Team:Washington/Gram Positive/Design
From 2010.igem.org
(→Making CapD a Better Anthrax Treatment) |
(→Using FoldIt to Make CapD_CP a Better Hydrolase) |
||
| (76 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Header}} | {{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Header}} | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
<!---------------------------------------PAGE CONTENT GOES BELOW THIS----------------------------------------> | <!---------------------------------------PAGE CONTENT GOES BELOW THIS----------------------------------------> | ||
=Making CapD a Better Anthrax Treatment= | =Making CapD a Better Anthrax Treatment= | ||
| - | There are two main obstacles limiting natural CapD as an Anthrax therapeutic. First, natural CapD is a difficult to express dimer, requiring an auto-cleavage to activate. Second, CapD is a better transpeptidase than poly-γ-D-glutamate hydrolase, limiting its Anthrax decapsulating potential. To solve the first problem, we created a circular | + | There are two main obstacles limiting natural CapD as an Anthrax therapeutic. First, natural CapD is a difficult to express dimer, requiring an auto-cleavage to activate [[#References | [1]]]. Second, CapD is a better poly-γ-D-glutamate transpeptidase than poly-γ-D-glutamate hydrolase, limiting its Anthrax decapsulating potential.[[#References | [1]]] To solve the first problem, we created a circular permutated, monomeric version of CapD that is easy to express and quantify. To improve hydrolysis, we used [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Washington/Project/Tools/FoldIt FoldIt], a computational toolbox, to design active site mutations aimed to increase hydrolysis over transpeptidation. |
| - | == | + | <span id=capdcp> |
| - | + | <span id = capdcp> | |
| - | + | ==Is CapD_CP a better version of CapD?== | |
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Washington_DtoCP_Graphic2.jpg|520px|right|Schematic of how we made a circularly permutated capD]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | When natural CapD is first translated, the key catalytic threonine residue is buried in the active site, rendering it inaccessible to poly-γ-D-glutamate. After auto-cleavage, this critical threonine becomes the new N terminus, which can take its place in the active site [[#References | [1]]]. By reordering the protein so the threonine is the first residue, and putting a FoldIt designed linker between the natural N and C terminus, we make a circular permutation of CapD that we named CapD_CP. CapD_CP is a monomer, historically easier to purify and more stable than dimers. | ||
| - | + | Since the first residue of any nascent protein must be methionine, we rely on E. Coli’s naturally occurring methionine aminopeptidase to remove the first methionine, making CapD_CP catalytically active. The removal of the first methionine has been verified via mass spectrometry. | |
| - | + | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | </span> | ||
| - | ==Using FoldIt to Make a Better Hydrolase== | + | ==Using [[Team:Washington/Tools_Used/Software|FoldIt]] to Make CapD_CP a Better Hydrolase== |
