Team:Uppsala-SwedenProject
From 2010.igem.org
Lovelyisland (Talk | contribs) (→Project Description:) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Uppsala}}<!--Do not remove the first and last lines in this page!--> | {{Template:Uppsala}}<!--Do not remove the first and last lines in this page!--> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== Project Description: == | == Project Description: == | ||
| Line 31: | Line 8: | ||
The concentration band detection mechanism makes use of a pair of of promoters with different efficiencies to detect the quantitative value of the input signal. | The concentration band detection mechanism makes use of a pair of of promoters with different efficiencies to detect the quantitative value of the input signal. | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Live clock.png|border|]] |
| - | + | ||
| + | [[Image:figure.jpg|600px|thumb|left|The interplay between the sender, the repressor and the receiver.]] | ||
== Band Detect: == | == Band Detect: == | ||
| + | |||
== Previous Work == | == Previous Work == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 26: | ||
The below diagram explains how we plan to use two sensitivity tuners in combination to get the band detect behaviour.The sensitivity tuners which detect different levels of the input signal will repress the output at levels below or above the band detect. | The below diagram explains how we plan to use two sensitivity tuners in combination to get the band detect behaviour.The sensitivity tuners which detect different levels of the input signal will repress the output at levels below or above the band detect. | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Modules1.png|800px|border|]] |
| - | == Proof | + | == Proof of Concept and Characterization: == |
| - | + | Generally speaking, there are two type of constructs to characterize: the sender system and the receiver system. The sender cells secrete AHL, causing the receiver cells to emit fluorescence in the designated band-detection fashion. In order to obtain a fully functional band detection sensor, it is vital to characterize each component by itself before putting together the entire system. | |
| + | |||
| + | The sender system can be characterized either quantitatively, in term of the amount of AHL it produces, or in a qualitative fashion, by checking its effect on a reporter construct. This reporter construct could be as easy as two parts consisting of a regulatory promoter coupled to a GFP-gene. The quantitative measurement involves usage of equipment from the analytical chemistry discipline, e.g. HPLC and mass-spectrometry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The receiver constructs can be characterized using commercially available AHL. AHL can be applied to receiver cell cultures with concentration gradient. Their fluorescence intensity can be measured. Using concentration gradient is also crucial to our original band-detection concept, as different receiver constructs should only react to AHL in certain concentration intervals. | ||
== References: == | == References: == | ||
| Line 58: | Line 41: | ||
2.Danino T, Mondragón-Palomino O, Tsimring L, Hasty J, A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks, 2010, Nature, Vol 463(7279): 301-2. | 2.Danino T, Mondragón-Palomino O, Tsimring L, Hasty J, A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks, 2010, Nature, Vol 463(7279): 301-2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. The iGEM Cambridge team 2009 Biobrick Characterisation | ||
| + | https://2009.igem.org/Team:Cambridge/Project/Amplification/Characterisation | ||
Latest revision as of 15:33, 27 October 2010



Project Description:
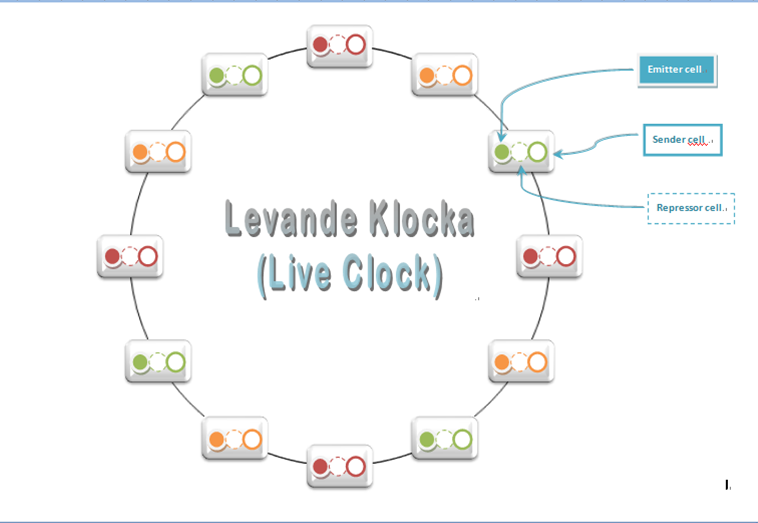
Our project for iGEM 2010 involves building a biological concentration band detection sensor and demonstrating its usefulness in building a bio-clock and color display unit.
