Team:Tsinghua/project/outline
From 2010.igem.org
(→Comparison between natural antibody production and E. Coli system) |
|||
| (105 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<script> | <script> | ||
| - | navlist=new Array("Background", "Project Outline", "Module I", "Module II", "Future"); | + | navlist=new Array("Background", "Project Outline", "Module I", "Module II", "Conclusion", "Future"); |
| - | linkl = new Array("/Team:Tsinghua/project", "#outline", " | + | linkl = new Array("/Team:Tsinghua/project", "#outline", "/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1", "/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2", "con", "future"); |
subs = new Array(2,3); | subs = new Array(2,3); | ||
writenav(navlist, linkl, 1, subs); | writenav(navlist, linkl, 1, subs); | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<div id="main_content"><a name="outline"></a> | <div id="main_content"><a name="outline"></a> | ||
<h1>Outline</h1> | <h1>Outline</h1> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="content_block"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | In order to realize the production of antibodies in prokaryotic cells, we firstly investigate the whole process of antibody production in mammalian immune system and try to simulate the whole process via the methods and concepts of synthetic biology. Finally, we successfully constructed the desired system. The comparison between the key steps involved in antibody generation and corresponding synthetic methods are shown in the chart below. | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table border="2" bordercolor="maroon" bgcolor="silver"> | ||
| + | <tbody> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th colspan=3>Antibody Production</th> | ||
| + | <th width=50px></th> | ||
| + | <th colspan=2>E Coli. Production System</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=4 width=70px><a href="#VDJ_Recombination_vs_Lading_Pad_Recombination">VDJ Recombination</a></td> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=3 width=70px>Preparation</td> | ||
| + | <td width=70px>RSS Sequence</td> | ||
| + | <td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/6/69/THUarrow1.png" width=50 /></td> | ||
| + | <td width=70px><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#Landing_Pad_Construction_and_Insertion">Landing Pad Insertion</a></td> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=4 width=70px><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1">Module I: Recombination System</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>VDJ Recombinase</td> | ||
| + | <td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/6/69/THUarrow1.png" width=50 /></td> | ||
| + | <td><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#hpi">Helper Plasmid Insertion</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>VDJ Library</td> | ||
| + | <td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/6/69/THUarrow1.png" width=50 /></td> | ||
| + | <td><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#dpc">Donor Plasmid Construction</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Recombination</td> | ||
| + | <td colspan=2><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/d/d6/THUarrow2.png" width=180></td> | ||
| + | <td><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#dpiri">DP Insertion and Recombination Induction</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=2><a href="#Somatic_hyper-mutation_vs_Junctional_mutation">Somatic Hypermutation</a></td> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=2 colspan=3><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/4/48/THUarrow.png" width=325 ></td> | ||
| + | <!---------<td>Junctional Diversity</td>----------------------> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=2><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2#m2s1">CBD-based Microarray</a></td> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=4><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2">Module II: Selection System</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=3><a href="#Antigen-specific_Selection_vs_CBD-Based_Microarray_and_ToxR-Based_Transmembrane_pathway_method">Antigen Selection</a></td> | ||
| + | <td rowspan=3 colspan=3><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/4/48/THUarrow.png" width=325 ></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2#m2s2">ToxR-based Transmembrane Pathway</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2#Strategy_3">Cooperation With Macquarie_Australia</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </tbody> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | + | <br/> | |
| - | + | Generally speaking, antibody production in our project can be divided into two modules. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | === | + | <html> |
| - | + | <body bgcolor="#336699" text="#ffffff" link="#60a179"> | |
| - | ==== | + | <br/> |
| - | + | <span class="rightfloat"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size="4">Module I: Generation of antibody library</font><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/3/3c/Right_Arrow.png" width="30px"></a></span> | |
| - | + | <br/><br/> | |
| + | <span class="rightfloat"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size="4">Module II: Selection of specific antibodies</font><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/3/3c/Right_Arrow.png" width="30px"></a></span> | ||
| + | <br/><br/> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| - | + | ==Project Design== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | === | + | ===Module 1=== |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
'''Antibodies Library Diversity & Randomicity''' | '''Antibodies Library Diversity & Randomicity''' | ||
[[Image:TSModule1.PNG|650px]] | [[Image:TSModule1.PNG|650px]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | The first module is carried out by a novel method called E coli in vivo recombination system. The theoretical and experimental basis comes from the work of Thomas E. Kuhlman and Edward C. Cox. We managed to modify their system, wishing to utilize it for simulation of antibody recombination. | |
