Team:TU Delft/Project/alkane-degradation/results
From 2010.igem.org
(→Resting cell assays) |
(→ALDH) |
||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
We called this protocol "the last resource" because the others didn't work. Which means that alcohols and aldehydes do not cross the cell membrane, thus in order to grow cell on these compounds as sole carbon sources... WE NEEDED TO ADD TRANSPORTERS =( | We called this protocol "the last resource" because the others didn't work. Which means that alcohols and aldehydes do not cross the cell membrane, thus in order to grow cell on these compounds as sole carbon sources... WE NEEDED TO ADD TRANSPORTERS =( | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====BBa_K398030 and BBa_K398029==== | ||
| + | Both Biobricks are the protein generators of Bt-ALDH. We compared the activities of bot parts, parental strain with an empty plasmid (J13002) and a natural oil-degrader (Pseudomonas putida). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TU_Delft_ALDH_comp.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | View [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K398029 BBa_K398029 in the '''parts registry'''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Specified Components''' | ||
| + | <partinfo>K398029 SpecifiedComponents</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Designer:''' <partinfo>K398029 Designer</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Status:''' <partinfo>K398029 Status</partinfo> | ||
| + | <html><span style="clear:both;display:block;width:100%;"></span></html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | View [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K398030 BBa_K398030 in the '''parts registry'''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Specified Components''' | ||
| + | <partinfo>K398206 SpecifiedComponents</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Designer:''' <partinfo>K398030 Designer</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Status:''' <partinfo>K398030 Status</partinfo> | ||
| + | <html><span style="clear:both;display:block;width:100%;"></span></html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/0/00/TU_Delft_project_navigation.jpg" usemap="#projectnavigation" border="0" /></center><map id="projectnavigation" name="projectnavigation"><area shape="rect" alt="Characterization" title="" coords="309,3,591,45" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/alkane-degradation/characterization" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Results" title="" coords="609,3,891,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/alkane-degradation/results" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Parts" title="" coords="9,3,290,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/alkane-degradation/parts" target="" /></map></html> | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/0/00/TU_Delft_project_navigation.jpg" usemap="#projectnavigation" border="0" /></center><map id="projectnavigation" name="projectnavigation"><area shape="rect" alt="Characterization" title="" coords="309,3,591,45" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/alkane-degradation/characterization" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Results" title="" coords="609,3,891,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/alkane-degradation/results" target="" /><area shape="rect" alt="Parts" title="" coords="9,3,290,44" href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:TU_Delft#page=Project/alkane-degradation/parts" target="" /></map></html> | ||
Revision as of 21:36, 25 October 2010

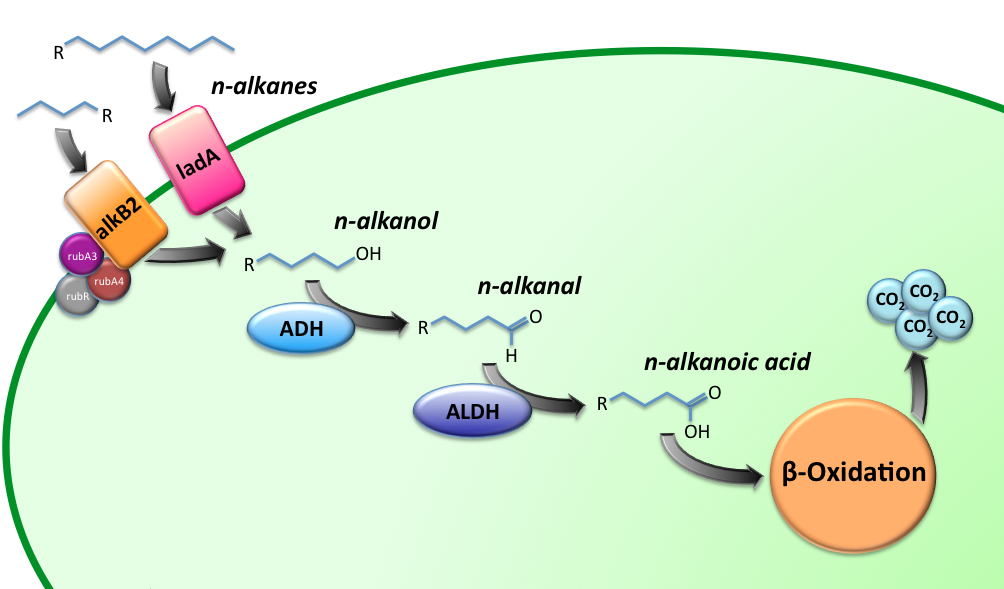
Alkane Degradation Results & Conclusions
Alkane hydroxylase (AH) system
LadA
Alcohol DeHydrogenase (ADH) system
= Results
Growth on alcohols as sole carbon source
- As we described before, we tried to grow our strain Escherichia coli 018A (Biobrick BBa_K398018 on the plasmid pSB1A2) on the alkanols Octanol-1 and Dodecanol-1. No growth was observed after 48 hours. We abandoned this experiment after this result.
