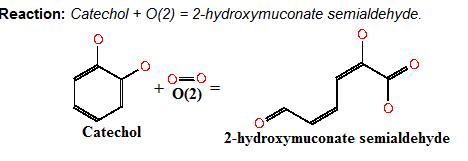Team:Imperial College London/Modules/Fast Response
From 2010.igem.org
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{:Team:Imperial_College_London/Templates/SmallModuleHeader}} | {{:Team:Imperial_College_London/Templates/SmallModuleHeader}} | ||
{| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | {| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | ||
| - | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"|Fast Response Module | + | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"|Fast Response Module Output Overview |
|- | |- | ||
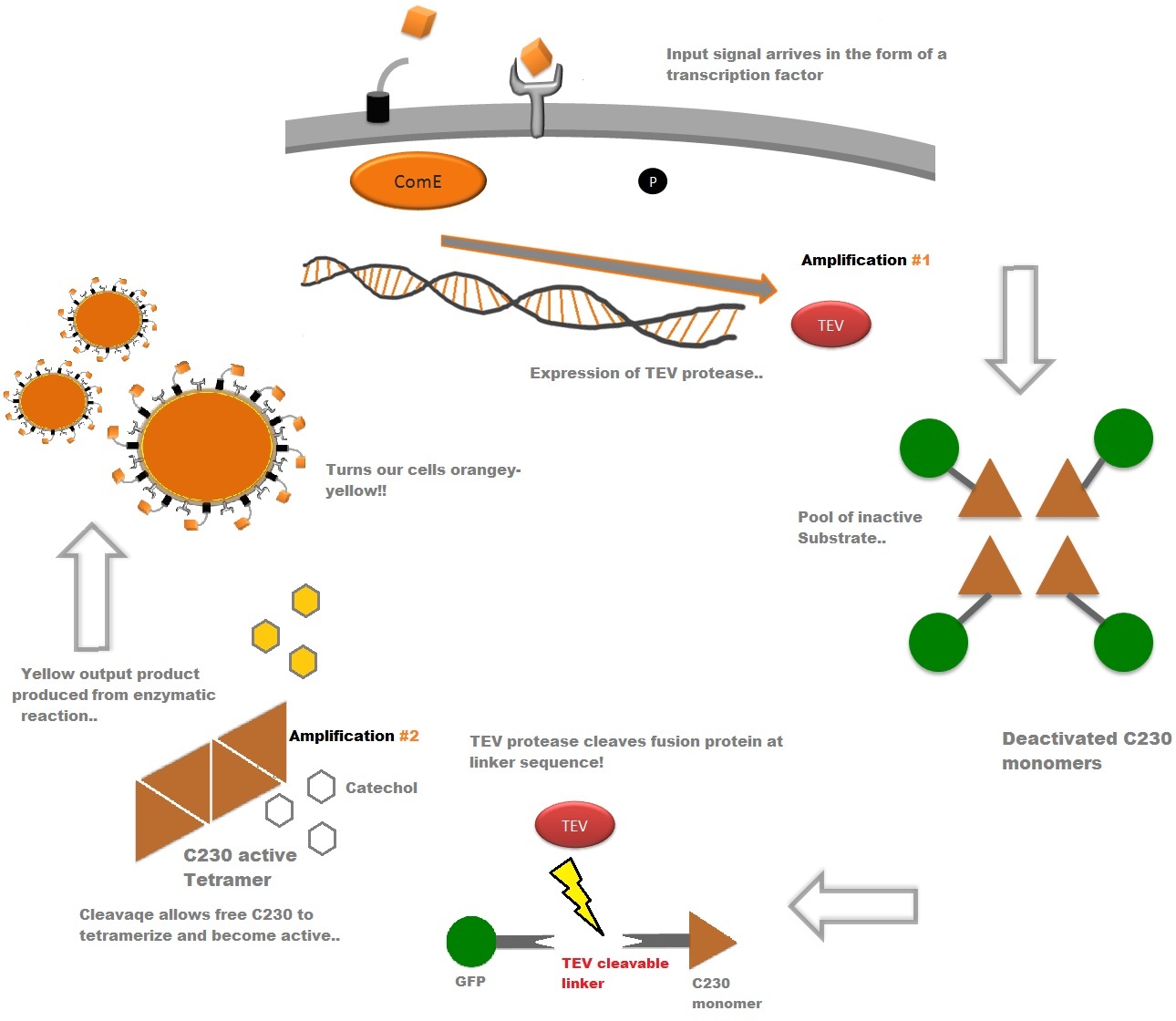
| - | | | + | |The third component of our bacterial detector is a fast response reporter module that upon detection of an input signal gives out a yellow signal output visible by the naked eye. Reporters in biochemical research traditionally rely on transcription-translation of a specific reporter molecule (e.g. green fluorescent protein) which can be time consuming and/or might involve sophisticated equipment for its detection. In this module we introduce a novel reporter system. This system involves the expression of a low molecular weight protease which acts on an pre-existing pool of substrate and facilitates a double amplification step. This should result in an output signal several orders of magnitude faster than traditional reporters. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | The third | + | |
| - | + | An overview of our system can be found below followed by a more in-depth analysis of the system. | |
<div ALIGN=CENTER> | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
{| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| Line 23: | Line 19: | ||
|align="center"|<html><object width="425" height="344"><param name="movie" value="http://www.youtube.com/v/ILkBPGdsOR8?hl=en&fs=1"></param><param name="allowFullScreen" value="true"></param><param name="allowscriptaccess" value="always"></param><embed src="http://www.youtube.com/v/ILkBPGdsOR8?hl=en&fs=1" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="true" width="425" height="344"></embed></object></html> | |align="center"|<html><object width="425" height="344"><param name="movie" value="http://www.youtube.com/v/ILkBPGdsOR8?hl=en&fs=1"></param><param name="allowFullScreen" value="true"></param><param name="allowscriptaccess" value="always"></param><embed src="http://www.youtube.com/v/ILkBPGdsOR8?hl=en&fs=1" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="true" width="425" height="344"></embed></object></html> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
{| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | {| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | ||
|style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;" colspan="2"| C230 and C230-GFP fusion | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;" colspan="2"| C230 and C230-GFP fusion | ||
| Line 36: | Line 33: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| | | | ||
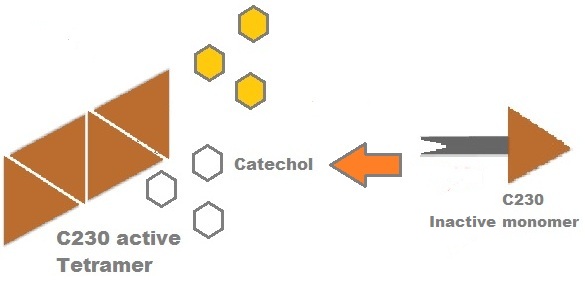
| - | Catechol (2,3) dioxygenase ( | + | Catechol (2,3) dioxygenase (C23O) is the protein product of the XylE gene. It originates from ''Pseudomonas putida'' and the active protein is made up of a homotetramer of C2,3O monomers. The enzyme catalyses the conversion of a colourless substrate (catechol or substituted catechols) into a bright yellow product (2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde) within seconds of substrate addition. |
