Team:Lethbridge/Results
From 2010.igem.org
Liszabruder (Talk | contribs) (→References) |
JustinVigar (Talk | contribs) (→Method) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
<BLOCKQUOTE> | <BLOCKQUOTE> | ||
| - | =<font color="white"> | + | =<font color="white">Catechol Degradation= |
| - | One of the sub-projects for the bioremediation of the tailings ponds is to create synthetic <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project/Compartamentalization"><font color="#00DC00"> microcompartments</font></a></html> that we can then use to isolate various | + | The focus of our <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project"><font color="#00DC00">project</font></a></html> is to decrease the toxicity of tailings pond water through bioremediation. We are specifically interested in the <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project/Catechol_Degradation"><font color="#00DC00">degradation of the toxic molecule catechol</font></a></html> into 2-hydroxymuconate semialdyhyde (2-HMS); a bright yellow substrate that can be metabolized by the cell. This conversion is accomplished by a protein called catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (xylE). |
| + | |||
| + | ==<font color="white">Characterization of Catechol 2,3-Dioxygenase== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color="white">Characterized Parts</font>=== | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K118021" target="new"><font color="#00DC00" size="+1">BBa_K118021</font></a></html> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color="white">Hypothesis</font>=== | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | The addition of the catechol to a suspension of cells expressing catechol 2,3-dioxygenase will result in the production of 2-HMS. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color="white">Method</font>=== | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_K118021" target="new"><font color="#00DC00">BBa_K118021</font></a></html> was transformed into <i>Escherichia coli</i> DH5α (E. coli) cells using our transformation protocol. We confirmed that the cells hosted the plasmid containing the BBa_118021 part and we begun experiments to characterize catechol degredation. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | In our first experiment we grew a 5 mL culture of our engineered <i>E. coli</i> cells in M9 minimal media overnight. The cells were spun down at 14000 rfc for 2 minutes. We raised the catechol concentration of this solution to 100 mM, the solution immediately turned bright yellow. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <body> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <table border="0" cellpadding="8" width="28%" style="background-color:#000000"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/1/1a/UofLcatecholfigure1.jpg"/> | ||
| + | </th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="1" align="left"> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | <font color="white">Figure 1. Left: M9 media containing 100 mM catechol. The solution contains <i>E. coli</i> cells hosting the pUC19 plasmid. Right: M9 media containing 100 mM catechol. The solution contains <i>E. coli</i> cells hosting part BBa_118021. The yellow colour suggests the production of 2-HMS. | ||
| + | </th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | </body> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In our second experiment we wanted to measure the absorbance of 2-hydroxymuconate semialdehyde over time. We grew a 5 mL culture of our engineered <i>E. coli</i> cells in M9 media overnight. 1 mL of the cell solution was removed for analysis. Catechol was added to a final concentration of 100mM in the cell suspension. Immediately the formation of 2-HMS was tracked. The formation of 2-HMS can easily be tracked, as it absorbs light at 375 nm. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <body> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <table border="0" cellpadding="8" width="28%" style="background-color:#000000"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/a/a5/UofLcatecholfigure2.jpg" width="450"/> | ||
