Team:Washington/Tools Created/New Software
From 2010.igem.org
(→Update 11/30/2010:This page will be locked soon, so be sure to visit the TinkerCell and PartsRobot sites for more current information.) |
|||
| (87 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Header}} | + | {{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Header}}<html><script type="text/javascript"> |
| - | <html><script type="text/javascript"> | + | |
$(function() { | $(function() { | ||
var mainimg = document.getElementById("mainimg"); | var mainimg = document.getElementById("mainimg"); | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
}, restore_mainimg); | }, restore_mainimg); | ||
}); | }); | ||
| - | </script></html> | + | </script></html>__NOTOC__As synthetic biologists create ever more complex systems, automation and computer-aided design are becoming indispensable. Computational tools will eventually play a central role in the design, construction, and testing of new devices. To meet the emerging needs of the synthetic biology community, the University of Washington 2010 iGEM team has developed a standard for the electronic distribution of diagrams, detailed in [[Team:Washington/Tools_Created/New_Software#A Standard for Electronic Diagrams|BBF RFC 68]]. We also created two new software tools: [[Team:Washington/Tools_Created/New_Software#wikidust|WikiDust]] and [[Team:Washington/Tools_Created/New_Software#partsrobot|PartsRobot]]. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ===Update 11/30/2010:<br />This page will be locked soon, so be sure to visit the [http://www.tinkercell.com/plugins/wikidust WikiDust] and [http://sourceforge.net/p/partsrobot/home/ PartsRobot] sites for more current information.=== | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
<span id="wikidust"> | <span id="wikidust"> | ||
| + | |||
==[[Image:wikidust_banner.png|500px|center]]== | ==[[Image:wikidust_banner.png|500px|center]]== | ||
| - | + | ||
====<center>A Standard for Electronic Diagrams</center>==== | ====<center>A Standard for Electronic Diagrams</center>==== | ||
| - | + | Standard, unambiguous diagrams are central to communication in many established fields of engineering, but have not yet been widely adopted by synthetic biologists. Through the use of diagrams based on SBOL-visual ([http://bbf.openwetware.org/RFC.html#BBF_RFC_16:_Synthetic_Biology_Open_Language_Visual_.28SBOLv.29_Specification BBF RFC 16]) symbols, we hope to facilitate communication about synthetic DNA constructs between research groups. Usefulness of shared diagrams depends both on a standard set of symbols and on the method of distribution. Therefore the two main requirements for our proposed standard, [http://openwetware.org/wiki/The_BioBricks_Foundation:RFC#BBF_RFC_68:_Standard_for_the_Electronic_Distribution_of_SBOLv_Diagrams BBF RFC 68], are: | |
# The use of SBOLv symbols | # The use of SBOLv symbols | ||
| - | # The linking of symbols to reference entry pages on the Registry of Standard Biological Parts using http URLs | + | # The linking of symbols to reference entry pages on the [http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page Registry of Standard Biological Parts] using http URLs |
| - | + | In the resulting diagram, the reader can click on portions which correspond to SBOLv symbols and read the reference information about that particular portion of the diagram. This makes research easier and promotes better part descriptions. | |
| + | <br /> | ||
====<center>Software to Create and Share Standards-Compliant Diagrams</center>==== | ====<center>Software to Create and Share Standards-Compliant Diagrams</center>==== | ||