| - | [[Image:WashingtonPointMutation.png| | + | [[Image:WashingtonPointMutation.png|270px|frameless|right]][[Image:WashingtonShake.png|270px|frameless|right]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | To | + | To increase the hydrolytic ability of CapD_CP, we made point mutations to the active site. We focused our attention on two types of mutations. [[Image:WashingtonWiggle.png|270px|frameless|right]] First type of mutations is to increase hydrolysis by lowering the activation energy. To accomplish this, we created point mutations that can establish hydrogen bondings to a modeled transition state of our substrate. Second type of mutations concerns with the openness and polarity of the active site. To accomplish this, we mutated the active site into a more open and polar area so water molecules can enter and participate in hydrolysis easily. |
| + | |||
| + | To make these point mutation designs, we used a computer program named FoldIt to predict how changes in protein structure and composition will affect protein stability. FoldIt provides a 3D representation of a protein's crystal structure that can be manipulated. Manipulation functions include point mutations, insertions, deletions, repacking of side chains (rotamer optimization), and backbone movement, which FoldIt then assesses for stability. This allows the user to quickly interact with a protein and easily predict how mutations will affect a protein. | ||
| - | [ | + | [[Team:Washington/Tools_Used/Software|A more in depth explanation of FoldIt here.]] |
| + | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | 1. Wu R, Richter S, Zhang RG, Anderson VJ, Missiakas D, Joachimiak A. Crystal structure of Bacillus anthracis transpeptidase enzyme CapD. J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24406-14. Epub 2009 Jun 16. PMID: 19535342 | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
<!---------------------------------------PAGE CONTENT GOES ABOVE THIS----------------------------------------> | <!---------------------------------------PAGE CONTENT GOES ABOVE THIS----------------------------------------> | ||
<div style="text-align:center"> | <div style="text-align:center"> | ||
| - | '''← [[Team:Washington/ | + | '''← [[Team:Washington/Gram Positive|Overview of Gram(+) Therapeutic]]''' |
| | ||
| | ||
| | ||
| - | '''[[Team:Washington/ | + | '''[[Team:Washington/Gram Positive/Build|Building the Gram(+) Therapeutic]] →''' |
| - | + | ||
{{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Footer}} | {{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 06:05, 27 October 2010
Making CapD a Better Anthrax Treatment
There are two main obstacles limiting natural CapD as an Anthrax therapeutic. First, natural CapD is a difficult to express dimer, requiring an auto-cleavage to activate [1]. Second, CapD is a better poly-γ-D-glutamate transpeptidase than poly-γ-D-glutamate hydrolase, limiting its Anthrax decapsulating potential. [1] To solve the first problem, we created a circular permutated, monomeric version of CapD that is easy to express and quantify. To improve hydrolysis, we used FoldIt, a computational toolbox, to design active site mutations aimed to increase hydrolysis over transpeptidation.
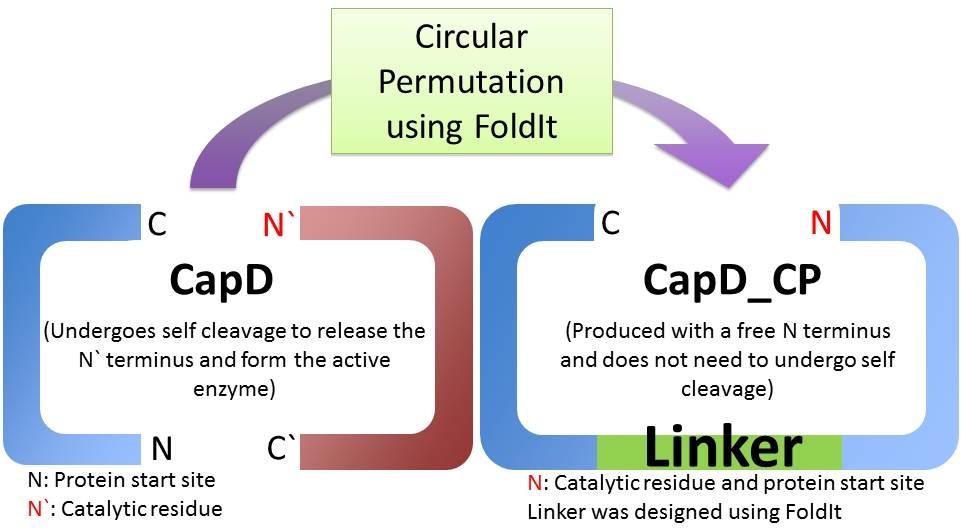
Is CapD_CP a better version of CapD?
When natural CapD is first translated, the key catalytic threonine residue is buried in the active site, rendering it inaccessible to poly-γ-D-glutamate. After auto-cleavage, this critical threonine becomes the new N terminus, which can take its place in the active site [1]. By reordering the protein so the threonine is the first residue, and putting a FoldIt designed linker between the natural N and C terminus, we make a circular permutation of CapD that we named CapD_CP. CapD_CP is a monomer, historically easier to purify and more stable than dimers.