Resting cell assays
- We grew Escherichia coli 018A and Escherichia coli negative control (Biobrick BBa_J13002 on plasmid pSB1A2 ) in 50 mL of M9 medium with glucose and CAS aminoacids.
| Strain | O.D. |
| J13002 | 0.327 |
| 018A | 0.338 |
- The cells were harevested when the O.D. at 600nm was around 0.3; they were spun down at 4000 rpm, for 10 min at 4ºC.
- The pellet was resuspended in 5 mL of phosphate buffer with glucose and salts. This was a washing step, then the cells were spun down again (same conditions) and resuspended in the same amount of phosphate buffer.
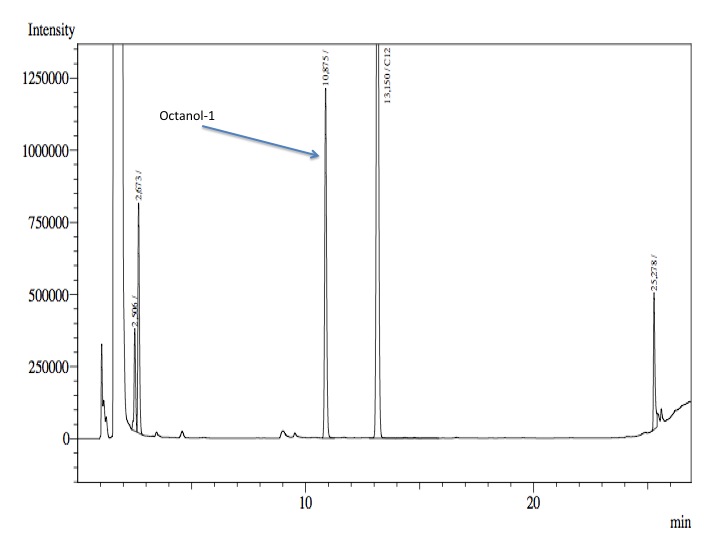
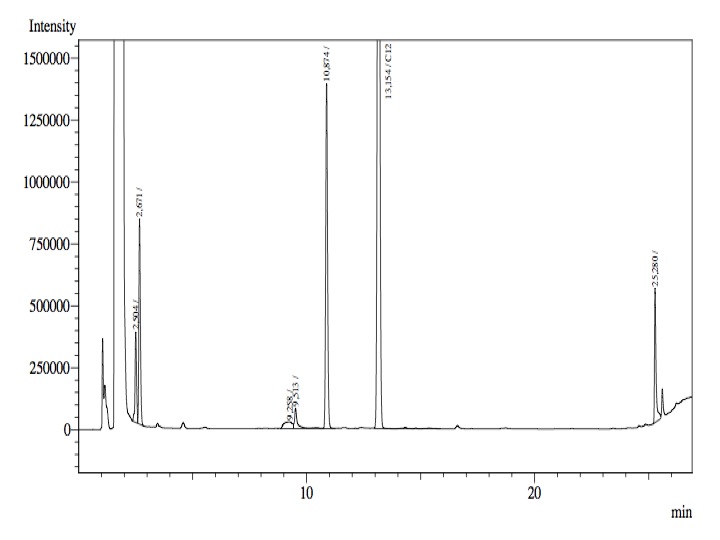
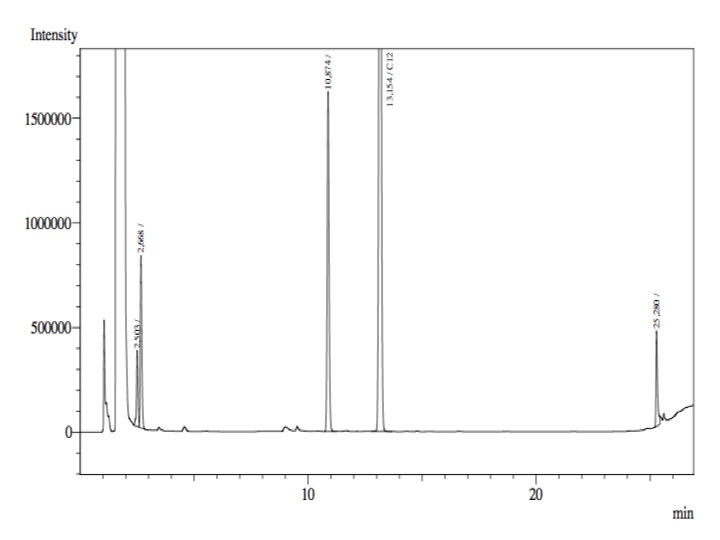