| - | + | WikiDust is a plugin for [[Team:Washington/Tools Used/Software#tinkercell|TinkerCell]], a computer-aided design tool developed here at the [http://www.washington.edu/ University of Washington]. WikiDust can be used to export diagrams of TinkerCell models to the iGEM wiki or other webpages. Our goal in creating WikiDust is to provide an easy way to share models and to encourage iGEM teams and researchers to describe their parts more completely. This, in turn, will help others reuse them in future projects. | |
| - | WikiDust is a plugin for [[Team:Washington/Tools Used/Software#tinkercell|TinkerCell]], a computer-aided design tool developed here at the [http://www.washington.edu/ University of Washington]. WikiDust can be used to export TinkerCell models to the iGEM wiki or other webpages | + | |
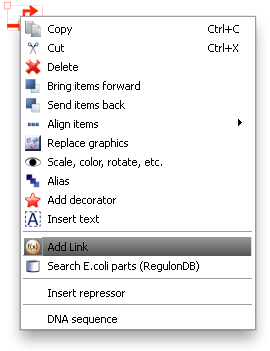
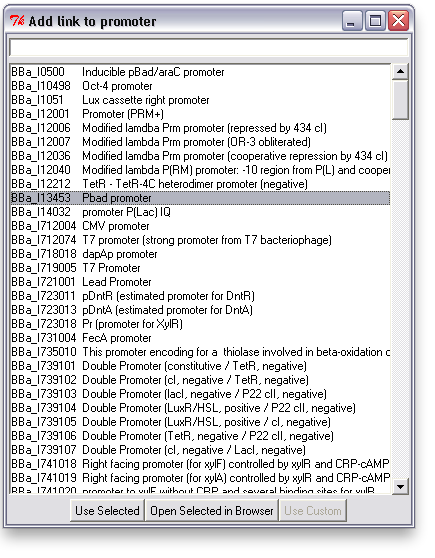
[[Image:washington_rightclick.png|200px|left]][[Image:uw_sauro_linkpanel.png|300px|left]] | [[Image:washington_rightclick.png|200px|left]][[Image:uw_sauro_linkpanel.png|300px|left]] | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | One thing WikiDust does is provide a method to associate TinkerCell items, such as promoters or coding sequences, with parts on the Registry. The same mechanism could also be extended in the future to download reaction kinetics and other parameters from sources like the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20160009 Standard Virtual Parts Repository] or the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16381960 Biomodels Database]. For now though, it demonstrates the feasability of using the publicly available [http://www.sbolstandard.org Standard Biological Parts Knowledgebase (SBPkb)] to retrieve part information using Semantic Web standards. | |
| - | + | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 56: | Line 53: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | + | To associate a link with an item in TinkerCell, right click on it and choose "Add Link". This will bring up a search window with suggested parts. You can search for a phrase, a BioBrick ID, etc. You can also open parts in a browser to read more about them or confirm that you've found the right one. Click "Use Selected" to choose one from the list, or enter your own link and click "Use Custom". | |
| - | + | ||
| - | To associate a link with an item in TinkerCell, right click on it and choose "Add Link". This will bring up a search window with suggested parts. You can search for a phrase, a BioBrick ID, etc. You can also open parts in a browser to read more about them or confirm that you've found the right one. | + | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
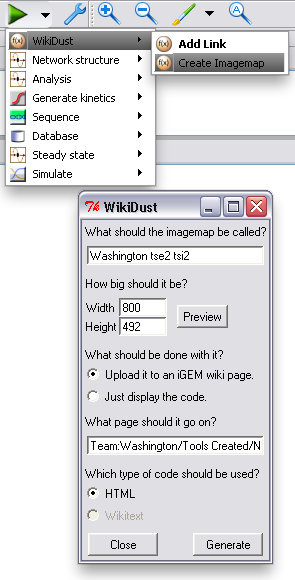
| - | After the model of your device or system is finished, and you've added all the links you want, you can upload a | + | After the model of your device or system is finished, and you've added all the links you want, you can upload a diagram of it to a webpage. Just choose "Create Imagemap" from the TinkerCell plugins menu, and change any options you want in the window that pops up. WikiDust will automatically handle uploading to the iGEM wiki, or it can just display code for you to copy and paste to another site. The diagram will be interactive; clicking an item will take you to the correct part page. In fact, [https://2010.igem.org/Team:Washington/Gram_Negative/Design#diagram our tse2/tsi2 diagram] was generated using WikiDust. |
<!-- [[Image:uw_sauro_model_on_wiki.png|500px|left]] --> | <!-- [[Image:uw_sauro_model_on_wiki.png|500px|left]] --> | ||
<!--[https://2010.igem.org/Team:Washington/Gram_Negative/Design#diagram https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/4/44/Washington_Diagram_F2620_Tse2_Tsi2_2.png]--> | <!--[https://2010.igem.org/Team:Washington/Gram_Negative/Design#diagram https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/4/44/Washington_Diagram_F2620_Tse2_Tsi2_2.png]--> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | '''To start using WikiDust | + | |
