Team:UNAM-Genomics Mexico/Modules/In vivo
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Kurupaclau (Talk | contribs) |
Kurupaclau (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Tertiary cycle== | ==Tertiary cycle== | ||
| - | [[Image:Tertiary-cycle.jpg|thumb|center| | + | [[Image:Tertiary-cycle.jpg|thumb|center|680px| '''Coupling together Biological Chassis through Light communication''' ]] |
===Chassis Description=== | ===Chassis Description=== | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
The structure of the device was designed as follows: | The structure of the device was designed as follows: | ||
| - | [[Image:LuxAB.jpg|center| | + | [[Image:LuxAB.jpg|center|150px]] |
*Design LuxY biobrick, send to synthesize and transfer the construction from Mr. Gene plasmid to pSB1C3 DNA submission backbone. | *Design LuxY biobrick, send to synthesize and transfer the construction from Mr. Gene plasmid to pSB1C3 DNA submission backbone. | ||
| Line 236: | Line 236: | ||
The structure of the device is designed as follows: | The structure of the device is designed as follows: | ||
| - | [[Image:Promoter%26LovTAP.jpg| | + | [[Image:Promoter%26LovTAP.jpg|150px|center]] |
=====METHODOLOGY===== | =====METHODOLOGY===== | ||
| Line 286: | Line 286: | ||
2.trpL promoter fused to RFP protein(BBa_E1010): | 2.trpL promoter fused to RFP protein(BBa_E1010): | ||
| - | [[Image:TrpL_RFP.jpg| | + | [[Image:TrpL_RFP.jpg|200px|center]] |
*LovTAP activator activity: Reporter system | *LovTAP activator activity: Reporter system | ||
trpL promoter fused to lambda Repressor cI (BBa_P0451 + BBa_K098991) regulating GFP protein (BBa_E0240). Whit this system a double repression is generated to have a final activation response. | trpL promoter fused to lambda Repressor cI (BBa_P0451 + BBa_K098991) regulating GFP protein (BBa_E0240). Whit this system a double repression is generated to have a final activation response. | ||
| - | [[Image:CI.jpg |center]] | + | [[Image:CI.jpg |300px|center]] |
=====Characterizing LovTAP===== | =====Characterizing LovTAP===== | ||
| Line 310: | Line 310: | ||
The qualitative approach was designed to observe and compare the RFP production in the cells harboring LovTAP exposed to light versus dark conditions, both in wild type and trpR mutant strains. Under blue light conditions, when LovTAP repressor activity is activated, it is expected to observe a lower level of RFP in comparison to the cells maintained in the dark state. | The qualitative approach was designed to observe and compare the RFP production in the cells harboring LovTAP exposed to light versus dark conditions, both in wild type and trpR mutant strains. Under blue light conditions, when LovTAP repressor activity is activated, it is expected to observe a lower level of RFP in comparison to the cells maintained in the dark state. | ||
| - | Experimental procedure | + | '''Experimental procedure''' |
The samples used were: trpL+RFP reporter system in plasmid pSB1C3, Lausanne trpL-RFP reporter system, LovTAP under promoters J23117, J23114, J23105 and J23102. | The samples used were: trpL+RFP reporter system in plasmid pSB1C3, Lausanne trpL-RFP reporter system, LovTAP under promoters J23117, J23114, J23105 and J23102. | ||
| - | + | Only one colony of each co-transformation was used along the experiment and was tested under light and dark conditions. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | TrpR mutant and wild type cells were co transformed using 5 µL of each plasmid (trpL-RFP in pSB1C3/ pSB1A2 and each LovTAP construction in pSB3K3). For each co transformation one tube containing 5 ml of LB medium with Kanamicyn and chloramphenicol or Kanamicyn and ampicillin, was inoculated from a single colony of DH5α. Cultures were grown overnight (~15hrs) at 37°C with spinning at 250rpm in dark conditions. Then, 1 ml of broth was taken and transferred into 5 ml of fresh LB medium with antibiotics. The cultures were grown for approximately 13 hours under the previous conditions but some were exposed to blue light (470nm) while others were maintained in dark. Finally, the cultures were spun down and compared as follows: the RFP pellets obtained under blue-light versus dark condition, and wild type samples versus mutant samples. | |
| - | + | ====Results==== | |
In a first approach was observed that wt and trpR mutant cells co-transformed with LovTAP under J23102 promoter grew in dark and light, produced very low levels of RFP protein in comparison with the control sample (wild type cells with only the reporter construction, trpL+RFP). Besides, there was no a visible difference between dark and light conditions, which is the expected behavior under high expression levels of LovTAP. Considering this result we decided to continue the co-transformations procedure without considering the LovTAP construction under J23102 promoter. | In a first approach was observed that wt and trpR mutant cells co-transformed with LovTAP under J23102 promoter grew in dark and light, produced very low levels of RFP protein in comparison with the control sample (wild type cells with only the reporter construction, trpL+RFP). Besides, there was no a visible difference between dark and light conditions, which is the expected behavior under high expression levels of LovTAP. Considering this result we decided to continue the co-transformations procedure without considering the LovTAP construction under J23102 promoter. | ||