| - | + | ||
| + | Firstly, we try to insert a DNA segment called”Landing Pad(LP)” into the specific sites of E coli via Att recombination, the manner in which lambda phage integrates its DNA into E Coli genome. Landing pad sequence consists of the following parts(from 5’ to 3’ in the sequence): | ||
| - | + | 1)25bp-long random sequence | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | 2)15bp-long recognition sequence of restriction enzyme I-scel | |
| - | + | 3) antibiotic resistance gene used for antibody selection | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | 4) 15bp-long recognition sequence of restriction enzyme I-scel(corresponding to 2) | |
| + | 5) 25bp-long random sequence (corresponding to 1) | ||
| - | + | After integrating DNA segment of Landing pad into the genome of E coli, we completed the genetic engineering of the genome of E coli. All the five parts of landing pad are designed for subsequent recombination. | |
| - | + | Besides, in order to achieve different recombination goals, we designed several landing pads of different sequences. | |
| - | |||
| - | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#Landing_Pad_Construction_and_Insertion"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>'Landing Pad Construction and Insertion'</font></a></html> to learn about the details of Landing Pad design. | |
| - | |||
| - | + | PLEASE refer to this <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#att"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>'link'</font></a></html> to learn more about ATT recombination. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | After the integration of landing pad, we have to insert another DNA fragment called Helper Plasmid(HP), which provides necessary tools for in vivo recombination. | ||
| - | + | In this plasmid(Helper Plasmid), there are two genes used for recombination. | |
| - | + | The first one encodes restriction enzyme I-scel after induction of L-arabinose. I-scel is able to recognize the 15bp-length sequence flanking a target DNA fragment and cut out the fragment, therefore providing DNA segments for recombination mediated by other components. | |
| - | + | The second one encodes the enzyme responsible for recombination called Lamda-Red. With the presence of IPTG, Lamda-Red will recombine DNA fragments flanked by the same DNA sequence recognized by Lamda-Red. | |
| - | + | In addition, Helper Plasmid contains a specific temperature-sensitive replicon, which is used to control the replication via temperature changes. We can remove the replicon when necessary. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#hpi"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>'HP insertion'</font></a></html> to learn more about Helper Plasmid. | |
| - | |||
| - | + | Up till now, we successfully engineered a ‘recepient strain’. Then we have to transform the ‘recepient strain’ with the Donor Plasmid(DP) containing recombination fragments. Donor Plasmid contains several Insertion Fragments and each Insertion Fragment contains following five parts: | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | 1) one 15bp-long restriction enzyme I-scel recognition site | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | 2) one 25bp-long random sequence | |
| - | + | 3) one fragment for insertion and recombination | |
| - | + | 4) one 25bp-long random sequence | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | 5) one 15bp-long restriction enzyme I-scel recognition site(in correspondence with 1) | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | (Note: the order of the five parts differ from that of landing pad) | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Donor plasmid | + | As we previously mentioned, Donor plasmid contains several Insertion Fragments. Based on the flanking landing pad sequence, we can ascribe Insertion Fragments to the same group as long as the flanking landing pad sequences of those Insertion Fragments are the same. |
| - | + | In order to achieve different goals, we design different Donor Plasmids, different Donor Plasmids contain different number of Insertion Fragments, which belong to different groups. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | === | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#dpc"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>‘DP construction’</font></a></html> to learn about the details of Donor Plasmid and Insertion Fragments and the strategies employed in our design. |
| - | |||
| - | + | As we all know, antibody diversity mainly lean on the number of the fragments used for recombination. Therefore, in order to mimic the antibody generation process, we need to construct Donor Plasmid which contains large sum of Insertion Fragments. Theoretically, we can construct Donor Plasmid of this kind. However, due to the time limit of the competition, we didn’t try to construct DP containing many Insertion Fragments. | |
| - | + | In spite of this, in order to meet the needs, we designed two methods to construct plasmids on a large scale and attempted the usage in parts of our Donor Plasmids. | |
| - | |||
| - | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#Strategies"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>'DP construction and Strategies'</font></a></html> for the methods of rapid plasmid construction. | |
| - | |||
| - | + | Besides, we have applied for two BBFRFC, which are BBFRFC61 and BBFRFC 62 respectively. | |