| + | '''To start using WikiDust you’ll need the main TinkerCell program, as well as Python and Subversion. All three can be found on the [http://www.tinkercell.com/downloads-2 TinkerCell download page].''' | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
<span id="partsrobot"> | <span id="partsrobot"> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 71: | ||
==[[Image:partsrobot_banner.png|500px|center]]== | ==[[Image:partsrobot_banner.png|500px|center]]== | ||
| - | ====<center> | + | ====<center>Registry Submission Made Easy</center>==== |
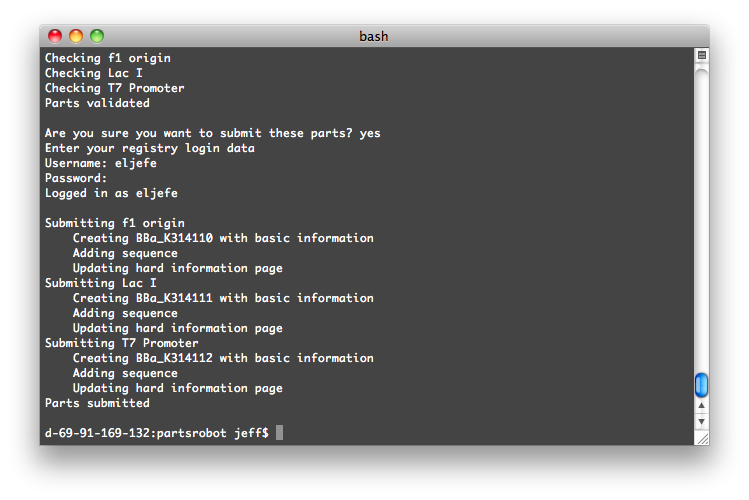
| - | + | PartsRobot is a command-line tool that can submit many parts to the [http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page Registry] at once. This makes it fast and easy to enter information about a series of similar parts—promoters of different strengths, variations on a protein, etc. | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 110: | Line 106: | ||
<code>python partsrobot.py submit yourspreadsheet.csv </code> | <code>python partsrobot.py submit yourspreadsheet.csv </code> | ||
| - | < | + | <font size=1> |
| - | + | (Exact command varies with OS and file locations. See the README for details.) | |
| + | </font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once launched, the program will log into the Registry and check your parts for syntax errors. After you give the go-ahead, it will submit them. Most of [[Team:Washington/Parts|our parts]] were submitted this way. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | ''' | + | '''You can download PartsRobot from the [http://sourceforge.net/p/partsrobot/home/ SourceForge page].''' |
<br clear=both> | <br clear=both> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<!---------------------------------------PAGE CONTENT GOES ABOVE THIS----------------------------------------> | <!---------------------------------------PAGE CONTENT GOES ABOVE THIS----------------------------------------> | ||
<div style="text-align:center"> | <div style="text-align:center"> | ||
'''← [[Team:Washington/Tools Created/New Vectors|New Vectors]]''' | '''← [[Team:Washington/Tools Created/New Vectors|New Vectors]]''' | ||
| | ||
| - | '''[[Team:Washington/Tools Used|Tools Used]] →''' | + | '''[[Team:Washington/Tools Used|Overview of Tools We Used]] →''' |
</div> | </div> | ||
{{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Footer}} | {{Template:Team:Washington/Templates/Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:31, 6 December 2010
Update 11/30/2010:
This page will be locked soon, so be sure to visit the [http://www.tinkercell.com/plugins/wikidust WikiDust] and [http://sourceforge.net/p/partsrobot/home/ PartsRobot] sites for more current information.
A Standard for Electronic Diagrams
Standard, unambiguous diagrams are central to communication in many established fields of engineering, but have not yet been widely adopted by synthetic biologists. Through the use of diagrams based on SBOL-visual ([http://bbf.openwetware.org/RFC.html#BBF_RFC_16:_Synthetic_Biology_Open_Language_Visual_.28SBOLv.29_Specification BBF RFC 16]) symbols, we hope to facilitate communication about synthetic DNA constructs between research groups. Usefulness of shared diagrams depends both on a standard set of symbols and on the method of distribution. Therefore the two main requirements for our proposed standard, [http://openwetware.org/wiki/The_BioBricks_Foundation:RFC#BBF_RFC_68:_Standard_for_the_Electronic_Distribution_of_SBOLv_Diagrams BBF RFC 68], are:
- The use of SBOLv symbols
- The linking of symbols to reference entry pages on the [http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page Registry of Standard Biological Parts] using http URLs
In the resulting diagram, the reader can click on portions which correspond to SBOLv symbols and read the reference information about that particular portion of the diagram. This makes research easier and promotes better part descriptions.