| Line 329: | Line 324: | ||
Using LovTAP with promoters J23105, J23114 and J23117 (in order of high to lower strength), we obtained the following pellets that are show in the next images: | Using LovTAP with promoters J23105, J23114 and J23117 (in order of high to lower strength), we obtained the following pellets that are show in the next images: | ||
| - | [[Image:TrpLWiFiassay.jpg|thumb|center|450 px|Testing LovTAP with trpL+RFP reporter system (without the double transcriptional terminator | + | [[Image:TrpLWiFiassay.jpg|thumb|center|450 px|'''Testing LovTAP with trpL+RFP reporter system in plasmid pSB1C3'''(without the double transcriptional terminator). The figure shows the pellets obtained from the cellular cultures. The non aligned tube at the right is a sample of WT cells harboring only trpL+RFP construction.]] |
| - | [[Image:TrpLassayLaussane.jpg|thumb|center|450px|Testing LovTAP with Lausanne trpL+RFP reporter system in plasmid pSB1A2. The figure shows the pellets obtained from the cellular cultures. The non aligned tube at the left is a sample of WT cells harboring only trpL+RFP from Lausanne team construction.]] | + | [[Image:TrpLassayLaussane.jpg|thumb|center|450px|'''Testing LovTAP with Lausanne trpL+RFP reporter system in plasmid pSB1A2'''. The figure shows the pellets obtained from the cellular cultures. The non aligned tube at the left is a sample of WT cells harboring only trpL+RFP from Lausanne team construction.]] |
According to the images trpR mutants seem to have a lower RFP expression levels versus WT both in dark and light conditions. This is a surprising result because it was expected that showed higher levels than WT as they don’t have the possible crass-talk with trpR native E.coli repressor. Maybe there is another process of trpL repression independent to LovTAP and trpR. | According to the images trpR mutants seem to have a lower RFP expression levels versus WT both in dark and light conditions. This is a surprising result because it was expected that showed higher levels than WT as they don’t have the possible crass-talk with trpR native E.coli repressor. Maybe there is another process of trpL repression independent to LovTAP and trpR. | ||
| Line 343: | Line 338: | ||
'''Quantitative experiment''' | '''Quantitative experiment''' | ||
| - | With the aim to have a better characterization of LovTAP, we designed a new protocol considering the methodology describe by Jason R Kelly | + | With the aim to have a better characterization of LovTAP, we designed a new protocol considering the methodology describe by Jason R Kelly, we include some changes that are detailed below. |
We decided to start the protocol under blue light conditions to test the dark state, expecting that in dark exposed samples the RFP levels increase in comparison with those samples that are always under blue light. We did this in order to face better the issue of the long half life of the RFP due to it doesn’t have a degradation tag. | We decided to start the protocol under blue light conditions to test the dark state, expecting that in dark exposed samples the RFP levels increase in comparison with those samples that are always under blue light. We did this in order to face better the issue of the long half life of the RFP due to it doesn’t have a degradation tag. | ||
| - | + | '''Experimental procedure''' | |
| - | + | The samples used were: trpL+RFP reporter system in plasmid pSB1C3, Lausanne trpL-RFP reporter system, LovTAP under promoters J23117, J23114, J23105 and RFP under J23102. | |
| - | + | Only one colony of each co-transformation was used along the experiment and was tested under light and dark conditions. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | TrpR mutant and wild type cells were co transformed using 5 µL of each plasmid (trpL-RFP in pSB1C3/ pSB1A2 and each LovTAP construction in pSB3K3). As controls RFP constitutively expressed under J23102 promoter was used and wild type cells transformed just with trpL-RFP. For each transformation one tube containing 5 ml of LB medium with Kanamicyn and chloramphenicol or Kanamicyn and ampicillin, was inoculated from a single colony of DH5α. Cultures were grown overnight (~14hrs) at 37°C with spinning at 100rpm under blue light (470nm) conditions. Then cultures were diluted 1:1000 into 5ml of fresh LB media with antibiotics. These were grown for approximately 4.5 hours under the previous conditions under blue light (470nm). After this step the OD600 was measured from each culture. Based on this OD measurement, the cultures were diluted to the same OD (0.15) in 5 ml of LB fresh media. Then three 200 µL aliquots from each culture were transferred into a flat-bottomed 96 well plate. Samples were loaded in the plate as is shown in the next picture: | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | 5. | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | Samples were loaded in the plate as is shown in the next picture: | + | |
