Team:Heidelberg/Modeling
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Neural Network theory) |
(→Input/target pairs) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
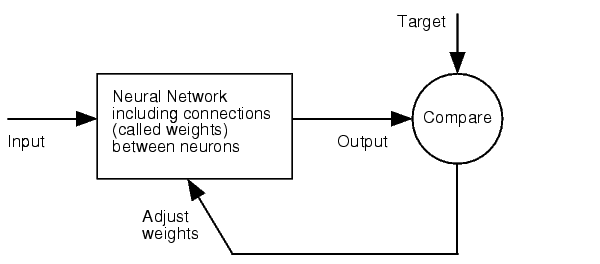
The NN model has been created with the MATLAB NN-toolbox. The input/target pairs used to train the network comprise experimental and literature data (Bartel et al. 2007). The experimental data were obtained by measuring via luciferase assay the strength of knockdown due to the interaction between the shRNA and the binding site situated on the 3’UTR of luciferase gene. Nearly 30 different rational designed binding sites were tested and the respective knockdown strength calculated with the following formula->(formula anyone???). | The NN model has been created with the MATLAB NN-toolbox. The input/target pairs used to train the network comprise experimental and literature data (Bartel et al. 2007). The experimental data were obtained by measuring via luciferase assay the strength of knockdown due to the interaction between the shRNA and the binding site situated on the 3’UTR of luciferase gene. Nearly 30 different rational designed binding sites were tested and the respective knockdown strength calculated with the following formula->(formula anyone???). | ||
| - | ====Input/target pairs==== | + | =====Input/target pairs===== |
Each input was represented by a four elements vector. Each element corresponded to a score value related to a specific feature of the binding site. The four features used to describe the binding site were: seed type, the 3’pairing contribution the AU-content and the number of binding site. The input/target pair represented the relationship between a particular binding site and the related percentage of knockdown. | Each input was represented by a four elements vector. Each element corresponded to a score value related to a specific feature of the binding site. The four features used to describe the binding site were: seed type, the 3’pairing contribution the AU-content and the number of binding site. The input/target pair represented the relationship between a particular binding site and the related percentage of knockdown. | ||
Once the network was trained than it was used to predict percentages of knockdown given certain inputs. The predictions were then validated experimentally. | Once the network was trained than it was used to predict percentages of knockdown given certain inputs. The predictions were then validated experimentally. | ||
Revision as of 00:58, 25 October 2010

 "
"