Team:TU Delft/Project/solubility/results
From 2010.igem.org
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
==Hydrocarbon Solubility Results & Conclusions== | ==Hydrocarbon Solubility Results & Conclusions== | ||
| - | + | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/0/00/TU_Delft_project_navigation.jpg" usemap="#projectnavigation" border="0" /></center><map id="projectnavigation" name="projectnavigation"><area shape="rect" alt="Characterization" title="" coords="309,3,591,45" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/solubility/characterization" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Results" title="" coords="609,3,891,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/solubility/results" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Parts" title="" coords="9,3,290,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/solubility/parts" target="" /></map></html> | |
| - | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/0/00/TU_Delft_project_navigation.jpg" usemap="#projectnavigation" border="0" /></center><map id="projectnavigation" name="projectnavigation"><area shape="rect" alt="Characterization" title="" coords="309,3,591,45" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft | + | |
Our goal was to enhance the solubility of alkanes in water. Therefore we constructed a new part that expresses the emulsifier protein [[Team:TU_Delft/Project/solubility/alna|AlnA]] after induction by IPTG. By using our own [[Team:TU_Delft/Project/solubility/characterization|emulsification assay]] we measured the increase in hydrophobic compounds in the water phase. | Our goal was to enhance the solubility of alkanes in water. Therefore we constructed a new part that expresses the emulsifier protein [[Team:TU_Delft/Project/solubility/alna|AlnA]] after induction by IPTG. By using our own [[Team:TU_Delft/Project/solubility/characterization|emulsification assay]] we measured the increase in hydrophobic compounds in the water phase. | ||
| Line 83: | Line 82: | ||
===Continue Reading about Solubility=== | ===Continue Reading about Solubility=== | ||
| - | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/0/00/TU_Delft_project_navigation.jpg" usemap="#projectnavigation" border="0" /></center><map id="projectnavigation" name="projectnavigation"><area shape="rect" alt="Characterization" title="" coords="309,3,591,45" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft | + | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/0/00/TU_Delft_project_navigation.jpg" usemap="#projectnavigation" border="0" /></center><map id="projectnavigation" name="projectnavigation"><area shape="rect" alt="Characterization" title="" coords="309,3,591,45" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/solubility/characterization" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Results" title="" coords="609,3,891,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/solubility/results" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Parts" title="" coords="9,3,290,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/solubility/parts" target="" /></map></html> |
Revision as of 13:59, 22 October 2010
Hydrocarbon Solubility Results & Conclusions

Our goal was to enhance the solubility of alkanes in water. Therefore we constructed a new part that expresses the emulsifier protein AlnA after induction by IPTG. By using our own emulsification assay we measured the increase in hydrophobic compounds in the water phase.
Results
For the production of large amounts of protein, 1 L shake flasks cultures were induced with IPTG after the OD measuremnts started to show the start of the exponential phase. The experiment was done 3 seperate times.
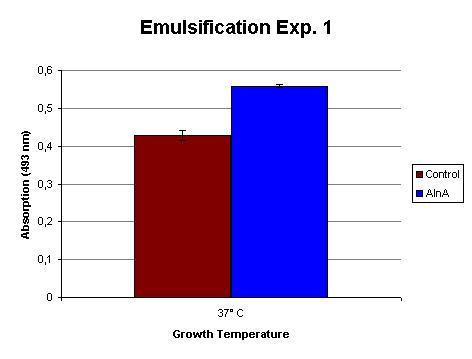
Experiment 1
This was the first time the experiment was done in a large volume (1 L) and carried out at 37 C. The OD measurements at the induction time point and harvest are shown in Table 1.
| # | Culture | OD600 at induction | OD600 at harvest |
| 1 | Control (J13002) 37 C | 0.367 | 0.882 |
| 2 | AlnA (K398206) 37 C | 0.434 | 0.880 |
The total volume of sample at the end after completion of the isolation protocol was 3 mL. The protein concentration was determined by Bradford analysis and showed that the control contained 19 mg mL-1 and the AlnA sample contained 16 mg mL-1.
The emulsification capacity of the samples was determined using our emulsifier assay. 0.75 mg protein was used in the assay displayed in Figure 2. The 30% increase in absorption in the AlnA sample indicates a higher amount of Sudan II that is in solution, thus a higher emulsification by the proteins. A statistical T test shows that this is a significant increase (p = 3 x 10-3).
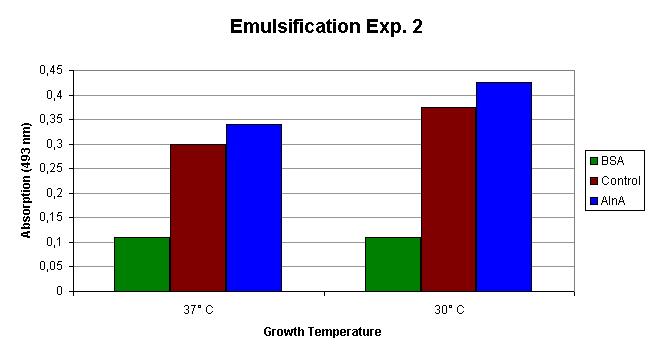
Experiment 2
The second experiment was carried out at 37 C and 30 C. This was done, because it was expected that IPTG causes a stronger induction at lower temperatures. The OD measurements at the induction time point and harvest are shown in Table 2.
| # | Culture | OD600 at induction | OD600 at harvest |
| 1 | Control (J13002) 30 C | 0.073 | 0.451 |
| 2 | Control (J13002) 37 C | 0.088 | 0.810 |
| 3 | AlnA (K398206) 30 C | 0.060 | 0.393 |
| 4 | AlnA (K398206) 37 C | 0.067 | 0.624 |
The total volume of sample at the end after completion of the isolation protocol was 1 mL. The protein concentration was determined by Bradford analysis and showed that from the culture grown at 37 C the control contained 1.7 mg mL-1 and the AlnA sample contained 1.5 mg mL-1. The control samples from the culture grown at 30 C contained 2.41 mg mL-1 and the AlnA sample contained 2.29 mg mL-1.
The emulsification capacity of the samples was determined using our emulsifier assay. 0.75 mg protein was used in the assay displayed in Figure 2. The 13% increase in absorption in the AlnA samples indicate a higher amount of Sudan II that is in solution, thus a higher emulsification by the proteins.
Experiment 3
The experiments were repeated one last time to confirm the positive outcome.
Conclusions
For enabling E. coli to degrade hydrocarbons we equiped it with the ability to produce a known emulsifying protein, called AlnA. The production was induced by IPTG, but could not be shown on SDS-PAGE. This is probably due to the fact that we grew the cultures in minimal medium.
The results from the emulsifier assays do show an increased amount of hydrophobic Sudan II in solution by proteins isolated from cultures transformed with K398206 compared to the control J13002. This indicates that these samples contain a higher amount of proteins capable of emulsifying Sudan II. We assume that this is caused by the production of AlnA.
In further research we would advise to add a tag to the protein, so it can be isolated with greater ease and purity.
Continue Reading about Solubility

 "
"