Team:Heidelberg/Modeling
From 2010.igem.org
(→Modeling of binding site efficiency) |
(→Neural Network theory) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Neural Network Model=== | ===Neural Network Model=== | ||
====Neural Network theory==== | ====Neural Network theory==== | ||
| + | Artificial Neural Network usually called (NN), it is a computational model that is inspired by the biological nervous system. The network is composed by simple elements called artificial neurons that are interconnected and operate in parallel. In most cases the NN is an adaptive system that can change its structure depending on the internal or external information that flow into the network during the learning process. The NN can be trained to perform a particular function by adjusting the values of the connection (weights) between the artificial neurons. | ||
| + | During the learning process the difference between the desired output (target) and the network output is minimized. This difference is usually called cost; the cost function is the measure of how far is the network output from the desired value. A common cost function is the mean-squared error and there are several algorithms that can be used to minimize this function. | ||
| + | [[Image:/Users/ecristiano/Desktop/01_nnblk.gif]] | ||
| + | Figure 1: Normally Neural Networks are trained so that a particular input leads to a specific target output. | ||
| + | Neural networks have been trained to perform complex functions in various fields, including pattern recognition, identification, classification, speech, vision, and control systems. | ||
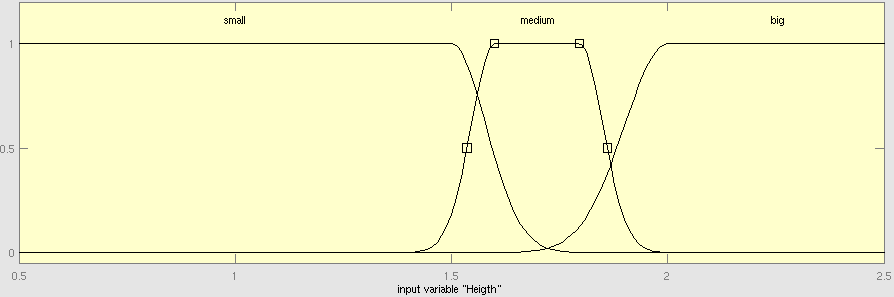
===Fuzzy Inference Model=== | ===Fuzzy Inference Model=== | ||
Revision as of 00:06, 25 October 2010

|
|
||||||||||||
 "
"