Team:USTC/Project/shell/empty
From 2010.igem.org
EMPTY ORGANELLE ASSEMBLY
… (This part will be uploaded later)…
We also designed a standard for our Proteinaceous Artificial Organelles Platform, which allows scarless protein fusion. RFC53 standard involves SacI, SapI, EarI, bglII and several other restriction endonucleases besides these endonucleases selected by RFC10. Compatible with RFC10 standard, the RFC53 standard provide an advanced way for parts assembly, especially in protein fusion.
 [Image:EarI.png|EarI]
[Image:sacI.png|SaciI]
[Image:sapI.png|SapI]
[Image:EarI.png|EarI]
[Image:sacI.png|SaciI]
[Image:sapI.png|SapI]
To construct a backbone plasmid of RFC53, a “meta-prefix” and a “meta-suffix” are added between the original prefix and suffix of plasmid pSB1C3 (as ??????? shown). Moreover, an EarI site in pSB1C3 is also mutated to avoid unexpected incision in the plasmid. The new plasmid (named pSB1C7) has an extensive affix as shown below: (From 5’ to 3’)
From above description, we can learn that the cleavage sites of EarI does not overlap their recognition sites. After the digestion by EarI, a 3 bp cohesive end composed of any sequence designed by user will be formed, whose length just fit to one coden. There is a EarI cleavage site in each end of the insert part, so that the start codon (must be modified to “ATG” if not) and a 3’ end (must be modified to be “GGT” if not) will be exposed as cohesive ends for subsequent ligation. Moreover, these two cleavage sites can also be cut separately: When digested by SapI, the 5’ EarI recognition site will be destroyed; the BglII site in 3’ EarI recognition site is designed to perform an analogous function. There is another restriction site of SapI, whose restriction site is at the same location with 5’ EarI site, allowing cleavage at 5’ EarI site separately without BglII digestion. These characters permit a flexible strategy of assembly. The following is an introduction to Metaparts Assembly Strategy, the most frequently used strategy in RFC53 standard.
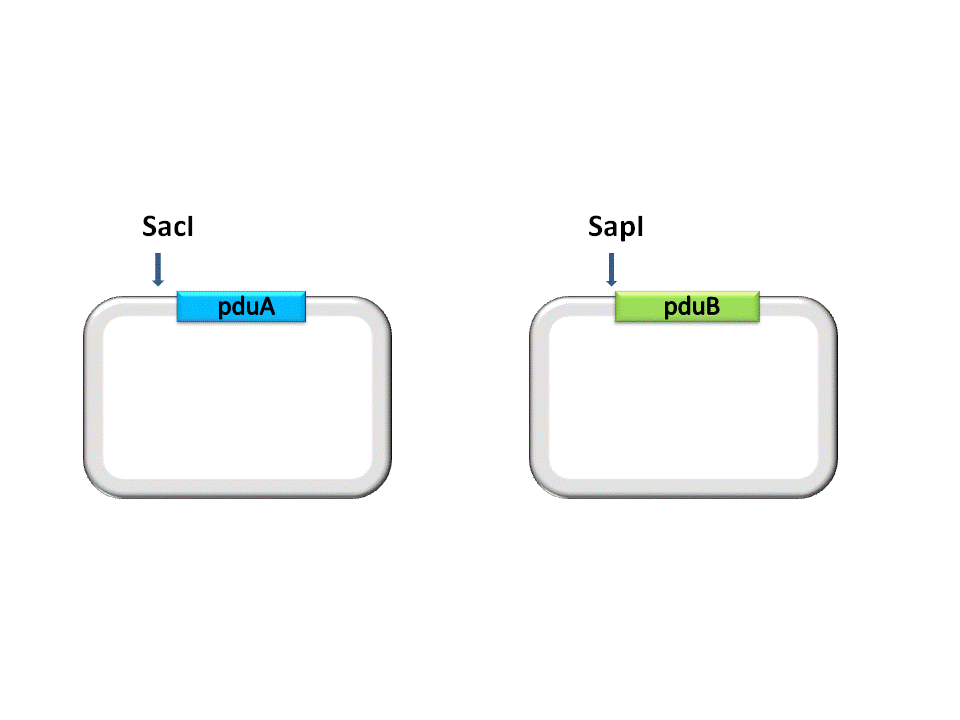
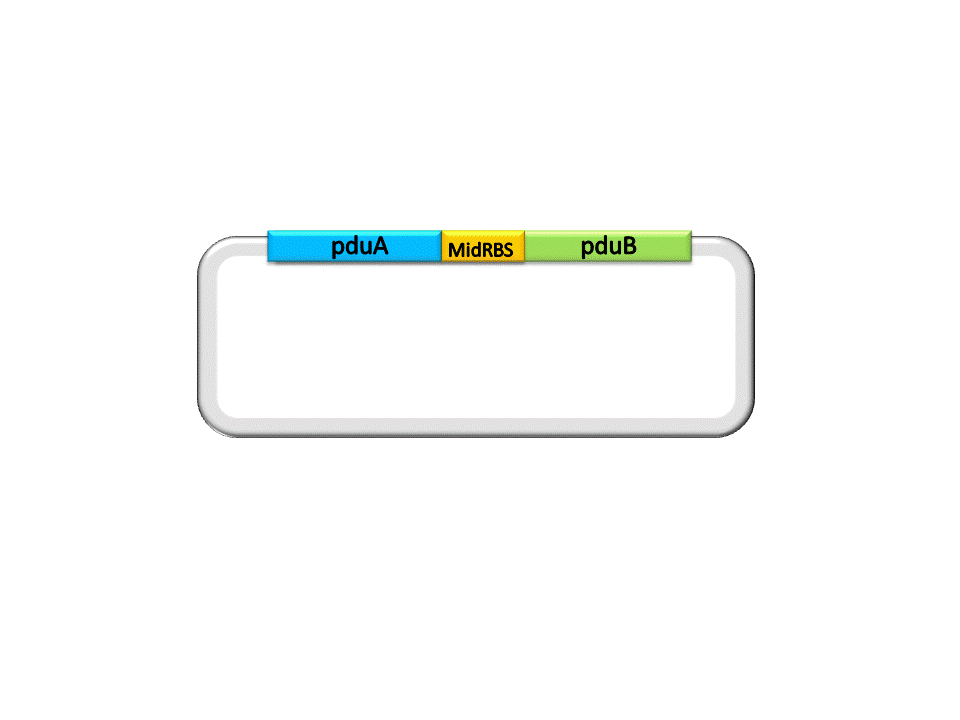
Take the assembly of pduA and pduB for instance. Different from RFC10 assembly, the digestion of RFC53 assembly is divided into two steps. For the Insert Plasmid, the purpose of the first step is to break the 5’ recognition site of EarI. And SapI should be used to cut the Vector Plasmid.
