Team:TU Delft/Project/solubility/characterization
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Ptmvanboheemen (Talk | contribs)
(New page: =Characterization of the Solubility Parts= ==Emulsifier Production== The alna gene was induced when the culture reached a density of about 108 bacteria per mL. Bacterial and medium sample...)
Newer edit →
(New page: =Characterization of the Solubility Parts= ==Emulsifier Production== The alna gene was induced when the culture reached a density of about 108 bacteria per mL. Bacterial and medium sample...)
Newer edit →
Revision as of 13:59, 8 September 2010
Characterization of the Solubility Parts
Emulsifier Production
The alna gene was induced when the culture reached a density of about 108 bacteria per mL. Bacterial and medium samples were taken for sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-gel electrophoresis to monitor AlnA production. The results shown in Fig. ? indicate that expression of AlnA begins ? min after induction and peaks after ? h.
Emulsifier Assay
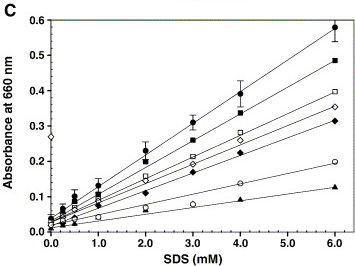
Calibration graph showing a linear increase in absorbance at 660 nm for increasing concentrations of SDS (●). Under the standard detergent assay conditions, various components like 200 mM NaCl (□), 2.0 mM CaCl2 (♦), 10% glycerol (■), 100 μg microsomal membranes (open diamond), 0.2 mM Triton X-100 (▲) and 2.5 mM CHAPS (○) were added and the turbidity was measured. Error bars represent the deviation from five independent experiments and each one performed in duplicate. Rajakumari et al (2006) Biochemical and Biophysical Methods
 "
"