|} | |} | ||
{| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | {| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | ||
|style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"| | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"| | ||
|- | |- | ||
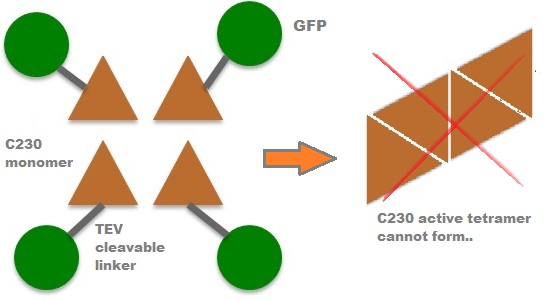
| - | |In our project, we take advantage of the fact that | + | |In our project, we take advantage of the fact that C23O is only active as a tetramer as the active site forms as a result of intersubunit and interface interactions after oligomerisation. We have constructed a gene product that encodes a fusion protein. This fusion protein is made of GFP fused to the N-terminus of C23O. The GFP does not allow C23O monomers to associate due to a steric hindrance effect, so that the active tetramer cannot form. Instead the fusion protein remains as a monomer in the cytosol of the cell. |
| | | | ||
<div ALIGN=CENTER> | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 63: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| | | | ||
| - | A very important feature of the fusion protein is its potential for induction of the system. A closer look at the fusion gene construct reveals the secret of the inducibility of our system. The GFP gene is fused to the XylE gene through a protein sequence that is recognised and cleaved by TEV protease. This amino acid sequence is | + | A very important feature of the fusion protein is its potential for induction of the system. A closer look at the fusion gene construct reveals the secret of the inducibility of our system. The GFP gene is fused to the XylE gene through a protein sequence that is recognised and cleaved by TEV protease. This amino acid sequence is recognised by the active site of the TEV protease so that when TEV is present in the cell, GFP is cleaved off C23O monomers. The free monomers are no longer sterically hindered by the GFP and are now able to associate with each other. Tetramerisation of the monomers produces the active C23O enzyme, which in the presence of catechol substrate produces a yellow colour. |
|} | |} | ||
{| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | {| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | ||
|style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"| | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"| | ||
|- | |- | ||
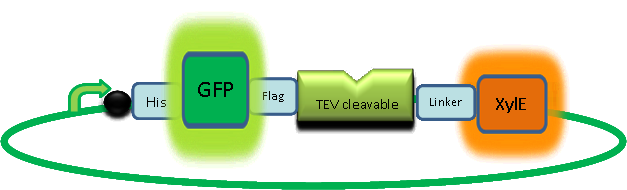
| - | |Our GFP-XylE gene construct | + | |Our GFP-XylE gene construct also has some other addition features, which make it easier to work with. It contains an N-terminal His-tag which would assist in purification and for ''in vitro'' characterisation. The same applies to the flag tag sequence which can be recognised by monoclonal antibodies for easier detection and purification. The linker sequence is there to ensure that the TEV recognition sequence is readily accessible to the protease for cleavage. |
| | | | ||
<div ALIGN=CENTER> | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| Line 95: | Line 92: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| | | | ||
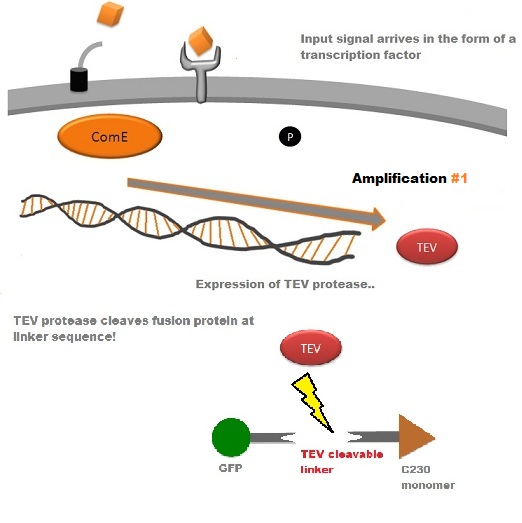