| + | </th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="1" align="left"> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | <font color="white">Figure 2. Production of 2-HMS over time. | ||
| + | </th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | </body> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Catechol 2,3-dioxygenase contains an iron molecule in its active site. Our hypothesis was that the iron molecule is oxidized after converting a single catechol molecule to 2-HMS; rendering the catechol 2,3-dioxygenase inactive. We also want to test how catechol 2,3-dioxygenase would behave <i>in vitro</i> compared to <i>in vivo</i>. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | To test this hypothesis we grew <i>E. coli</i> containing BBa_K118021 in 500 mL of LB media with ampicillin. <i>E.coli</i> containing the pUC19 plasmid were also grown in 500 mL of LB media with ampicillin to act as a negative control throughout the course of the experiment. The cells were grown to a final optical density of 4.55 AU (measured at 600 nm). The cells were first spun down at 3800 rcf for 5 minutes. The supernatant was decanted and the cells were re-suspended in 40 mL M9 minimal media and incubated with 10 mg of lysozyme for 10 minutes. This cell extract was spun down at 10000 rcf for 30 minutes. The supernatant was taken off and spun at 30000 rcf (S30) for 1 hour. The supernatant of the S30 samples was divided. Half the samples were flash frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80<sup>o</sup>C. The second half was spun at 100000 rcf for 45 minutes (S100). | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | In order to measure the 2-HMS production we needed to determine the concentration of protein per volume of cell extract. To determine the total protein concentration of the S30 and S100 extracts a Bradford assay was conducted using a standard curve of BSA. Concentrations of the negative controls (<i>Escherichia coli</i> DH5α hosting the pUC19 plasmid) for each of the S30 and S100 samples were also determined. Absorbance readings were taken at a 595 nm wavelength and concentration reported in µg/mL. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color="white">Results of the Bradford Assay=== | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <table><table border="3"> | ||
| + | <tr><td>Sample<td>Concentration | ||
| + | <tr><td>S30<td>779µg/mL | ||
| + | <tr><td>S30 Control<td>104.5µg/mL | ||
| + | <tr><td>S100<td>519.3µg/mL | ||
| + | <tr><td>S100 Control<td>100.1µg/mL | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | Protein mass of S30 and S100 (and S30 Control/S100 Control) extracts were normalized to between 2µg and 10µg in 1mL of either 20mM Tris pH 8.0 or double distilled water. Catechol was added to normalized cell extract at a final concentration of 0.05 mM. The subsequent production of 2-HMS was observed as a function of time by recording absorbance at 375 nm over the ten minute period immediately following the addition of catechol. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color="white">Results=== | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | Figure 3 displays that catechol 2,3-dioxygenase can degrade catechol <i>in vitro</i>, producing 2-HMS. We also observe that when approximately twice the amount of S30 extract is added to an excess catechol solution, production of 2-HMS is increased approximately twofold. This suggests that the enzyme (rather than substrate) is the limiting component in catechol degradation by catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. This result corresponds with our hypothesis that the catechol 2,3-dioxygenase active site iron is reduced upon catalysis, rendering our enzyme inactive. The samples in Figure 3 were carried out in double distilled water. However, duplicates of the readings were measured in a buffer (20mM Tris pH 8.0). We do not observe a significant difference in 2-HMS production in samples containing buffer compared to samples containing double distilled water. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <body> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <table border="0" cellpadding="8" width="28%" style="background-color:#000000"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/b/b7/Catecholgood.jpg" width="450"/> | ||
