}. Although the understanding of their biological functions is progressing remarkably, the exact mechanisms of regulation are still not unambiguously defined. However, it is commonly believed that miRNAs '''trigger target mRNA regulation''' by binding to 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of its target {{HDref|Chekulaeva and Filipowicz, 2009}. <!--The discovery of the first miRNA (lin-4) revealed sequence complementarity to multiple conserved sites in the 3’UTR of the lin-14 mRNA {{HDref|Lee et al., 1993; Wightman et al., 1993}}. --> Exact principles of expression knockdown mediated by miRNA are still in debate {{HDref|Eulalio et al., 2008}}.<br/> | + | MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short endogenous, non-coding RNAs that mediate gene expression in a diversity of organisms {{HDref|Bartel, 2004}}. Although the understanding of their biological functions is progressing remarkably, the exact mechanisms of regulation are still not unambiguously defined. However, it is commonly believed that miRNAs '''trigger target mRNA regulation''' by binding to 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of its target {{HDref|Chekulaeva and Filipowicz, 2009}}. <!--The discovery of the first miRNA (lin-4) revealed sequence complementarity to multiple conserved sites in the 3’UTR of the lin-14 mRNA {{HDref|Lee et al., 1993; Wightman et al., 1993}}. --> Exact principles of expression knockdown mediated by miRNA are still in debate {{HDref|Eulalio et al., 2008}}.<br/> |
'''Binding site properties''' have an essential impact on miRNA-mRNA interaction. <!--[figure, short explanations on seed regions, flanking regions, spacers, mismatches and resulting bulges]. Some functionally important sections of miRNAs have been described in literature, such as the seed region {{HDref|Grimson et al., 2007; Bartel, 2009}}. It is defined as a miRNA region of seven nucleotides length that shows perfect pairing the mRNA target sequence. --><!--The seed usually consists of the nucleotides on position 2-8 of a miRNA binding sites in the 5'UTR of the mRNA. Based on this simple principle, we randomized our miRNA binding sites between nucleotide 9 - 12 or 9 - 22 in the so called flanking region. Alternatively, we tried rational exchanges of nucleotides to see how they effect binding of the miRNA to its target mRNA. --> Depending on pairing specificity translational repression is mediated through the imperfect miRNA-mRNA hybrids. The potential for stringent regulation of transgene expression makes the miRNA world a promising area of gene therapy {{HDref|Brown et al.,2009}}. | '''Binding site properties''' have an essential impact on miRNA-mRNA interaction. <!--[figure, short explanations on seed regions, flanking regions, spacers, mismatches and resulting bulges]. Some functionally important sections of miRNAs have been described in literature, such as the seed region {{HDref|Grimson et al., 2007; Bartel, 2009}}. It is defined as a miRNA region of seven nucleotides length that shows perfect pairing the mRNA target sequence. --><!--The seed usually consists of the nucleotides on position 2-8 of a miRNA binding sites in the 5'UTR of the mRNA. Based on this simple principle, we randomized our miRNA binding sites between nucleotide 9 - 12 or 9 - 22 in the so called flanking region. Alternatively, we tried rational exchanges of nucleotides to see how they effect binding of the miRNA to its target mRNA. --> Depending on pairing specificity translational repression is mediated through the imperfect miRNA-mRNA hybrids. The potential for stringent regulation of transgene expression makes the miRNA world a promising area of gene therapy {{HDref|Brown et al.,2009}}. | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
Revision as of 21:59, 26 October 2010

|
|
||
 "
"