Team:Cambridge/Tools/microMeasure
From 2010.igem.org
(→Co-reporters) |
(→Co-reporters) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[Image:Cambridge-Coreporter.png|700px]] | [[Image:Cambridge-Coreporter.png|700px]] | ||
Applications of co-reporters include: | Applications of co-reporters include: | ||
| - | * Using one output as a control to check for biosensor viability | + | * Using one output as a control to check for biosensor viability, avoiding false negatives |
* Measuring two or more quantities concurrently, e.g. a number of different toxins | * Measuring two or more quantities concurrently, e.g. a number of different toxins | ||
{{:Team:Cambridge/Templates/footer}} | {{:Team:Cambridge/Templates/footer}} | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 26 October 2010

Real life isn't black and white

In every application of a biosensor it is useful to know the amount of the factor being measured. There are a numerous existing reporters. However to our knowledge there are none which are both affordable and quantitative. Some teams attempt to solve this problem by using a series of wells sensitive to increasing concentrations of the substance. But this requires a great deal of work to tune the sensors correctly.
We have already shown that the amount of the light produced by a bacterial culture can be assayed affordably with our E.glometer. Such devices could be mass produced lowering production costs further and distributed with the bacterial biosensors.
Co-reporters
It is often useful to have one cell measuring reporting two different outputs. Light is an effective means of achieving this, since it has different wavelengths which can be easily separated by inexpensive filters. The various coloured outputs that we have created would be useful tools for achieving this.
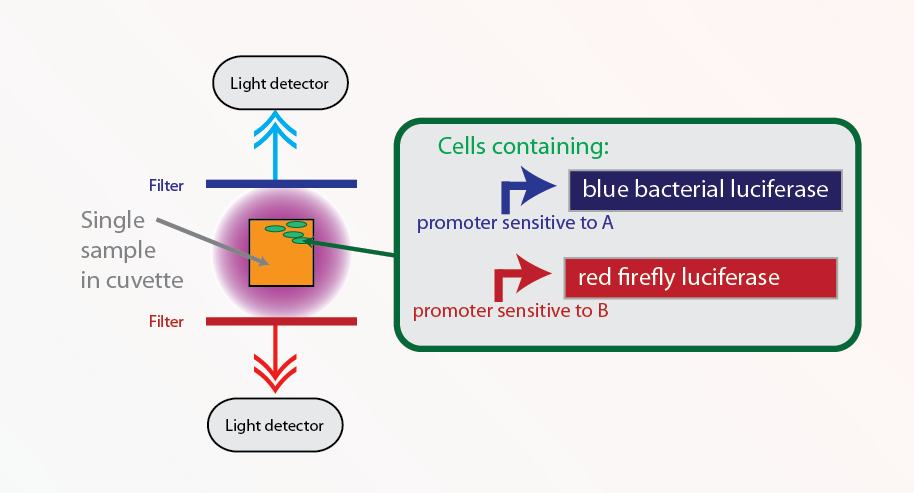 Applications of co-reporters include:
Applications of co-reporters include:
- Using one output as a control to check for biosensor viability, avoiding false negatives
- Measuring two or more quantities concurrently, e.g. a number of different toxins
 "
"
