Team:UTDallas/Results
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Results) |
(→Results) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Template:UTDallasMenu}} | {{Template:UTDallasMenu}} | ||
<span style="color:#EDE8E8"> | <span style="color:#EDE8E8"> | ||
| - | == | + | {{Template:UTDallasTop}} |
| - | + | {{Template:UTDallasMenu}} | |
| + | <span style="color:#EDE8E8"> | ||
| + | ===Results=== | ||
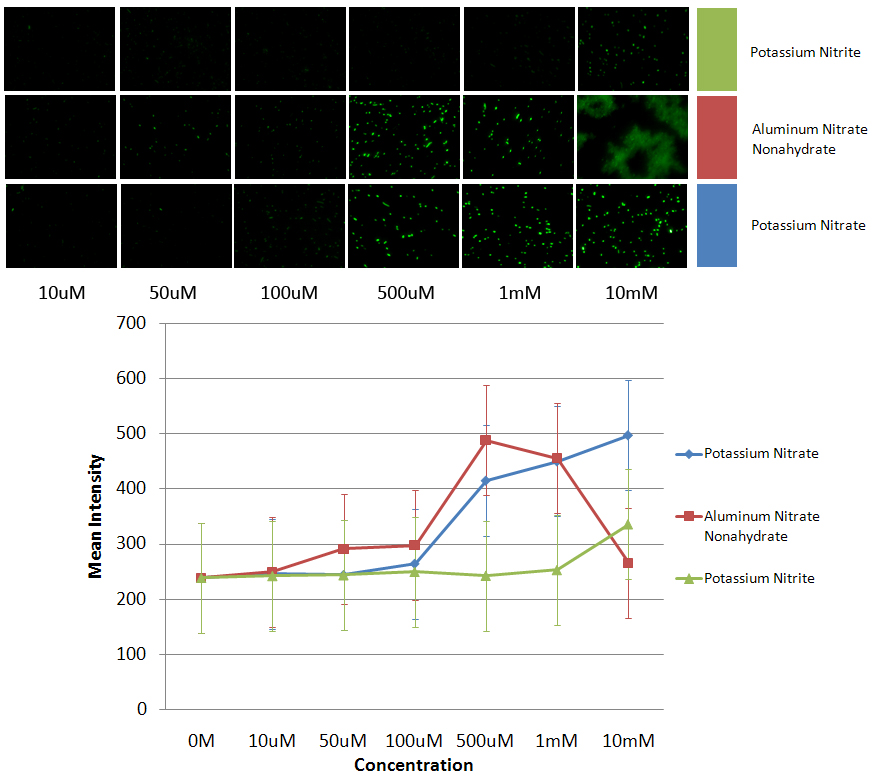
| + | *All images were taken with Olympus IX81 automated inverted microscope specially equipped for live cell imaging. All microscope images were taken from live DH5α E.coli cells. The filter sets we used are: 545/30x (excitation) and 620/60m (emission) filters for DsRed, 470/40x (excitation) and 525/50m (emission) for GFP. Data collection and processing was performed by the SlideBook software. | ||
| + | *The data was taken using cells that were grown overnight in 2mL of LB broth that had 50ug/mL of the appropriate antibiotic at 37C and 220rpm. This was used in a 1:50 dilution. Each sample had 40uL from the broth grown overnight and 2mL of the LB broth with the appropriate antibiotic. These were allowed to grow until a predetermined OD. Then the contaminants were added and the cells were allowed to grow for another 2 hours, before the images were taken. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *PyeaR+GFP (BBa_K412000) | ||
[[Image:Ver2.jpg | 650 px | center]] | [[Image:Ver2.jpg | 650 px | center]] | ||
| - | + | *The images shown are the images used to get the data. From left to right the image is the negative control to a 10mM concentration of the respective contaminants. The graph shows the average of all the maximum intensities of the cells in the image vs the concentration of nitrate/nitrite added to the sample. The data shows that PyeaR+GFP responds better to nitrates than nitrites. It also shows that the cell is more sensitive to aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, and therefore starts dying at a lower concentration. | |
| - | + | *PyeaR+RFP (BBa_K412001) | |
[[Image:Pyear_RFP.jpg | 650 px | center]] | [[Image:Pyear_RFP.jpg | 650 px | center]] | ||
| - | + | *The images and the graph are from PyeaR+RFP incubated with potassium nitrite. The graph is of the average of all the maximum intensities of the cells in the picture vs the concentration of nitrite added to the sample. We also took data from potassium nitrate and aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, but the cells were not responsive to these. | |
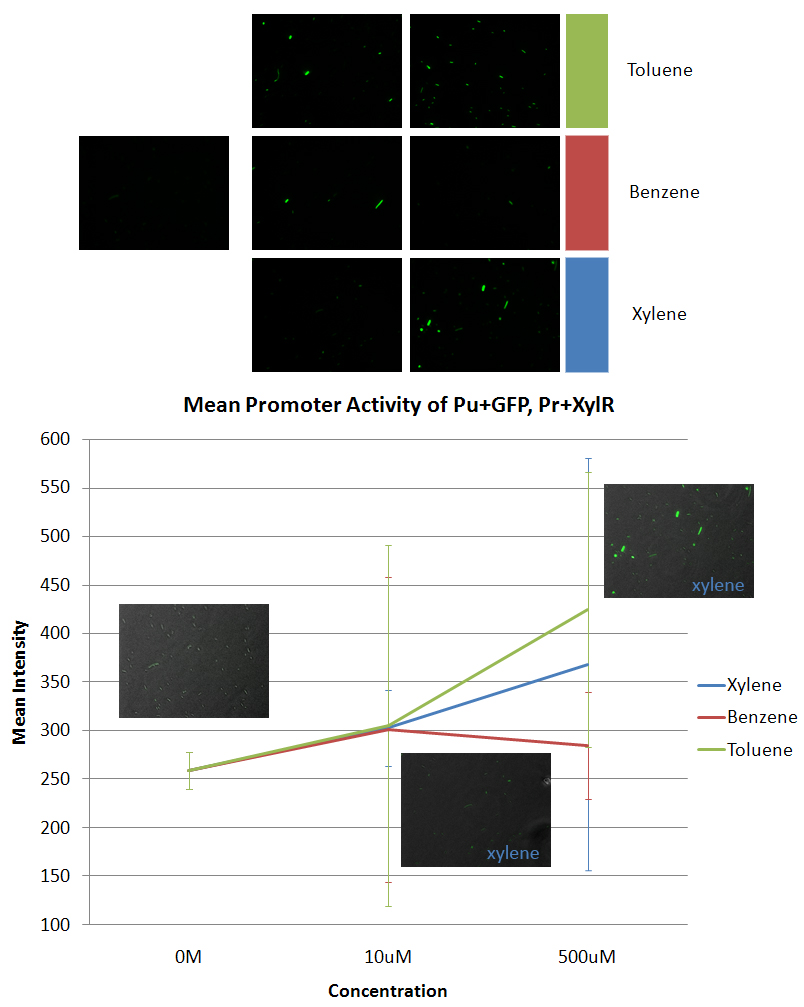
| - | + | *Pu+GFP (BBa_K270003) | |
[[Image:Pu_GFP.jpg | 650 px | center]] | [[Image:Pu_GFP.jpg | 650 px | center]] | ||
| + | *The data was taken using E. coli DH5α that was co-transformed with Pu+GFP and Pr+XylR. | ||