| + | </th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="1" align="left"> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | <font color="white">Figure 3. The production of 2-hydroxymuconate semialdehyde by different concentrations of S30 extract. Green and red lines are 2µg and 4µg respectively of S30 cell extract from cells expressing catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. The blue line is 4µg of control S30 cell extract. | ||
| + | </th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | </body> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color="white">Conclusion=== | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | We have successfully show that our <i>E. coli</i> cells carrying the K118021 biobrick is capable of converting catechol into 2-HMS. Moreover, the reduction Figure 3 shows a reduction of 2-HMS concentration in the solution. It is more than likely, considering that 2-HMS can be metabolized by the cell, that the soluble metabolic machinery of <i>E. coli</i> is metabolizing 2-HMS into its breakdown products. This is a feature of the system that we intend to exploit in our remediation project. <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | With this in mind, it is inefficient to utilize a single turnover enzyme such as catechol 2,3-dioxygenase in an industrial setting. We have identified a protein that will reduce the iron that is oxidized in the conversion of catechol to 2-HMS. The gene coding for this enzyme (<i>xylT</i>) codes for a ferredoxin protein, and is located on the same operon as <i>xylE</i> in <i>Pseudomonas putida</i><sup>1</sup></i>. <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We intend to introduce ferredoxin to our bioremediation project next year with the aim of increasing catechol 2,3-dioxygenase efficiency by allowing it to catalyze multiple turnovers of catechol to 2-HMS<br> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<font color="white">References=== | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <sup>1</sup>Polissi A., Harayama S. (1993) <b>In vivo reactivation of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase mediated by a chloroplast-type ferredoxin: a bacterial strategy to expand the substrate specificity of aromatic degradative pathways.</b>. <i>EMBO J.</i>, <b>12</b>(8); 3339-3347 | ||
| + | |||
| + | =<font color="white">Compartmentalization Parts= | ||
| + | One of the sub-projects for the bioremediation of the tailings ponds is to create synthetic <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project/Compartamentalization"><font color="#00DC00"> microcompartments</font></a></html> that we can then use to isolate various pathways within an <i>Escherichia coli</i> cell. To do this we need to have a microcompartment as well as a means to characterize the compartment so that the system can be optimized. Here are the experiments we have performed so far towards the characterization of the microcomparments. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
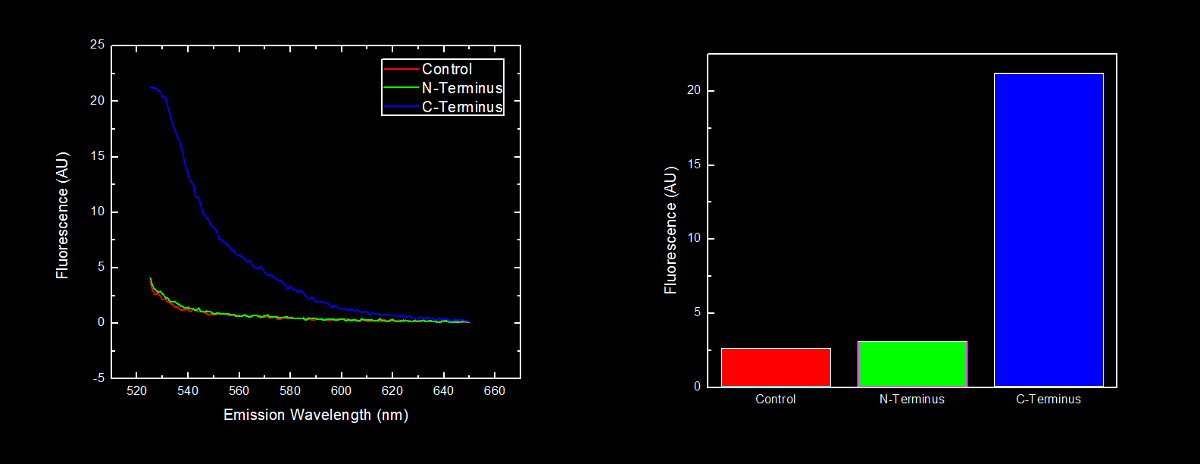
==<font color="white">Placement of Oligoarginine Tail on Proteins</font>== | ==<font color="white">Placement of Oligoarginine Tail on Proteins</font>== | ||
| Line 171: | Line 302: | ||
===<font color="white">Conclusion</font>=== | ===<font color="white">Conclusion</font>=== | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
| - | Our results | + | Our results showing that the placement of arginine residues at the N-terminus of our YFP results in no observable fluorescence over control cells are consistent with the general N-terminal rule reported by Bachmair <i>et al.</i> Assuming that transcription of this K331030 and K331031 are equivalent, these data suggest that the N-terminal oligoarginine is reducing the half-life of the protein to which it is fused, ie YFP. |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