| - | + | Then, after transformation of the prepared ‘recepient strain’ with Donor Plasmid and the induction of corresponding agents, I-scel enzyme cuts out DNA fragments from DP and LP, generating numerous Insertion Fragments. Besides, antibiotic resistance gene integrated into E coli genome is also cut out, providing recombination sites for Insertion Fragments. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Provided with Insertion Fragments mentioned above and Lamda-Red expressed by Donor Plasmid, Insertion Fragments recombine with the corresponding landing pad sequence in the genome and thus get inserted into the correct site of the genome. Based on our design of Landing pad, we can ensure that only one Insertion Fragment from one group is randomly inserted into the genome, therefore mimicking the VDJ recombination process. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m1#dpiri"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>‘DP Insertion and Recombination Induction’</font></a></html> to learn more about this part. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | Engineered E coli cells which have undergone successful recombination can be selected out of the pool through specific screening methods. After tests on different strains, our project achieve a recombination rate above 50% based on our current techniques. | |
| - | |||
| - | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/experiments#res"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>‘Result’</font></a></html> to learn more about the identification of recombination rate. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <br/><br/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | ==Module | + | ===Module 2=== |
| - | + | ||
| + | The goal of the second module in our project is aimed at selection of specific antibodies. Due to the maturity of existing antibody screening technique, our work mainly focuses on imitation of mammalian antibody selection, thus providing possible alternatives for existing methods. | ||
| - | + | The outline of our ideas is to find mechanisms similar to in vivo antibody selection and take in,to account the industry production costs, controllability and reliability, thus developing new methods for antibody selection. | |
| - | + | In fact, in mammalian system, antibody selection is achieved through the activation of B lymphocytes and thus the rapid proliferation of the B lymphocytes that express the specific antibodies that bind to antigen. Simply put, the whole process relies on the interaction between antigen epitopes and membrane integral immunoglobins. | |
| + | To mimic the activation mediated by membrane integral immunoglobins, we develop ToxR-mediated transmembrane activation signal system. In this system, the interaction between antibodies and antigen triggered downstream expression of reporter genes, thus providing signals for selection. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | === | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2#m2s2"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>‘ToxR-based Transmembrane Signaling Pathway Method’</font></a></html> for detailed description of this method. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | In addition, we develop a technique called ‘Bacterial based Microarray’ for selection purpose. In this method, we combine membrane display technique and high throughput microarray technique, that is, a bacterial based microarray method. | |
| - | |||
| - | === | + | PLEASE refer to <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2#m2s1"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>’Bacterial based microarray’</font></a></html> for details. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | In order to find methods for antibody selection, we cooperate with other iGEM teams. For example, we talked with Macquarie_Australia iGEM team about the project. The techniques involved in their project might be useful for our selection methods. Therefore, members from both teams worked together to research on this problem. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | === | + | PLEASE refer to this <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Tsinghua/project/outline/m2#Strategy_3"><font face="Comic Sans MS" size=3>'link'</font></a></html> to learn more about our cooperation. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | Antibody Coding Gene Recombination, also known as V(D)J recombination, somatic recombination, is a mechanism of genetic recombination in the early stages of immunoglobulin (Ig) and T cell receptors (TCR) production of the immune system. V(D)J recombination nearly-randomly combines Variable, Diverse, and Joining gene segments of vertebrates, and because of its randomness in choosing different genes, is able to diversely encode proteins to match antigens. | |
| - | + | Our system is aiming at imitating this recombination process, using E.coli as the gene carrier. | |
| - | + | It is known to all that regional genes (V, D, J) are flanked by Recombination Signal Sequences (RSSs), and the recombination occurs when VDJ recombinase are expressed. We choose RecA enzyme to induce the recombination, while use I-Sel enzyme to cut the genome, just mimicking the process happened in B cells. | |
| - | + | <br/> | |
| - | + | <br/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <br | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | </ | + | |
Latest revision as of 17:16, 27 October 2010

Outline
In order to realize the production of antibodies in prokaryotic cells, we firstly investigate the whole process of antibody production in mammalian immune system and try to simulate the whole process via the methods and concepts of synthetic biology. Finally, we successfully constructed the desired system. The comparison between the key steps involved in antibody generation and corresponding synthetic methods are shown in the chart below.
| Antibody Production | E Coli. Production System | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDJ Recombination | Preparation | RSS Sequence |  |
Landing Pad Insertion | Module I: Recombination System |
| VDJ Recombinase |  |
Helper Plasmid Insertion | |||
| VDJ Library |  |
Donor Plasmid Construction | |||
| Recombination |  |
DP Insertion and Recombination Induction | |||
| Somatic Hypermutation |  |
||||
| CBD-based Microarray | Module II: Selection System | ||||
| Antigen Selection |  |
||||
| ToxR-based Transmembrane Pathway | |||||
| Cooperation With Macquarie_Australia | |||||
Generally speaking, antibody production in our project can be divided into two modules.
