Team:TU Munich/Glossary
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Attenuation) |
(→Attenuation) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
{| style="background-color:transparent" | {| style="background-color:transparent" | ||
| [[Image:TUM2010 attenuation1.png | 200 px left| mRNA without Ribosome]] | | [[Image:TUM2010 attenuation1.png | 200 px left| mRNA without Ribosome]] | ||
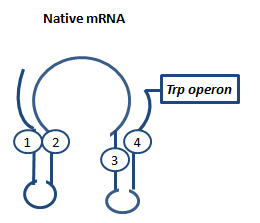
| - | | [[Image:TUM2010_attenuation2.png | | + | |Attenuation is a very smart way of gene regulation which is known from bacterial cells using two alternatice hairpin structures. For example, ''E. coli'' only needs very little amounts of Tryptophan in its metabolism, so the amino-acyl-Synthetase for Tryptophan is only rarely synthesized. So the trp-operon contains an attenuator before the actual enzymes. If Tryptophan is absent, the rare tRNA loaded with Tryptophan will not be available at once, so the Ribosome is stalled. Sterics do not allow the formation of a certain stemloop with the ribosome attached. If there is Tryptophan available and many tRNA<sup>Trp</sup> float through the cell, the ribosome can just continue, a stem loop is formed and the ribosome falls off: The transcription of the following trp-operon is terminated |
| + | |- [[Image:TUM2010_attenuation2.png | 400 px | left | mRNA with Ribosome - stalled without tRNA-Trp]] | ||
| - | + | . <br> | |
<!-- ############## WIKI-PAGE STOPS HERE ############## --> | <!-- ############## WIKI-PAGE STOPS HERE ############## --> | ||
{{:Team:TU_Munich/Templates/End}} | {{:Team:TU_Munich/Templates/End}} | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 7 September 2010
|
||||||||
|
|
Attenuation | |||||||
 "
"