| - | TEV protease is a natural polyprotein cutting viral protease. In our system ComE transcription factors bind to their native ComCDE promoter which was engineered as the promoter for TEV protease. This means that TEV protease is '''only''' transcribed and translated upon detection of the Schistosoma parasite. | + | TEV protease is a natural polyprotein cutting viral protease. In our system ComE transcription factors bind to their native ComCDE promoter which was engineered as the promoter for TEV protease. This means that TEV protease is '''only''' transcribed and translated upon detection of the ''Schistosoma'' parasite. |
'''Why TEV protease?''' | '''Why TEV protease?''' | ||
| Line 108: | Line 105: | ||
| | | | ||
So what are the key features that make our system a novel example of a fast response mechanism? | So what are the key features that make our system a novel example of a fast response mechanism? | ||
| - | | [[Team:Imperial_College_London/Modelling | Modelling]] | + | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:1.5em;color:#ea8828;"| [[Team:Imperial_College_London/Modelling | Modelling]] |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| - | *Due to the small size of the TEV gene, it is likely | + | *Due to the small size of the TEV gene, it is likely to be transcribed and translated very quickly and therefore will not introduce limiting kinetic factors within our fast response system. |
|<div ALIGN=CENTER> | |<div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
{| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| Line 120: | Line 117: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| - | *TEV protease would then act upon a pre-existing pool of inactive substrate already present in the cell. This substrate (GFP- | + | *TEV protease would then act upon a pre-existing pool of inactive substrate already present in the cell. This substrate (GFP-C23O fusion protein) is an inactive form of the chosen output enzyme C23O. Since TEV protease is a relatively fast enzyme, it has a high turnover rate of substrate molecules per unit of time. This is '''AMPLIFICATION STEP #1'''. |
|<div ALIGN=CENTER> | |<div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
{| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| Line 129: | Line 126: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| - | *The now activated | + | *The now activated C23O is itself an enzyme itself with a high turnover rate. As a consequence, a vast number of catechol molecules would be converted to yellow coloured product per unit of time. '''This is AMPLIFICATION STEP #2'''. |
|<div ALIGN=CENTER> | |<div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
{| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | {| style="background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| Line 139: | Line 136: | ||
{| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | {| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | ||
| - | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"|C23O | + | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"|C23O Additional Material |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 150: | Line 147: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
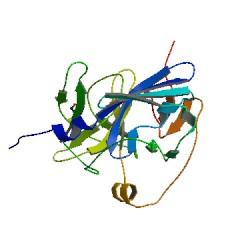
| - | |After observing | + | |After observing C23O in Pymol, and taking into account additional information obtained (Kita ''et al''), which shows that the projecting loop is needed for dimerisation and that this is very near to the N-terminus, we chose to engineer (by straightforward DNA synthesis) GFP plus a linker (GGGSGGGS ENYLFQG) onto the N-termini of our C230 monomers. |