Module I: Generation of antibody library

Module II: Selection of specific antibodies

Project Design
Module 1
Antibodies Library Diversity & Randomicity
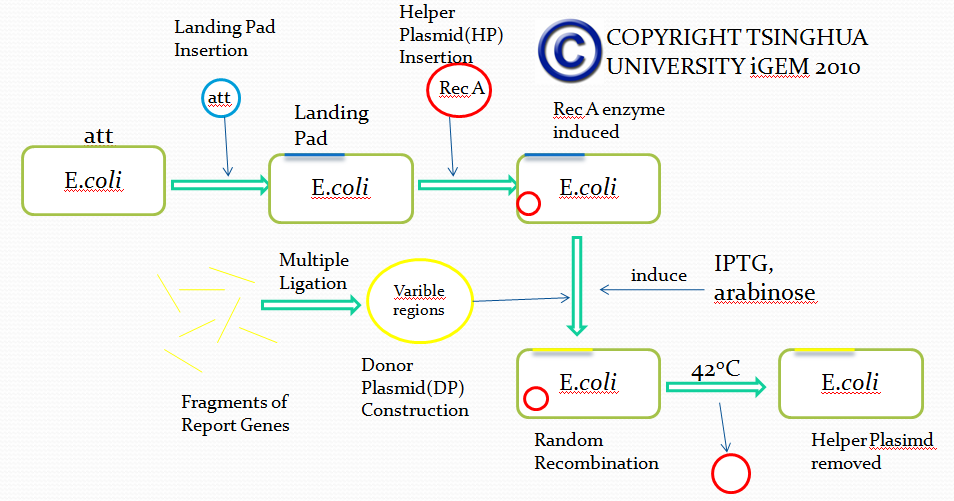
The first module is carried out by a novel method called E coli in vivo recombination system. The theoretical and experimental basis comes from the work of Thomas E. Kuhlman and Edward C. Cox. We managed to modify their system, wishing to utilize it for simulation of antibody recombination.
Firstly, we try to insert a DNA segment called”Landing Pad(LP)” into the specific sites of E coli via Att recombination, the manner in which lambda phage integrates its DNA into E Coli genome. Landing pad sequence consists of the following parts(from 5’ to 3’ in the sequence):
1)25bp-long random sequence
2)15bp-long recognition sequence of restriction enzyme I-scel
3) antibiotic resistance gene used for antibody selection
4) 15bp-long recognition sequence of restriction enzyme I-scel(corresponding to 2)
5) 25bp-long random sequence (corresponding to 1)
After integrating DNA segment of Landing pad into the genome of E coli, we completed the genetic engineering of the genome of E coli. All the five parts of landing pad are designed for subsequent recombination.
Besides, in order to achieve different recombination goals, we designed several landing pads of different sequences.
PLEASE refer to 'Landing Pad Construction and Insertion' to learn about the details of Landing Pad design.
PLEASE refer to this 'link' to learn more about ATT recombination.
After the integration of landing pad, we have to insert another DNA fragment called Helper Plasmid(HP), which provides necessary tools for in vivo recombination.
In this plasmid(Helper Plasmid), there are two genes used for recombination.
The first one encodes restriction enzyme I-scel after induction of L-arabinose. I-scel is able to recognize the 15bp-length sequence flanking a target DNA fragment and cut out the fragment, therefore providing DNA segments for recombination mediated by other components.
The second one encodes the enzyme responsible for recombination called Lamda-Red. With the presence of IPTG, Lamda-Red will recombine DNA fragments flanked by the same DNA sequence recognized by Lamda-Red.
In addition, Helper Plasmid contains a specific temperature-sensitive replicon, which is used to control the replication via temperature changes. We can remove the replicon when necessary.
PLEASE refer to 'HP insertion' to learn more about Helper Plasmid.
Up till now, we successfully engineered a ‘recepient strain’. Then we have to transform the ‘recepient strain’ with the Donor Plasmid(DP) containing recombination fragments. Donor Plasmid contains several Insertion Fragments and each Insertion Fragment contains following five parts:
1) one 15bp-long restriction enzyme I-scel recognition site
2) one 25bp-long random sequence
3) one fragment for insertion and recombination
4) one 25bp-long random sequence
5) one 15bp-long restriction enzyme I-scel recognition site(in correspondence with 1)
(Note: the order of the five parts differ from that of landing pad)
As we previously mentioned, Donor plasmid contains several Insertion Fragments. Based on the flanking landing pad sequence, we can ascribe Insertion Fragments to the same group as long as the flanking landing pad sequences of those Insertion Fragments are the same.