[[Image:LovTAPplate.jpg|center|500px| Overview of the samples organization for LovTAP characterization with the fluorimeter]] | [[Image:LovTAPplate.jpg|center|500px| Overview of the samples organization for LovTAP characterization with the fluorimeter]] | ||
| - | + | An initial measurement of OD600 and fluorescence (530/25 nm excitation filter, 590/35 nm emission filter) by triplicate was done. Using the light emission device to irradiate the incubator, the plate was maintained during 17 hrs at 37°C with spinning at 35rpm inside the incubator but with a mask in the samples selected for the dark conditions. Then, a second measurement of OD600 and fluorescence was done. Initial data with the second measurement were compared. Background absorbance and fluorescence were determined by measuring wells containing only media, and the values obtained were used to normalize the other samples. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
====Results==== | ====Results==== | ||
| - | + | The average ODs of the wells with only media and antibiotics changed drastically from the initial to the second measurement(km/amp from 0.282 to 0.09, and km/cm 0. to 0.093), dificulting the data analysis. So the data obtained | |
| - | initial | + | were inconsistent and even it was intented to analyse them, there was not the expected difference between light and dark conditions. |
====Conclusions==== | ====Conclusions==== | ||
| - | According to the aforementioned results, we think that LovTAP could possibly work well. However we have to improve the characterization protocols in order to support with enough evidence this conclusion. | + | According to the aforementioned results, we think that LovTAP could possibly work well. However we have to improve the characterization protocols in order to support with enough evidence this conclusion. As well, more replicates and controls must be included in the experiments. |
We also think that using other reporter system to describe the transcriptional activation activity of LovTAP using a cascade of double repression, might generate better results. So we will test LovTAP behavior with the cI inverter. | We also think that using other reporter system to describe the transcriptional activation activity of LovTAP using a cascade of double repression, might generate better results. So we will test LovTAP behavior with the cI inverter. | ||
| Line 420: | Line 396: | ||
In order to test the functionality of our Minimum Blue Promoter we succesfully ligated it to | In order to test the functionality of our Minimum Blue Promoter we succesfully ligated it to | ||
our Strong RBS BBa_K360031 and the GFP BBa_E0040. | our Strong RBS BBa_K360031 and the GFP BBa_E0040. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Characterizing YcgF/YcgE BLUE RECEPTION SYSTEM===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Experimental procedure''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is reported that the response of this promoter is weak in comparison to some others standard strong promoters registered in the Registry of Standard Biological Parts. We implemented a protocol for testing the response of our Minimum Blue Light Receptor Promoter (Min-BP) in which we irradiated cells with the construction Min-BP + RBS BBa_K360031 + GFP BBa_E0040 with blue light (470 nm) leds for different times. We also irradiated with green (540 nm) and red (660 nm) light leds to discard any crosstalk of these wavelengths. GFP expression was compared to a reference: J23101 promoter + RBS BBa_K360031 + GFP BBa_E0040. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We measured GFP expression of our constructions, in order to irradiate the cells with Min- BP + RBS BBa_K360031 + GFP BBa_E0040 we used blue leds and irradiated the cells for 300 minutes, we also measured GFP expression of cells that were incubated in the dark and cells with the constuction J23101 promoter + RBS BBa_K360031 + GFP BBa_E0040. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the experiment, cells were incubated overnight in M9 medium with glycerol (0.4%) as carbon source, in the morning OD600 was measured and cells diluted to 0.07 nm. After dilutions, we started irradiation with blue leds. Temperature is a very important factor in the function of the YcgF/YcgE system; it is reported that at 25ºC the ratio between the YcgE repressor and YcgF activator allows a good repression unless there is blue ligh irradiation, so we incubated cells with this promoter at 25ºC. Cells with the constitutive promoter BBa_J23101 were also incubated overnight at 37ºC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Results==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | A graph showing GFP expression of our Minimum Blue Promoter compared with a constitutive promoter is shown here: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Blue_promoter_Comparision_with_constitutive_promoter.jpg|250px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next graph shows GFP expression in presence and absence ob blue light: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Bluepromoter_light_vs_dark.jpg|250px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to the graphs we have shown that our Minimum Blue Light Receptor Promoter works as expected but the response is weak compared to a standard, constitutive promoter BBa_J23101. This results are consistent with previously reported data by the K.U. Leuven 2009 Team. