Team:ETHZ Basel/Modeling
From 2010.igem.org
Modeling & Information Processing Overview
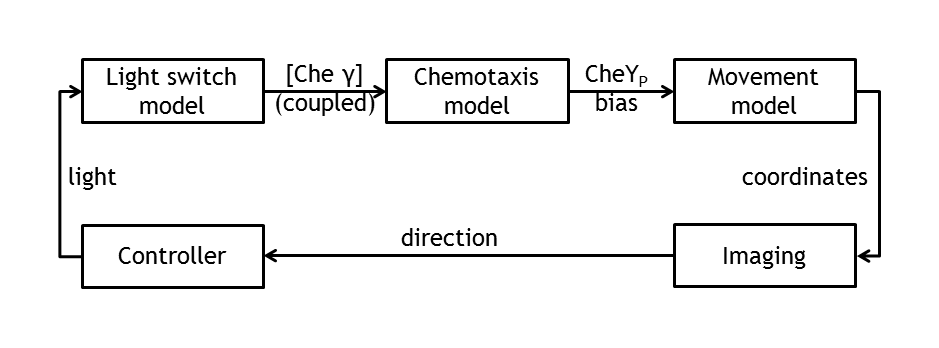
ETHZ’s project, E-Lemming, aims to modify the chemotaxis property of E.coli such that, instead of response to a chemical attractant/repellent, the bacterium responds to a light stimulus (phototaxis). Furthermore, this light sensitivity is used to control E.coli’s movement by deciding, at any given time, which type of motion will our ‘Lemming – in – disguise’ adopt (tumbling or straight run). This leads to a controllable E.coli, which can follow any pre – defined spatial path/maze/game, as a result of the combination of tumbling and going straight. The bacterium colony is imaged and, by image processing, the position of a single tracked cell is inferred. By activating a light switch, the user decides whether the bacterium should continue running or should change direction.
In the theory world, the steps we are following in mindlessly driving E.coli to our pre - defined target are the following:
• deterministic (ODE) & stochastic models of the chemotaxis pathway (documented from the literature)
• model of the movement of E.coli (built on the information of the pathway derived from the molecular models)
• control algorithms ( built on the user’s desire to play around with E.coli)
• image tracking & image processing algorithms
• java applications/movies of the E.Lemming (the fun part)
Model coupling
Besides the in vivo setup allowing the steering of a single Escherichia coli cell, the whole setup will be modeled. This allows us the testing of the cell detection & tracking as well as the design of the control algorithm in order to start verifying the different biological constructs and to record the successful control of bacterial movement.
 "
"