Team:Tsinghua/project/future
From 2010.igem.org
| (11 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<script> | <script> | ||
| - | navlist=new Array(" | + | navlist=new Array("Background", "Outline", "Conclusion", "Future"); |
| - | linkl = new Array(" | + | linkl = new Array("/Team:Tsinghua/project", "outline", "con", "#future"); |
| - | writenav(navlist, linkl); | + | writenav(navlist, linkl, 3); |
</script> | </script> | ||
<div id="main_content"> | <div id="main_content"> | ||
| - | <a name=" | + | <a name="fut"></a> |
| + | <h1>Future Work</h1> | ||
| + | <div class="content_block"> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | == | + | ==Construction of recombination library== |
| - | + | We just demonstrated the feasibility of construction of library of recombination segments like the one in humans. In future work, we hope to finish this part and make real antibody libraries. | |
| + | In human beings, our antibody comprises of two parts, the light chain and the heavy chain. During formation, the heavy chain undergoes recombination of V, D and J segments while the light one between V and J. The recombination of these gene segments gives rise to diversity to the scale of <math>10^5</math> to <math>10^6</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to construct a real antibody library, we need to ligate several dozen segments into a vector. The protocol for molecular manipulation is clear but we may need a larger vector, such as the BACs to harbor all the segments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Test of antibody function== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once the antibody library is accomplished, the major focus will be whether such antibodies can have normal function. We will settle such issues with antibody expression and subsequent assays. Immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence offers the opportunity to compare the specificity of such antibodies while equilibrium dialysis can measure its affinity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Specificity=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence stains certain proteins in the tissue marked with the antibody, which is a perfect check for antibody specificity. With the serum antibody as control, specificity can be checked by simply measuring the background and cross-reaction. This technique offers an intuitive way for checking specificity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Western blotting is a more precise method. Western blotting of cell lysates can reveal cross-reaction of the antibody, which will appear as extra bands on the film. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Affinity=== | ||
| + | |||
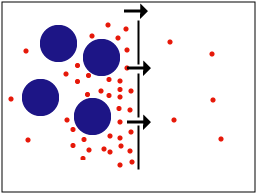
| + | Affinity can be checked with equilibrium dialysis, in which the antibody for a small hapten molecule is kept in the dialysis membrane with the hapten in the solution outside. When the system reaches its equilibrium, the concentration of the antigen reveals the equilibrium constant of antibody binding, which indicates the affinity quantitatively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Dialysis.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Other applications== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The recombination method is useful in other aspects. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nowadays, microbe based environmental monitoring is fast and real-time. However, certain phenomenon might be instant but reveal the hint for potential environmental hazards. In this case, our system might be quite useful, for recombination records the instant event permanently in the genome of the bacteria, just like a log. Thus, detection will discover the appearance of the hazards even if it's transient. For instance, the increase in phosphate concentration in some districts might be transient but will cause algae bloom in lakes downstream. With this recombination apparatus, the bacteria which have encountered such abnormal phosphate concentration can undergo recombination and record this event permanently. Culture and analysis will reveal such harmful events. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Besides, since the signal can be recorded firmly with recombination, it can be amplified during proliferation of the bacteria. This is crucial for detecting some weak yet important changes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
</div></div> | </div></div> | ||
</body> | </body> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:41, 27 October 2010

Future Work
Construction of recombination library
We just demonstrated the feasibility of construction of library of recombination segments like the one in humans. In future work, we hope to finish this part and make real antibody libraries.
In human beings, our antibody comprises of two parts, the light chain and the heavy chain. During formation, the heavy chain undergoes recombination of V, D and J segments while the light one between V and J. The recombination of these gene segments gives rise to diversity to the scale of <math>10^5</math> to <math>10^6</math>.
In order to construct a real antibody library, we need to ligate several dozen segments into a vector. The protocol for molecular manipulation is clear but we may need a larger vector, such as the BACs to harbor all the segments.
Test of antibody function
Once the antibody library is accomplished, the major focus will be whether such antibodies can have normal function. We will settle such issues with antibody expression and subsequent assays. Immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence offers the opportunity to compare the specificity of such antibodies while equilibrium dialysis can measure its affinity.
Specificity
Immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence stains certain proteins in the tissue marked with the antibody, which is a perfect check for antibody specificity. With the serum antibody as control, specificity can be checked by simply measuring the background and cross-reaction. This technique offers an intuitive way for checking specificity.
Western blotting is a more precise method. Western blotting of cell lysates can reveal cross-reaction of the antibody, which will appear as extra bands on the film.
Affinity
Affinity can be checked with equilibrium dialysis, in which the antibody for a small hapten molecule is kept in the dialysis membrane with the hapten in the solution outside. When the system reaches its equilibrium, the concentration of the antigen reveals the equilibrium constant of antibody binding, which indicates the affinity quantitatively.
Other applications
The recombination method is useful in other aspects.
Nowadays, microbe based environmental monitoring is fast and real-time. However, certain phenomenon might be instant but reveal the hint for potential environmental hazards. In this case, our system might be quite useful, for recombination records the instant event permanently in the genome of the bacteria, just like a log. Thus, detection will discover the appearance of the hazards even if it's transient. For instance, the increase in phosphate concentration in some districts might be transient but will cause algae bloom in lakes downstream. With this recombination apparatus, the bacteria which have encountered such abnormal phosphate concentration can undergo recombination and record this event permanently. Culture and analysis will reveal such harmful events.
Besides, since the signal can be recorded firmly with recombination, it can be amplified during proliferation of the bacteria. This is crucial for detecting some weak yet important changes.
 "
"