| + | *The leftmost image is the negative control. The other six images are the other concentrations (10uM and 500uM) in the specific aromatic: xylene, benzene, and toluene. The graph is of the average of all the maximum intensities of the cells in the picture vs the concentration of the aromatic added to the sample. We also took data from 10mM and 100mM concentrations of aromatics, but most of the cells died at these higher concentrations. | ||
Revision as of 02:01, 28 October 2010
Results
- All images were taken with Olympus IX81 automated inverted microscope specially equipped for live cell imaging. All microscope images were taken from live DH5α E.coli cells. The filter sets we used are: 545/30x (excitation) and 620/60m (emission) filters for DsRed, 470/40x (excitation) and 525/50m (emission) for GFP. Data collection and processing was performed by the SlideBook software.
- The data was taken using cells that were grown overnight in 2mL of LB broth that had 50ug/mL of the appropriate antibiotic at 37C and 220rpm. This was used in a 1:50 dilution. Each sample had 40uL from the broth grown overnight and 2mL of the LB broth with the appropriate antibiotic. These were allowed to grow until a predetermined OD. Then the contaminants were added and the cells were allowed to grow for another 2 hours, before the images were taken.
- PyeaR+GFP (BBa_K412000)
- The images shown are the images used to get the data. From left to right the image is the negative control to a 10mM concentration of the respective contaminants. The graph shows the average of all the maximum intensities of the cells in the image vs the concentration of nitrate/nitrite added to the sample. The data shows that PyeaR+GFP responds better to nitrates than nitrites. It also shows that the cell is more sensitive to aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, and therefore starts dying at a lower concentration.
- PyeaR+RFP (BBa_K412001)
- The images and the graph are from PyeaR+RFP incubated with potassium nitrite. The graph is of the average of all the maximum intensities of the cells in the picture vs the concentration of nitrite added to the sample. We also took data from potassium nitrate and aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, but the cells were not responsive to these.
- Pu+GFP (BBa_K270003)
- The data was taken using E. coli DH5α that was co-transformed with Pu+GFP and Pr+XylR.
- The leftmost image is the negative control. The other six images are the other concentrations (10uM and 500uM) in the specific aromatic: xylene, benzene, and toluene. The graph is of the average of all the maximum intensities of the cells in the picture vs the concentration of the aromatic added to the sample. We also took data from 10mM and 100mM concentrations of aromatics, but most of the cells died at these higher concentrations.
 "
"