===<font color="white">Reference</font>=== | ===<font color="white">Reference</font>=== | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
| Line 178: | Line 310: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | ==<font color="white">Characterization of Cyan Fluorescent Protein</font>== | + | |
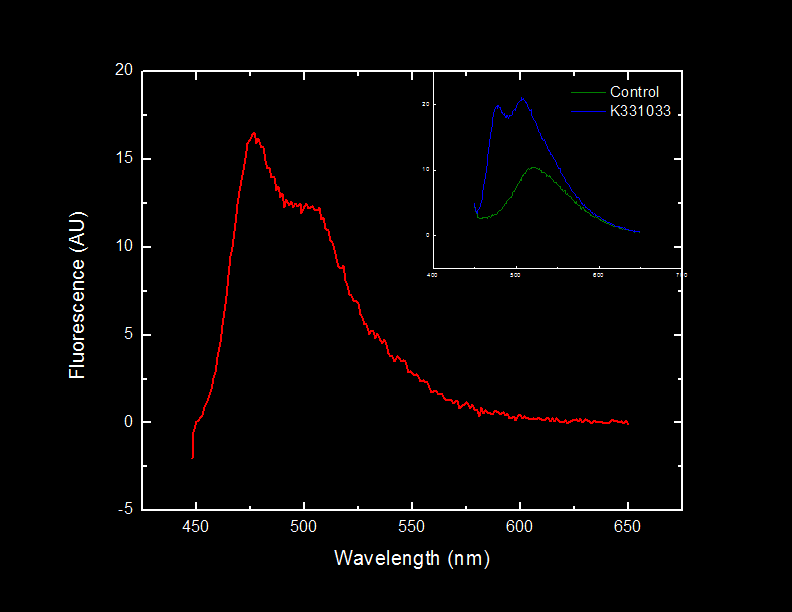
| + | ==<font color="white">Characterization of C-terminal Oligo Arginine Cyan Fluorescent Protein</font>== | ||
===<font color="white">Characterized Parts</font>=== | ===<font color="white">Characterized Parts</font>=== | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_K331033" target="new"><font color="#00DC00" size="+1">BBa_K331033</font></a></html> | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_K331033" target="new"><font color="#00DC00" size="+1">BBa_K331033</font></a></html> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 211: | Line 342: | ||
Fluorescence at 476 nm was observed. This peak, along with a shoulder occurring at approximately 510 nm is consistent with results obtained by McRae<sup>1</sup> <i>et al.</i> in their rapid purification of ECFP.<br> | Fluorescence at 476 nm was observed. This peak, along with a shoulder occurring at approximately 510 nm is consistent with results obtained by McRae<sup>1</sup> <i>et al.</i> in their rapid purification of ECFP.<br> | ||
[[image:UofLcfpfigureblack.jpg|450px|center]] | [[image:UofLcfpfigureblack.jpg|450px|center]] | ||
| - | + | <br> | |
===<font color="white">Conclusion</font>=== | ===<font color="white">Conclusion</font>=== | ||
| Line 228: | Line 359: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
<sup>2</sup>McRae S.R., Brown C.L., Bushell G.R. (2005), Rapid Purification of EGFP, EYFP, and ECFP with high yield and purity. <i>Protein Expression and Purification</i> 41. 1 121-127. | <sup>2</sup>McRae S.R., Brown C.L., Bushell G.R. (2005), Rapid Purification of EGFP, EYFP, and ECFP with high yield and purity. <i>Protein Expression and Purification</i> 41. 1 121-127. | ||
| - | <br><br> | + | <br> |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
=<font color="white">Magnetic Nanoparticles Parts= | =<font color="white">Magnetic Nanoparticles Parts= | ||
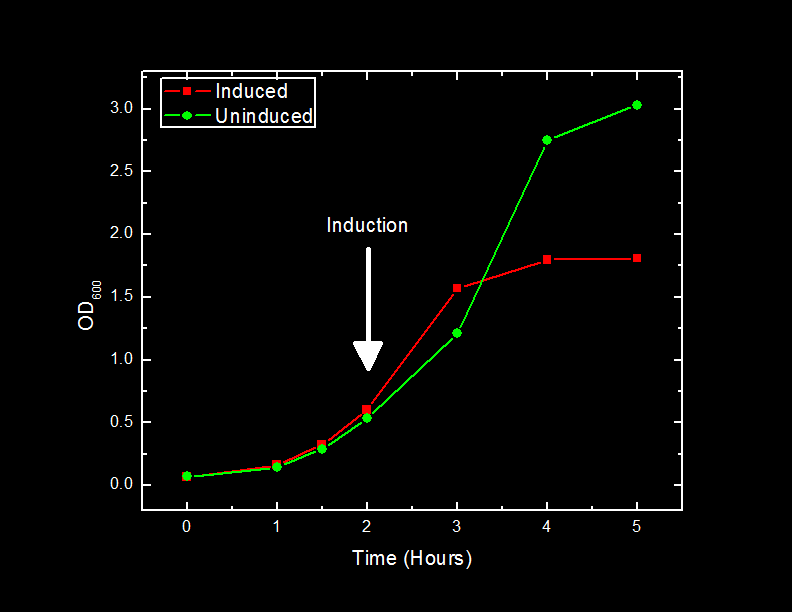
One of the sub-projects for the <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project" target="new"><font color="#00DC00"> bioremediation of the tailings ponds</font></a></html> is to reduce heavy metals to create <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project/Magnetic_Nanoparticles" target="new"><font color="#00DC00"> magnetic nanoparticles</font></a></html> that can then be removed from the pond. To do this we need to be able to produce Mms6 (the iron reducing protein) and show that it can successfully produce the nanoparticles within the <i>Escherichia coli</i> cell. He is the work we have accomplished so far to characterize Mms6. | One of the sub-projects for the <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project" target="new"><font color="#00DC00"> bioremediation of the tailings ponds</font></a></html> is to reduce heavy metals to create <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Lethbridge/Project/Magnetic_Nanoparticles" target="new"><font color="#00DC00"> magnetic nanoparticles</font></a></html> that can then be removed from the pond. To do this we need to be able to produce Mms6 (the iron reducing protein) and show that it can successfully produce the nanoparticles within the <i>Escherichia coli</i> cell. He is the work we have accomplished so far to characterize Mms6. | ||
| Line 260: | Line 393: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[image:UofLmms6growth.jpg|450px|center]] | [[image:UofLmms6growth.jpg|450px|center]] | ||
| - | + | <br> | |
===<font color="white">Conclusion=== | ===<font color="white">Conclusion=== | ||
 "
"