- Finally, from the cellular suspension it was used 1 mL; 4 mL of fresh phosphate buffer with glucose and salts were added and 100 nmol of Octanol-1.
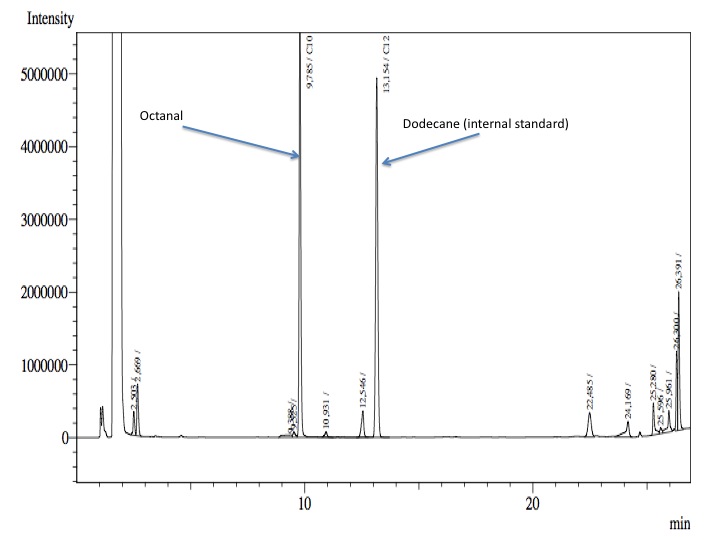
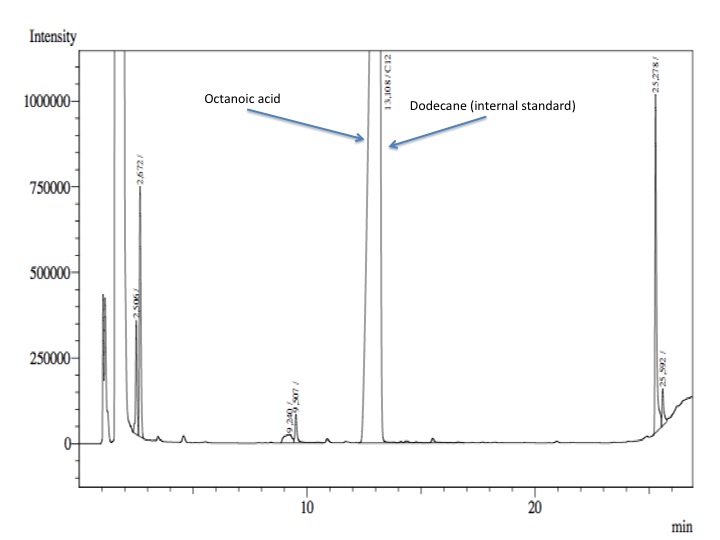
- After an overnight incubation at 37ºC, the organic phase was extracted using 3 mL of ethyl acetate (dodecane was used as internal standard). We tried to determine production of alkanals or alkanoic acids by Gas Chromatography measurements. The chromatograms are shown below:
- According to our results there was no degradation of octanol-1 ='( , after this experiment the protocol was abandoned. We think that the cells lack of transporters for long-chain alcohols, we preferred to check the cell extract in order to know if there was any biological activity in the cytoplasma.