In order to achieve different goals, we design different Donor Plasmids, different Donor Plasmids contain different number of Insertion Fragments, which belong to different groups.
PLEASE refer to ‘DP construction’ to learn about the details of Donor Plasmid and Insertion Fragments and the strategies employed in our design.
As we all know, antibody diversity mainly lean on the number of the fragments used for recombination. Therefore, in order to mimic the antibody generation process, we need to construct Donor Plasmid which contains large sum of Insertion Fragments. Theoretically, we can construct Donor Plasmid of this kind. However, due to the time limit of the competition, we didn’t try to construct DP containing many Insertion Fragments.
In spite of this, in order to meet the needs, we designed two methods to construct plasmids on a large scale and attempted the usage in parts of our Donor Plasmids.
PLEASE refer to 'DP construction and Strategies' for the methods of rapid plasmid construction.
Besides, we have applied for two BBFRFC, which are BBFRFC61 and BBFRFC 62 respectively.
Then, after transformation of the prepared ‘recepient strain’ with Donor Plasmid and the induction of corresponding agents, I-scel enzyme cuts out DNA fragments from DP and LP, generating numerous Insertion Fragments. Besides, antibiotic resistance gene integrated into E coli genome is also cut out, providing recombination sites for Insertion Fragments.
Provided with Insertion Fragments mentioned above and Lamda-Red expressed by Donor Plasmid, Insertion Fragments recombine with the corresponding landing pad sequence in the genome and thus get inserted into the correct site of the genome. Based on our design of Landing pad, we can ensure that only one Insertion Fragment from one group is randomly inserted into the genome, therefore mimicking the VDJ recombination process.
PLEASE refer to ‘DP Insertion and Recombination Induction’ to learn more about this part.
Engineered E coli cells which have undergone successful recombination can be selected out of the pool through specific screening methods. After tests on different strains, our project achieve a recombination rate above 50% based on our current techniques.
PLEASE refer to ‘Result’ to learn more about the identification of recombination rate.
Module 2
The goal of the second module in our project is aimed at selection of specific antibodies. Due to the maturity of existing antibody screening technique, our work mainly focuses on imitation of mammalian antibody selection, thus providing possible alternatives for existing methods.
The outline of our ideas is to find mechanisms similar to in vivo antibody selection and take in,to account the industry production costs, controllability and reliability, thus developing new methods for antibody selection. In fact, in mammalian system, antibody selection is achieved through the activation of B lymphocytes and thus the rapid proliferation of the B lymphocytes that express the specific antibodies that bind to antigen. Simply put, the whole process relies on the interaction between antigen epitopes and membrane integral immunoglobins.
To mimic the activation mediated by membrane integral immunoglobins, we develop ToxR-mediated transmembrane activation signal system. In this system, the interaction between antibodies and antigen triggered downstream expression of reporter genes, thus providing signals for selection.
PLEASE refer to ‘ToxR-based Transmembrane Signaling Pathway Method’ for detailed description of this method.
In addition, we develop a technique called ‘Bacterial based Microarray’ for selection purpose. In this method, we combine membrane display technique and high throughput microarray technique, that is, a bacterial based microarray method.
PLEASE refer to ’Bacterial based microarray’ for details.
In order to find methods for antibody selection, we cooperate with other iGEM teams. For example, we talked with Macquarie_Australia iGEM team about the project. The techniques involved in their project might be useful for our selection methods. Therefore, members from both teams worked together to research on this problem.
PLEASE refer to this 'link' to learn more about our cooperation.
Antibody Coding Gene Recombination, also known as V(D)J recombination, somatic recombination, is a mechanism of genetic recombination in the early stages of immunoglobulin (Ig) and T cell receptors (TCR) production of the immune system. V(D)J recombination nearly-randomly combines Variable, Diverse, and Joining gene segments of vertebrates, and because of its randomness in choosing different genes, is able to diversely encode proteins to match antigens.
Our system is aiming at imitating this recombination process, using E.coli as the gene carrier.
It is known to all that regional genes (V, D, J) are flanked by Recombination Signal Sequences (RSSs), and the recombination occurs when VDJ recombinase are expressed. We choose RecA enzyme to induce the recombination, while use I-Sel enzyme to cut the genome, just mimicking the process happened in B cells.
 "
"





