Team:Northwestern/Project/Chitin Synthesis
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
RaganSmash (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision not shown) | |||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
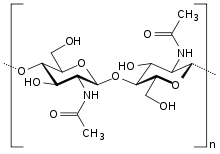
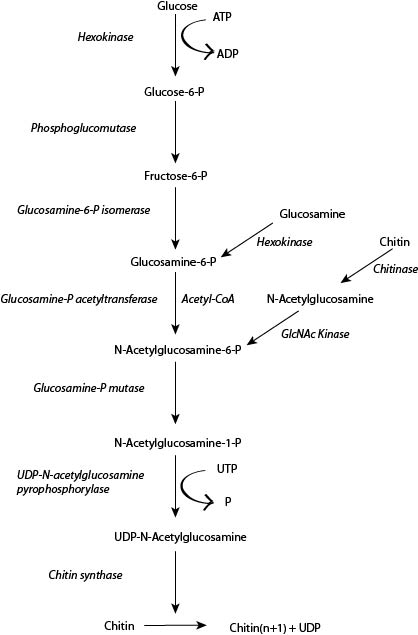
| - | Chitin is an abundant biopolymer found primarily in the exoskeletons of arthropods, including many insects and crustaceans. Composed of N-acetylglucosamine monomers (Figure 1), it functions analogously to keratin in mammalian skin, providing a support matrix for the protective outer surface of these animals. Similarly, most fungi produce chitin in their cell walls for structural support | + | Chitin is an abundant biopolymer found primarily in the exoskeletons of arthropods, including many insects and crustaceans. Composed of N-acetylglucosamine monomers (Figure 1), it functions analogously to keratin in mammalian skin, providing a support matrix for the protective outer surface of these animals. Similarly, most fungi produce chitin in their cell walls for structural support. Chitin production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on a series of enzymatic steps (Figure 2).[[image:chitin_wikipedia.png|frame|right|alt=alt text|'''Figure 1''' Chitin molecular structure. <br /> Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chitin Wikipedia - Chitin]]] <br /> |
| - | [[image: | + | One enzyme in this pathway, chitin synthase 3 (CHS3), was previously found to be among the most active chitin sythases in the chitin synthase family of enzymes and does not require additional cofactors to function. As a result, we use CHS3 as the chitin production mechanism in our inducible system ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K418007 BBa_K418007]). [[image:chitin synthesis small.jpg|frame|center|alt=alt text|'''Figure 2''' Chitin synthesis pathway. <br /> Adapted from Figure 3.1 of <u>Chitin: Fulfilling a Biomaterials Promise</u> by Eugene Khor.]]<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | Chitin has many applications, particularly in medicine and industry. Currently, nearly all chitin is obtained from natural sources (i.e. shells of crustaceans). Thus, a method of recombinant chitin production may have commercial applications. Several examples of chitin usage are listed below: | ||
'''SIGNIFICANCE OF CHITIN''': | '''SIGNIFICANCE OF CHITIN''': | ||
| Line 179: | Line 181: | ||
*Dietary supplement | *Dietary supplement | ||
*Water purification | *Water purification | ||
| - | |||
*Edible microcrystalline films used to preserve food | *Edible microcrystalline films used to preserve food | ||
*Sequestering of particles (i.e. oil) | *Sequestering of particles (i.e. oil) | ||
| - | + | *Biodegradable/non-pollutant | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Latest revision as of 20:11, 25 October 2010
| Home | Brainstorm | Team | Acknowledgements | Project | Human Practices | Parts | Notebook | Calendar | Protocol | Safety | Links | References | Media | Contact |
|---|
 "
"