NADH production in cell extracts
We called this assay: THE LAST RESOURCE =s
Basically, we grew cells until an O.D. (600nm) between 0.5-1.0. We needed chubby healthy happy exponential-growth cells because most of our constructions are meant for protein production in this growth phase.
Once, we got a lot of cells... we disrupted them by sonication and we analyze the NADH production by their guts using a simple spectrophotometrical analysis. If our parts are working, we should see a higher NADH production when the substrate (dodecanol-1 or dodecanal) to the buffer with microbial guts and NAD buffer. We can use this method because NAD is the natural co-factor of our proteins. Fortunately for us, NAD reduction could be easily quantified by absorbance measurements at 340 nm.
We called this protocol "the last resource" because the others didn't work. Which means that alcohols and aldehydes do not cross the cell membrane, thus in order to grow cell on these compounds as sole carbon sources... WE NEEDED TO ADD TRANSPORTERS =(
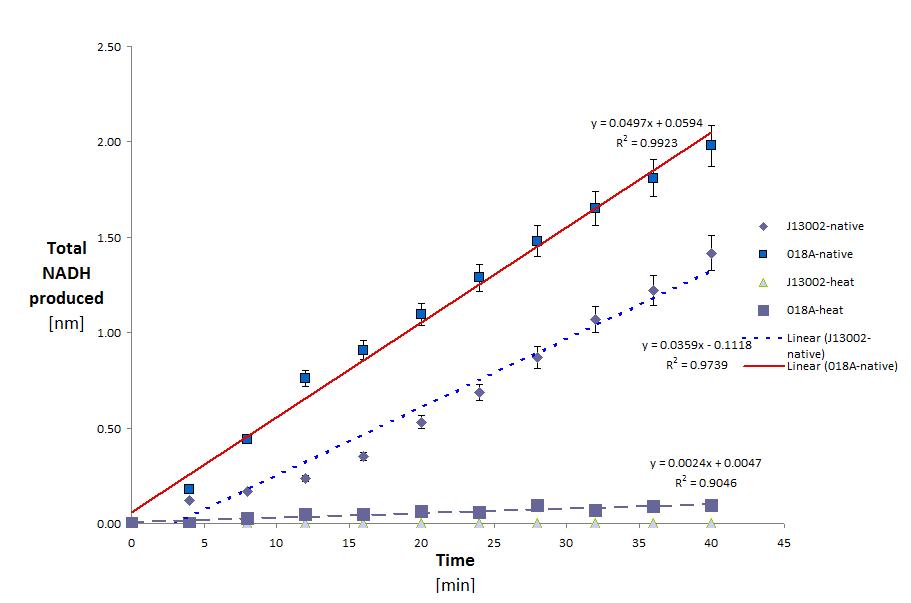
ADH was tested with Dodecanol (C12)
This yielded the following results:
| Conditions | Native | Native | Heated | Heated |
| Sample | J13002 | K398018 | J13002 | K398018 |
| Total protein in well | 3.303E-02 | 3.180E-02 | 7.351E-03 | 7.994E-03 |
| Specific activity (kat/mg) | 1.812E-11 | 2.606E-11 | 0.000E-00 | 5.041E-12 |
Conclusions
This shows two things. That E.Coli is partly able to degrade Dodecanol on it's own. And that this activity is greatly increased (43.83% normalized for the amount of protein) with the addition of the ADH gene. It is also clear that eventhough ADH is from a thermophilic organism it loses most (63.5%) of it's activity after heating. the raw data for these calculations can be seen below. (Although this decrease in activity could also be attributed to the host organism lacking the proper post translational modifications.)
