Team:Brown/Project/Ecargo
From 2010.igem.org
(→Experimental Design) |
(→Experimental Design) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
*The linear PCR products of Tat-linker and transcription factors were then subcloned into pGEM-T Easy | *The linear PCR products of Tat-linker and transcription factors were then subcloned into pGEM-T Easy | ||
*Perform BioBrick assembly to join Tat-linker to transcription factor in pGEM-T Easy | *Perform BioBrick assembly to join Tat-linker to transcription factor in pGEM-T Easy | ||
| - | *This entire Tat-TF construct was double digested | + | *This entire Tat-TF construct was double digested and ligated into pBlueScriptSK, an expression vector. We insert into competent XL1 Blues E. coli and use blue/white screening (Protocol here add link) and ampicillin resistance to select for successful transformants. |
*We cut the transcription factor out of pGEM-T Easy, run out on a gel to confirm successful cut, extract bands, then insert alongside the Tat-linker in pBlueScriptSK using sites for protein fusion in RFC25. (SHOW STEPWISE DIAGRAM OF CONSTRUCTION) | *We cut the transcription factor out of pGEM-T Easy, run out on a gel to confirm successful cut, extract bands, then insert alongside the Tat-linker in pBlueScriptSK using sites for protein fusion in RFC25. (SHOW STEPWISE DIAGRAM OF CONSTRUCTION) | ||
*Transform our Tat-TF in pBlueScriptSK into BL21 cell line, using Amp+ selection. | *Transform our Tat-TF in pBlueScriptSK into BL21 cell line, using Amp+ selection. | ||
Revision as of 05:13, 26 October 2010
TAT overview
IN SUMMARY
- We tried to create a modular BioBrick using the Tat protein transduction domain
- We fused this to transcription factors in RFC25 format. This would allow us to transiently deliver proteins to a cell and thus test components of our LRC.
Rationale and Background
OUTLINE
Trans-Activator of Transcription (Tat) is an HIV gene that functions to increase the transcription level of viral genes. The Tat Protein Transduction domain (Tat-PTD) is an 11-amino acid peptide that allows the protein to traverse cell and nuclear membranes in order to localize to the nucleus.
As a result of years of study, it is now known that there are multiple methods by which this domain operates. Most commonly, the Tat-PTD interacts with heparin sulfate proteogycans (HSPGs) to cause lipid-raft mediated endocytosis. In the endocytosed vesicles, heparinase causes degradation of the heparin sulfate, which releases the bound Tat-PTD
- Project was initially developed as a way of delivering scFv (single-chain antibody) to mammalian cells to fluorescently label cell structures.
- As the LRC project developed, we realized Tat-PTD could be used to test components of our circuit individually without the need to perform individual gene transformations
- To this end, we decided to test whether we could fuse Tat to transcription factors, and use these "Tat-TFs" to "remotely" induce gene expression.
Experimental Design
CONSTRUCTING TAT-TF
- The Tat sequence was initially ordered with an anti-histone scFv attached by a polyglycine linker. Our intention was to express this Tat-scFv fusion, purify, label with rhodamine, and apply to mammalian cells. We would've expected fluorscence to localize to nuclear histones to confirm that Tat was carrying the antibody through a live cell membrane. Our DNA construct was synthesized by DNA 2.0. (INSERT INITIAL SCHEMATIC, DIAGRAM OF CONSTRUCT AND WORKFLOW)
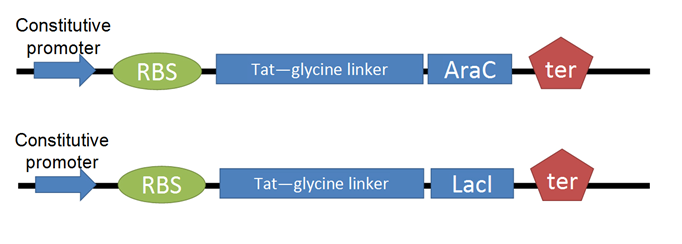
- For our Tat-TF, we needed to put the Tat-ptd with RFC25 ends (optimized for protein fusion). We used PCR to attach sites to the existing circular Tat DNA, avoiding the process of resynthesizing. (SHOW PRIMERS WE USED, DIAGRAM OF CONSTRUCT) This was biobricked as our Tat-linker.
- The next step was to adapt the transcription factor for use with Tat. We decided to use two TFs from the registry, [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I732100 LacI] and AraC. (PART #s?) We made several modifications through PCR: (removal of LVA rapid degradation tag, adding 6-his tag for nickel-column purification, RFC25 sites) (SHOW PRIMER SETS WE USED FOR EACH, SHOW DIAGRAM OF CONSTRUCT)
- The linear PCR products of Tat-linker and transcription factors were then subcloned into pGEM-T Easy
- Perform BioBrick assembly to join Tat-linker to transcription factor in pGEM-T Easy
- This entire Tat-TF construct was double digested and ligated into pBlueScriptSK, an expression vector. We insert into competent XL1 Blues E. coli and use blue/white screening (Protocol here add link) and ampicillin resistance to select for successful transformants.
- We cut the transcription factor out of pGEM-T Easy, run out on a gel to confirm successful cut, extract bands, then insert alongside the Tat-linker in pBlueScriptSK using sites for protein fusion in RFC25. (SHOW STEPWISE DIAGRAM OF CONSTRUCTION)
- Transform our Tat-TF in pBlueScriptSK into BL21 cell line, using Amp+ selection.
- Grow overnight of successful transformants, harvest cells and use Ni-affinity column to isolate purified Tat-TF protein.
TESTING THE TAT-TF
- To test for efficacy of Tat-TF control, we decided to use two reporter constructs. The LacI reporter construct was taken straight from the registry. The AraC reporter construct was assembled from registry parts:
1. Production of CyanFP is controlled by pLacI, which is constitutively on and repressible by addition of LacI protein.
- [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_E0020 Cyan Fluorescent Protein]
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K091110 LacI repressible promoter]
2. CherryFP production is linked to pAraC, which is inducible by addition of the AraC protein.
- [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_R0080 AraC inducible promoter]
- [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_J06702 RBS-Cherry Fluorescent Protein-terter]
- We then transformed each reporter construct into E.Coli (XL1B) and froze them into glycerol stocks for future use.
- Our intention is to regrow the cell lines containing our reporter constructs, apply purified Tat-TF
 "
"