The concentration band detection mechanism makes use of a pair of of promoters with different efficiencies to detect the quantitative value of the input signal.
Band Detect:
Previous Work
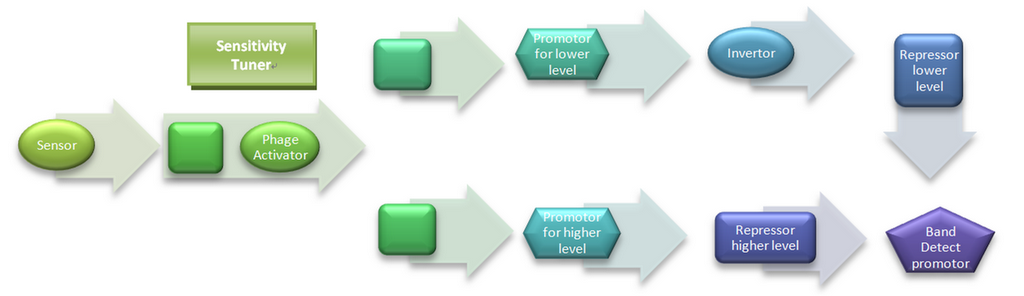
Being an engineering competition iGEM promotes building on previous projects.The Cambridge 2007 and 2009 teams built upon each other to produce the Sensitivity Tuner using phage activators and promoters.These Sensitivity Tuner's can detect different levels of a input signal and generate a corresponding output. You can find details of how the teams built and characterised their parts in the last years website.
Detecting specific Bands or concentration ranges
The sensitivity tuners do a pretty good job of detecting a signal above certain specific values each. However, they will still get activated when the next sensitivity tuner detects the input signal. For example, the construct [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_I746370 BBa_I746370] will start detecting at 0.85 uM while the construct [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_I746371 BBa_I746371] will start detecting at 0.92 uM. Both the constructs will detect the input signal at say 0.95 uM. Although this is good enough for detecting chemical concentrations, it will have to be able to detect specific bands to be able to perform concentration band specific actions.
The below diagram explains how we plan to use two sensitivity tuners in combination to get the band detect behaviour.The sensitivity tuners which detect different levels of the input signal will repress the output at levels below or above the band detect.
Proof of Concept and Characterization:
Generally speaking, there are two type of constructs to characterize: the sender system and the receiver system. The sender cells secrete AHL, causing the receiver cells to emit fluorescence in the designated band-detection fashion. In order to obtain a fully functional band detection sensor, it is vital to characterize each component by itself before putting together the entire system.
The sender system can be characterized either quantitatively, in term of the amount of AHL it produces, or in a qualitative fashion, by checking its effect on a reporter construct. This reporter construct could be as easy as two parts consisting of a regulatory promoter coupled to a GFP-gene. The quantitative measurement involves usage of equipment from the analytical chemistry discipline, e.g. HPLC and mass-spectrometry.
The receiver constructs can be characterized using commercially available AHL. AHL can be applied to receiver cell cultures with concentration gradient. Their fluorescence intensity can be measured. Using concentration gradient is also crucial to our original band-detection concept, as different receiver constructs should only react to AHL in certain concentration intervals.
References:
1.Basu S, Gerchman Y, Collins C.H, Arnold F.H, Weiss R, A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation, 2005, Nature, Vol 434, 1130-1134.
2.Danino T, Mondragón-Palomino O, Tsimring L, Hasty J, A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks, 2010, Nature, Vol 463(7279): 301-2.
3. The iGEM Cambridge team 2009 Biobrick Characterisation https://2009.igem.org/Team:Cambridge/Project/Amplification/Characterisation
 "
"