ALDH
Growth on alcohols as sole carbon source
As in the case of alkane monooxygenases, our first attempt was to grow our recombinant strains on long-chain alcohols and aldehydes; hoping that E. coli will do the further degradation steps. For that purpose, we used octanol-1 and dodecanol-1 for the ADH system; whereas we used octanal and dodecanal for the ALDH system. If everything goes well, we should see microbial growth on minimal medium with these compounds as sole carbon source.
Resting cell assays
Our second attempt was to grow cells, until the exponential phase is reached; then the cells were collected and the spent medium was changed for a buffer with glucose that lacked of N-source, this was done in order to avoid more biomass production. Additionally we added alcohols and aldehydes to the mixture, so that if our part is working they will be converted in other molecules: alcohols to aldehydes and aldehydes to alkanoic acids.
With this approach, we are hoping that the enzymes produced during the growth phase will remain inside the cells. The glucose added will serve for maintenance purposes and co-factor regeneration. If everything works well, there will be some nice peaks appearing on our GC analysis.
NADH production in cell extracts
We called this assay: THE LAST RESOURCE =s
Basically, we grew cells until an O.D. (600nm) between 0.5-1.0. We needed chubby healthy happy exponential-growth cells because most of our constructions are meant for protein production in this growth phase.
Once, we got a lot of cells... we disrupted them by sonication and we analyze the NADH production by their guts using a simple spectrophotometrical analysis. If our parts are working, we should see a higher NADH production when the substrate (dodecanol-1 or dodecanal) to the buffer with microbial guts and NAD buffer. We can use this method because NAD is the natural co-factor of our proteins. Fortunately for us, NAD reduction could be easily quantified by absorbance measurements at 340 nm.
We called this protocol "the last resource" because the others didn't work. Which means that alcohols and aldehydes do not cross the cell membrane, thus in order to grow cell on these compounds as sole carbon sources... WE NEEDED TO ADD TRANSPORTERS =(
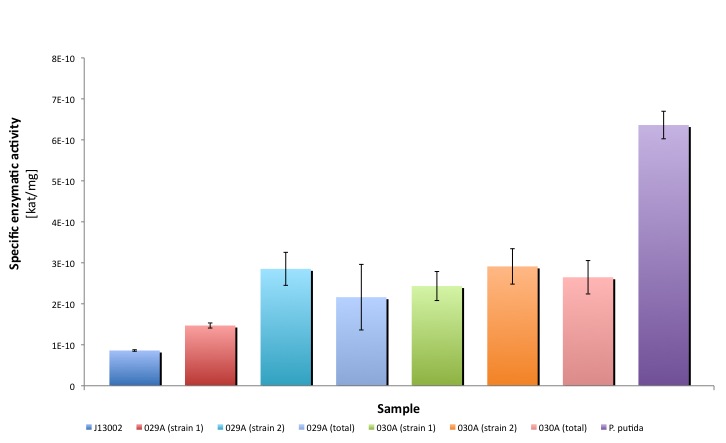
BBa_K398030 and BBa_K398029
Both Biobricks are the protein generators of Bt-ALDH. We compared the activities of bot parts, parental strain with an empty plasmid (J13002) and a natural oil-degrader (Pseudomonas putida).
View BBa_K398029 in the parts registry
Specified Components <partinfo>K398029 SpecifiedComponents</partinfo>
Designer: <partinfo>K398029 Designer</partinfo>
Status: <partinfo>K398029 Status</partinfo>
View BBa_K398030 in the parts registry
Specified Components <partinfo>K398206 SpecifiedComponents</partinfo>
Designer: <partinfo>K398030 Designer</partinfo>
Status: <partinfo>K398030 Status</partinfo>

 "
"