| - | Below is the reaction performed by our | + | Below is the reaction performed by our system’s enzyme: |
<div ALIGN=CENTER> | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
{| style="width:504px;background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | {| style="width:504px;background:#e7e7e7;text-align:center;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| Line 162: | Line 159: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | {| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | |
| + | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"|And one more assay.... | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |align="center"|<html><object width="425" height="344"><param name="movie" value="http://www.youtube.com/v/MrEh5nDNREE?hl=en&fs=1"></param><param name="allowFullScreen" value="true"></param><param name="allowscriptaccess" value="always"></param><embed src="http://www.youtube.com/v/MrEh5nDNREE?hl=en&fs=1" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="true" width="425" height="344"></embed></object></html> | ||
| + | |} | ||
{| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | {| style="width:900px;background:#f5f5f5;text-align:justify;font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#555555;margin-top:5px;" cellspacing="20" | ||
|style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"| References | |style="font-family: helvetica, arial, sans-serif;font-size:2em;color:#ea8828;"| References | ||
| Line 168: | Line 169: | ||
| | | | ||
| - | [1] An archetypical extradiol-cleaving catecholic dioxygenase: the crystal structure of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (metapyrocatechase) from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 | + | [1] 'An archetypical extradiol-cleaving catecholic dioxygenase: the crystal structure of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (metapyrocatechase) from Pseudomonas putida mt-2' 1999 Akiko Kita, Shin-ichi Kita, Ikuhide Fujisawa, Koji Inaka, Tetsuo Ishida, Kihachiro Horiike, Mitsuhiro Nozaki and Kunio Miki |
| - | Akiko | + | |
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:50, 28 October 2010
| Modules | Overview | Detection | Signaling | Fast Response |
| Our design consists of three modules; Detection, Signaling and a Fast Response, each of which can be exchanged with other systems. We used a combination of modelling and human practices to define our specifications. Take a look at the overview page to get a feel for the outline, then head to the full module pages to find out how we did it. | |
| Fast Response Module Output Overview |
| The third component of our bacterial detector is a fast response reporter module that upon detection of an input signal gives out a yellow signal output visible by the naked eye. Reporters in biochemical research traditionally rely on transcription-translation of a specific reporter molecule (e.g. green fluorescent protein) which can be time consuming and/or might involve sophisticated equipment for its detection. In this module we introduce a novel reporter system. This system involves the expression of a low molecular weight protease which acts on an pre-existing pool of substrate and facilitates a double amplification step. This should result in an output signal several orders of magnitude faster than traditional reporters.