Since the first residue of any nascent protein must be methionine, we rely on E. Coli’s naturally occurring methionine aminopeptidase to remove the first methionine, making CapD_CP catalytically active. The removal of the first methionine has been verified via mass spectrometry.
Using FoldIt to Make CapD_CP a Better Hydrolase
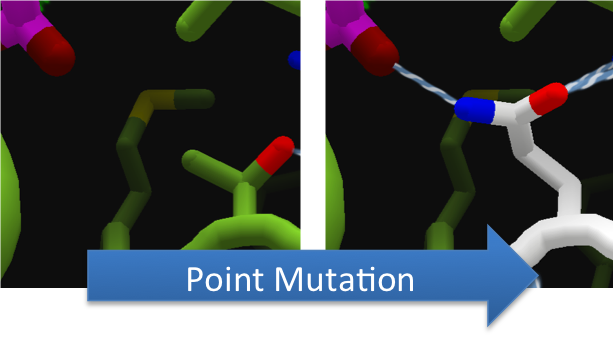
To increase the hydrolytic ability of CapD_CP, we made point mutations to the active site. We focused our attention on two types of mutations. First type of mutations is to increase hydrolysis by lowering the activation energy. To accomplish this, we created point mutations that can establish hydrogen bondings to a modeled transition state of our substrate. Second type of mutations concerns with the openness and polarity of the active site. To accomplish this, we mutated the active site into a more open and polar area so water molecules can enter and participate in hydrolysis easily.
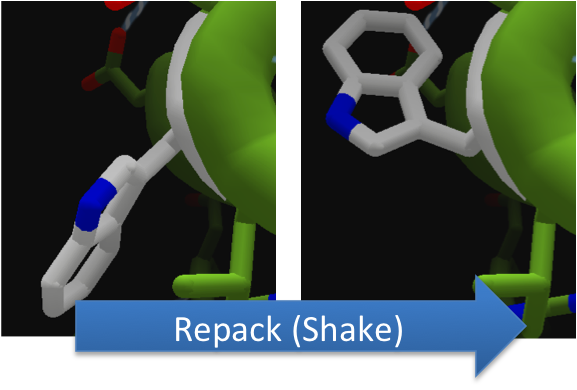
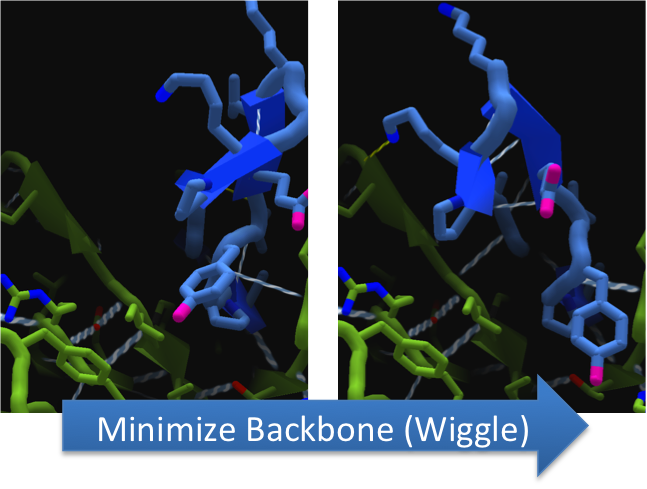
To make these point mutation designs, we used a computer program named FoldIt to predict how changes in protein structure and composition will affect protein stability. FoldIt provides a 3D representation of a protein's crystal structure that can be manipulated. Manipulation functions include point mutations, insertions, deletions, repacking of side chains (rotamer optimization), and backbone movement, which FoldIt then assesses for stability. This allows the user to quickly interact with a protein and easily predict how mutations will affect a protein.
A more in depth explanation of FoldIt here.
References
1. Wu R, Richter S, Zhang RG, Anderson VJ, Missiakas D, Joachimiak A. Crystal structure of Bacillus anthracis transpeptidase enzyme CapD. J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24406-14. Epub 2009 Jun 16. PMID: 19535342
 "
"