(Figure 1. here) (Figure 2. here)
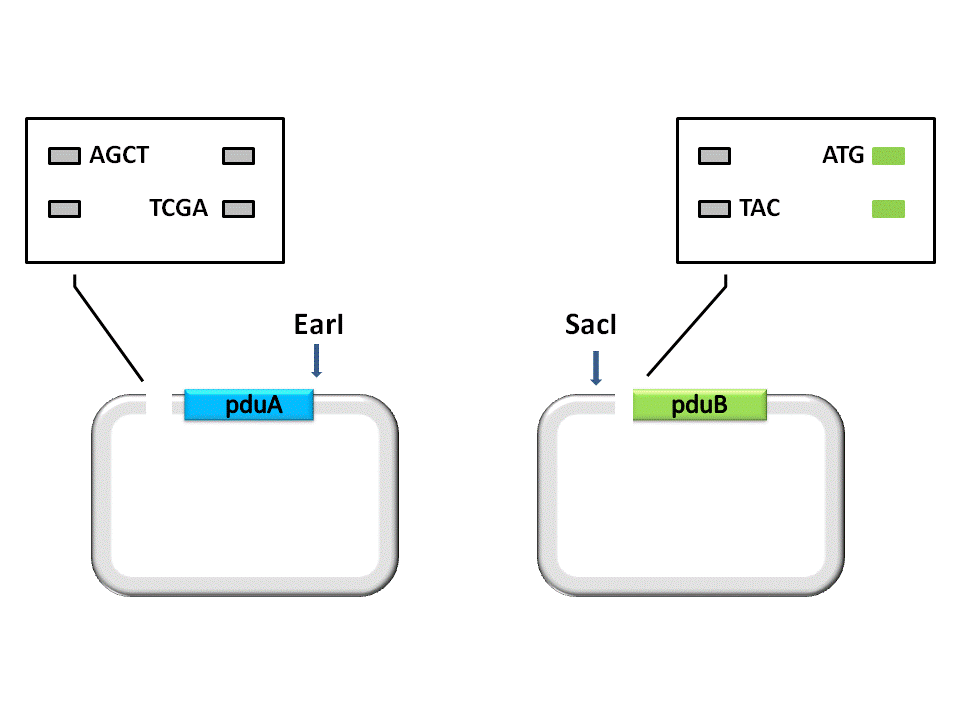
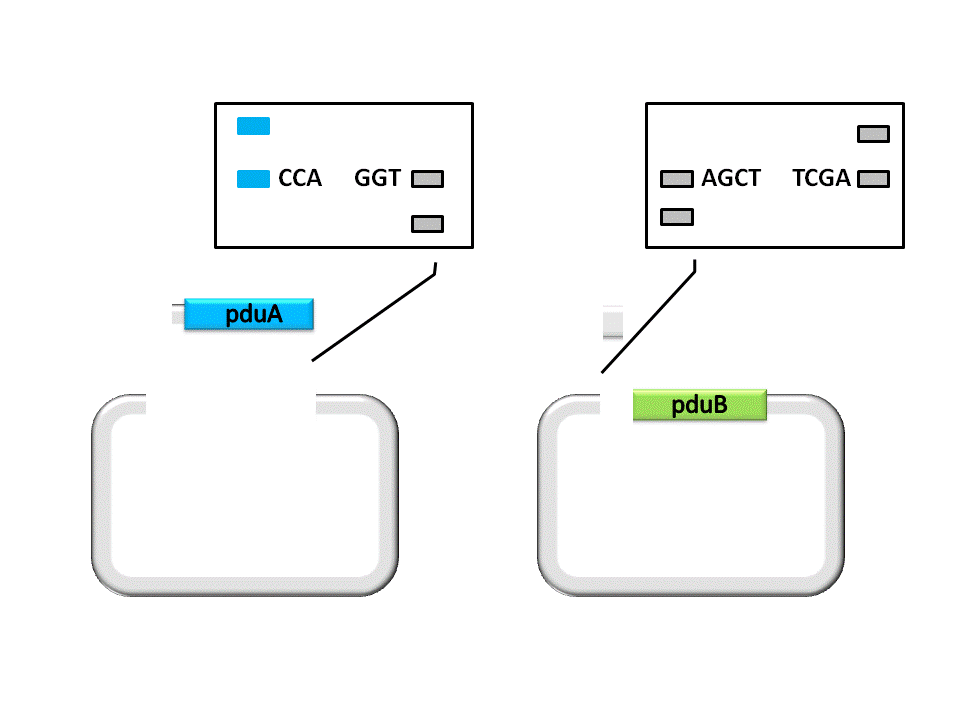
As shown in the figure ??????, the Insert, pduA, is cut off with a SacI cohesive end at 5’, and a EarI cohesive end(CCA) at 3’. The Vector, pduB, get a SacI cohesive end at 3’ (complementary with the 5’ end of pduA), as well as a EarI cohesive end(ATG).
(Figure 3. here)
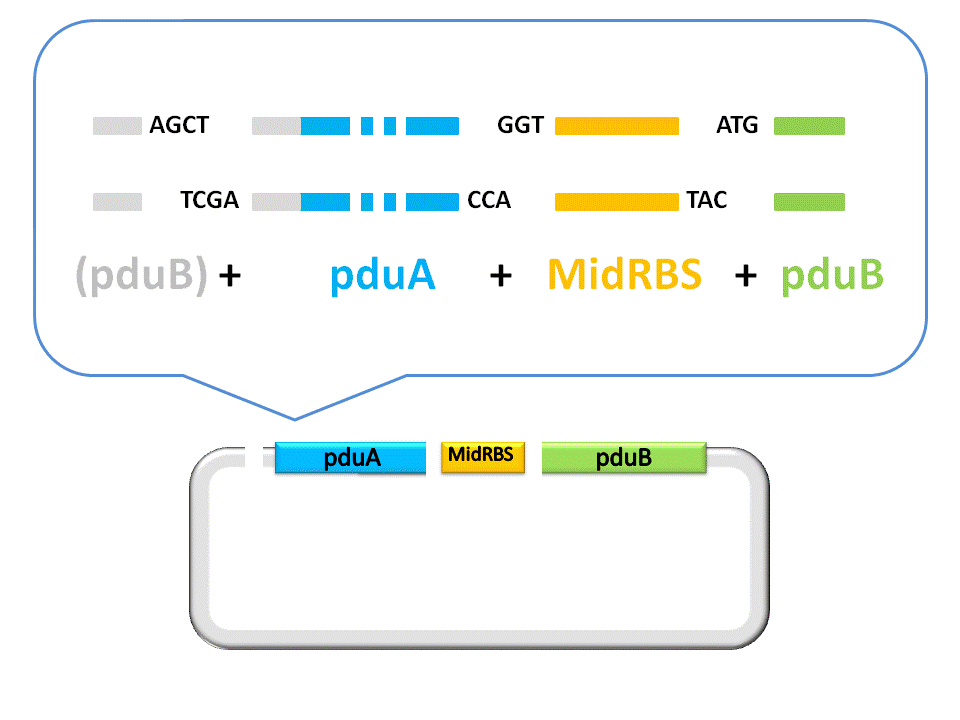
An linker segment with cohesive ends should be added for the ligation of Insert and Vector. The linker is designed to bridge the gap between the insert segment and the vector, as well as provide a new RBS for pduB, since its former RBS will be connected to pduA after ligation.
(Figure 4. here)
Finally, the assembly of pduA and pduB is accomplished by ligase under the right conditions. To see more details about RFC53 standard, please visit the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/The_BioBricks_Foundation:RFC#BBF_RFC_53:_USTC_MetaPart_Assembly_Standard_--_Extending_RFC_10_to_Enable_Scarless_Protein_Fusion_with_Type_IIS_Restriction_Enzyme_EarI_and_SapI BBF RFC 53] at OpenWetFare.
 "
"