An overview of our system can be found below followed by a more in-depth analysis of the system. |
| Video of a C230 assay! |
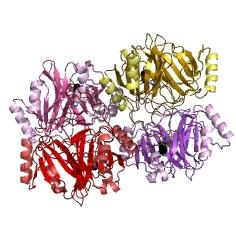
| C230 and C230-GFP fusion | |
|
Catechol (2,3) dioxygenase (C23O) is the protein product of the XylE gene. It originates from Pseudomonas putida and the active protein is made up of a homotetramer of C2,3O monomers. The enzyme catalyses the conversion of a colourless substrate (catechol or substituted catechols) into a bright yellow product (2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde) within seconds of substrate addition. | |
| In our project, we take advantage of the fact that C23O is only active as a tetramer as the active site forms as a result of intersubunit and interface interactions after oligomerisation. We have constructed a gene product that encodes a fusion protein. This fusion protein is made of GFP fused to the N-terminus of C23O. The GFP does not allow C23O monomers to associate due to a steric hindrance effect, so that the active tetramer cannot form. Instead the fusion protein remains as a monomer in the cytosol of the cell. |
|
A very important feature of the fusion protein is its potential for induction of the system. A closer look at the fusion gene construct reveals the secret of the inducibility of our system. The GFP gene is fused to the XylE gene through a protein sequence that is recognised and cleaved by TEV protease. This amino acid sequence is recognised by the active site of the TEV protease so that when TEV is present in the cell, GFP is cleaved off C23O monomers. The free monomers are no longer sterically hindered by the GFP and are now able to associate with each other. Tetramerisation of the monomers produces the active C23O enzyme, which in the presence of catechol substrate produces a yellow colour. |
| Our GFP-XylE gene construct also has some other addition features, which make it easier to work with. It contains an N-terminal His-tag which would assist in purification and for in vitro characterisation. The same applies to the flag tag sequence which can be recognised by monoclonal antibodies for easier detection and purification. The linker sequence is there to ensure that the TEV recognition sequence is readily accessible to the protease for cleavage. |
| TEV protease | |
|
TEV protease is a natural polyprotein cutting viral protease. In our system ComE transcription factors bind to their native ComCDE promoter which was engineered as the promoter for TEV protease. This means that TEV protease is only transcribed and translated upon detection of the Schistosoma parasite. Why TEV protease? This enzyme has been used extensively in protein engineering as it has a number of key qualities including a high specificity (ENYLFQG), and importantly for our system it has a relatively low molecular weight (242 aa) compared to other protease candidates available. This means that the synthesis of the protease will be relatively quick. For more information about TEV, please see the PDB file with the accession number 1Q31. TEV protease expression in E.Coli (and consequently B .subtilis) is made efficient by codon optimisation and inducing expression of additional tRNAs. |
| Fast < faster < Imperial College Turbo FAST | |
|
So what are the key features that make our system a novel example of a fast response mechanism? | Modelling |
| |
| |
| |
| C23O Additional Material | |||
| After observing C23O in Pymol, and taking into account additional information obtained (Kita et al), which shows that the projecting loop is needed for dimerisation and that this is very near to the N-terminus, we chose to engineer (by straightforward DNA synthesis) GFP plus a linker (GGGSGGGS ENYLFQG) onto the N-termini of our C230 monomers.
Below is the reaction performed by our system’s enzyme:
|
| And one more assay.... |
| References |
|
[1] 'An archetypical extradiol-cleaving catecholic dioxygenase: the crystal structure of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (metapyrocatechase) from Pseudomonas putida mt-2' 1999 Akiko Kita, Shin-ichi Kita, Ikuhide Fujisawa, Koji Inaka, Tetsuo Ishida, Kihachiro Horiike, Mitsuhiro Nozaki and Kunio Miki |
 "
"