WikiDust is a plugin for TinkerCell, a computer-aided design tool developed here at the [http://www.washington.edu/ University of Washington]. WikiDust can be used to export diagrams of TinkerCell models to the iGEM wiki or other webpages. Our goal in creating WikiDust is to provide an easy way to share models and to encourage iGEM teams and researchers to describe their parts more completely. This, in turn, will help others reuse them in future projects.
One thing WikiDust does is provide a method to associate TinkerCell items, such as promoters or coding sequences, with parts on the Registry. The same mechanism could also be extended in the future to download reaction kinetics and other parameters from sources like the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20160009 Standard Virtual Parts Repository] or the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16381960 Biomodels Database]. For now though, it demonstrates the feasability of using the publicly available [http://www.sbolstandard.org Standard Biological Parts Knowledgebase (SBPkb)] to retrieve part information using Semantic Web standards.
To associate a link with an item in TinkerCell, right click on it and choose "Add Link". This will bring up a search window with suggested parts. You can search for a phrase, a BioBrick ID, etc. You can also open parts in a browser to read more about them or confirm that you've found the right one. Click "Use Selected" to choose one from the list, or enter your own link and click "Use Custom".
After the model of your device or system is finished, and you've added all the links you want, you can upload a diagram of it to a webpage. Just choose "Create Imagemap" from the TinkerCell plugins menu, and change any options you want in the window that pops up. WikiDust will automatically handle uploading to the iGEM wiki, or it can just display code for you to copy and paste to another site. The diagram will be interactive; clicking an item will take you to the correct part page. In fact, our tse2/tsi2 diagram was generated using WikiDust.
To start using WikiDust you’ll need the main TinkerCell program, as well as Python and Subversion. All three can be found on the [http://www.tinkercell.com/downloads-2 TinkerCell download page].
Registry Submission Made Easy
PartsRobot is a command-line tool that can submit many parts to the [http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page Registry] at once. This makes it fast and easy to enter information about a series of similar parts—promoters of different strengths, variations on a protein, etc.
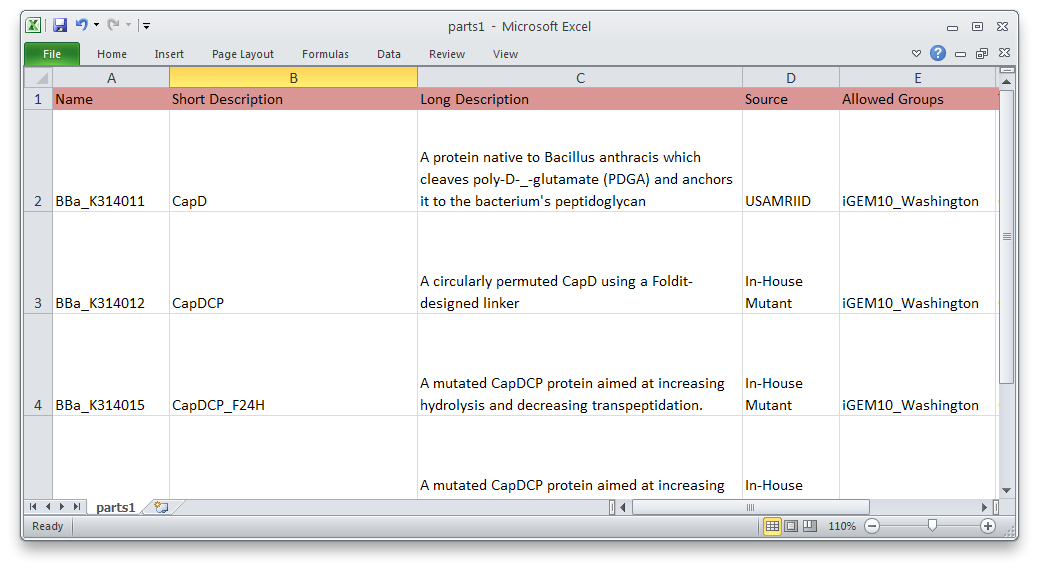
Using PartsRobot is simple. Just fill out the template spreadsheet with information about each part. Then, in a command prompt, type:
python partsrobot.py submit yourspreadsheet.csv
(Exact command varies with OS and file locations. See the README for details.)
Once launched, the program will log into the Registry and check your parts for syntax errors. After you give the go-ahead, it will submit them. Most of our parts were submitted this way.
You can download PartsRobot from the [http://sourceforge.net/p/partsrobot/home/ SourceForge page].
 "
"