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to increase GFP expression in response to blue light, an amplifier could be used. This means to ligate a T7 polymerase downstream the Minimum Blue Promoter and the GFP downstream a T7 promoter. Additionally, we can increment irradiation time and observe response of our blue light-induced promoter. | ||
| + | |||
====Emission module: Red Firefly Luciferase==== | ====Emission module: Red Firefly Luciferase==== | ||
| Line 431: | Line 432: | ||
*The final aim was the construction of the red light emission device, using the promoter region regulated by LovTAP with the red light emitting luciferase coupled to the Luciferin Regenerating Enzyme (LRE). The structure of the device is designed as follows: | *The final aim was the construction of the red light emission device, using the promoter region regulated by LovTAP with the red light emitting luciferase coupled to the Luciferin Regenerating Enzyme (LRE). The structure of the device is designed as follows: | ||
| - | [[Image:Red luciferase.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Red luciferase.jpg|350px|center]] |
*Design LRE biobrick and transfer the plasmid with the synthesised gene from Mr. Gene Plasmid to pSB1C3 DNA submission backbone and assemble it to a constitutive promoter. | *Design LRE biobrick and transfer the plasmid with the synthesised gene from Mr. Gene Plasmid to pSB1C3 DNA submission backbone and assemble it to a constitutive promoter. | ||
| Line 462: | Line 463: | ||
Our goal here was to couple both, luciferase and LRE, to be able to make the construction autonomous after the first and single input of luciferin. We sent to synthesize the LRE enzyme. | Our goal here was to couple both, luciferase and LRE, to be able to make the construction autonomous after the first and single input of luciferin. We sent to synthesize the LRE enzyme. | ||
| - | For more details see [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K360113 LRE | + | For more details see [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K360113 LRE (BBa_K360113)] entry at the Registry page. |
| + | |||
| + | ====REFERENCES==== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Kelly JR, Rubin AJ, Davis JH, Ajo-Franklin CM, Cumbers J, Czar MJ, de Mora K, Glieberman AL, Monie DD, Endy D: Measuring the activity of BioBrick promoters using an in vivo reference standard. J Biol Eng 2009, 3:4. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Yanofsky, C., R.L. Kelley, V. Horn 1984. Repression is relieved before attenuation in the trp operon of Escherichia coli as tryptophan starvation becomes increasingly severe. J.Bacteriol. 158:1018-1024 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Strickland, D., Moffat, K., & Sosnick, T. (2008). Light-activated DNA binding in a designed allosteric protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(31), 10709. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<html> | <html> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 02:38, 24 November 2010

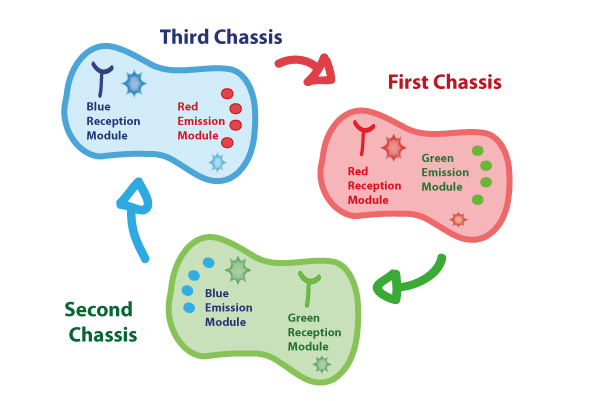
Coupling together Biological Chassis
In order to enable the light based communication between bacteria, we have designed a tertiary cycle of different bacteria chassis, assembling each module of reception and emission to construct a light-based feedback loop of red-green-blue light, which will make the proof of concept of communication over distance and proper signal decoding.
Tertiary cycle
Chassis Description
iGEM
iGEM is the International Genetically Engineered Machines Competition, held each year at MIT and organized with support of the Parts Registry. See more here.Synthetic Biology
This is defined as attempting to manipulate living objects as if they were man-made machines, specifically in terms of genetic engineering. See more here.Genomics
We are students on the Genomic Sciences program at the Center for Genomic Sciences of the National Autonomous University of Mexico, campus Morelos. See more here.This site is best viewed with a Webkit based Browser (eg: Google's Chrome, Apple's Safari),
or a Gecko one (eg: Mozilla's Firefox, Netscape). Some of the code requires an up-to-date browser.
Trident based (Microsoft's Internet Explorer) or Presto based (Opera) are not currently supported. Sorry.
Trident based (Microsoft's Internet Explorer) or Presto based (Opera) are not currently supported. Sorry.
 "
"