Team:Kyoto/HumanPractice
From 2010.igem.org
HumanPractice
Abstract
iGEM Kyoto suggested "Human Practice iGEM Japan" project to other iGEM teams in Japan. And 5 universities (including Kyoto) paticipated in this project. We lead the project, and successfully we have gotten over 1500 answers! According to the result, we revealed the difference between student and the other and that Japanese expect biotechnology, on the other hand they worry about it safety.
Introduction
This year, we iGEM Japan carried out ”iGEM Japan Human Practice” suggested by iGEM Kyoto. In this project, we drove an attitude survey on genetic engineering and biotechnology cooperating with one another. We attempted to recognize the current situation, and we will take advantage of this result for future human practice activities.
Motivation
According to previous teams' results of human practice activity, which was a survey with questions about genetic engineering, more Japanese people chose "negative" or "neutral" than the other nationalities [1]. In addition, it is often said that many Japanese people hate or avoid genetically modified food [2]. We are interested in this tendency. Thus, we attempted to indicate the reason why many Japanese people have a negative impression on genetic engineering. We made a questionnaire below, asking about the impressions on genetic engineering and words related to iGEM, or Synthetic biology.
Advantages
- By cooperating with several teams to share some steps of human practice activities, we can not only reduce the burden but also improve the quality of the survey result with rich amount of samples.
- We can lead more attention from mass-media by driving this activity as iGEM Japan, than as one university team. This will be a great help for many purposes, such as announcing the activities of iGEM, inviting sponsors, or further human practice activities.
- This project will be a good opportunity to deepen the relationships between each Japanese iGEMers. Actually, we are planning iGEM JAPAN project, which includes not only human practice activities but also construction of iGEM JAPAN Website, PR by magazines and participation in symposiums for example.
[ This is the common Introduction article of participating universities of “iGEM Japan Human Practice”(KIT-Kyoto, Kyoto, Osaka, Tokyo_Metropolitan, and UT-Tokyo). iGEM Kyoto has the responsibility for the wording. ]
Methods
Five out of the nine Japanese teams, KIT-Kyoto, Kyoto, Osaka, Tokyo_Metropolitan, and UT-Tokyo took part in this project. We all used paper-based questionnaire, but the places and terms are different depending on teams.
We conducted a survey from June 30 to September 26 in the places near the universities.
Targets, Terms, and Places
KIT-Kyoto
- Students
- July 12 - September 26 at Kyoto Institute of Technology University
- Others
- August 10 at Open Campus in Kyoto Institute of Technology University
Kyoto
- Students
- July 12 - September 26 at Kyoto University
- Others
- August 28, 29 at Masukata Shopping Street, Kyoto
- September 4 at Grace Tanaka, a supermarket, Kyoto
- September 11, 12 at Coop Shimogamo, Kyoto
Osaka
- Others
- August 10 at Osaka University from high school student or their parents
Tokyo_Metropolitan
- Students
- July 1 - September 26 at Tokyo Metropolitan University
- July 30 - September 26 (Tokyo_Metropolitan team member’s friends)
- Others
- June 30 - July 2 in BIO EXPO JAPAN (http://www.bio-expo.jp/en/Home/) at Tokyo.
- July 16 in Public Forum on Education Development Project at Tokyo Metropolitan University
- July 18, August 20 in Open Lab at Tokyo Metropolitan University
- September 18, 19 in Mitaka Science and Technology Fair at Tokyo
- August 7 - September 26 (Tokyo_Metropolitan team member's family and acquaintances)
UT-Tokyo
- Others (High School Students)
- July 31 at SEG, a cram school, Tokyo
Questionnaire
We made 2 similar kinds of questionnaire. One is "Attitude survey of genetic engineering" and the other is "Attitude survey of biotechnology." They are almost the same, but "Attitude survey of biotechnology" has a little different question from "Attitude survey of genetic engineering". We only changed the word "genetic engineering" of the survey for "biotechnology" in order to make "Attitude survey of biotechnology."
And we attempted to indicate difference of image between "genetic engineering" and "biotechnology".
Attitude survey of ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )
- When shopping, do you buy "not genetically modified food”?
- [ Always buy / Tend to buy / Hardly mind / Not mind / I have never seen such an indication ]
- What do you associate with ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )? (※Please encircle all that apply)
- [ Clone / GM crops (foods) / Patent / DNA / Genome / Medicine / Cosmetic / Bioethics / Virus / Artificial Life / Novel Prize / Environment / Biological weapon / iPS cells, ES cells / Biofuel / Biohazard / Others( ) ]
- If there is no difference in effectiveness, what do you think about using the drugs manufactured by ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )?
- [ Not mind I use / Hardly mind I use / If possible, I don't want to use / I must not use / I don't know ]
- What do you think of the artificial genetic mutation by ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )?
- [ Bad / Little bad / Little good / Good ]
- Which trend of information about ( genetic engineering or biotechnology ) is major, negative or positive?
- [ Negative / About the same degree / Positive / No idea ]
- Do you think Japan actively tackles on ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )?
- [ Yes / Partly yes / Not so much / No ]
- Do you think the research on ( genetic engineering or biotechnology ) should continue?
- [ Yes / No ]
- If you answered [Yes], please encircle every fit reason from below.
- Because it may be useful for food crisis.
- Because it may solve environmental problems.
- Because it may solve energy problems.
- Because it may be applied to medicine.
- Because it may create a business opportunity.
- Because it can be used in the preservation of the species.
- Because it symbolizes the development of science and technology.
- Because it has already been put to practical use in many countries.
- Because it has many possibilities.
- Because it is interesting as an academic subject or a research topic.
- Others( )
- If you answered [No], please encircle every reason from below.
- Because it can create evil things harmful to environment and humans.
- Because products of it can be harmful to ecosystem.
- Because products of it can be harmful to human body.
- Because it is unethical.
- Because people say it is dangerous.
- Because it can be applied to evil use.
- Because there are not enough laws governing it.
- Because it can be replaced by other technologies.
- Because it seems to have less potential than other technologies.
- Because I feel somehow uneasy in using it.
- Others( )
- Have you ever heard the word, "Synthetic biology"?
- [ Yes / No ]
[ This is the common Method article of participating universities of “iGEM Japan Human Practice”(KIT-Kyoto, Kyoto, Osaka, Tokyo_Metropolitan, and UT-Tokyo).iGEM Kyoto has the responsibility for the wording. ]
Results
We drove this survey from July to September 26th.
All data: HumanPractice.xls
Our result is too much to write all on this page. So we write only graphs on this page and upload all result data. We analyzed mainly following points.
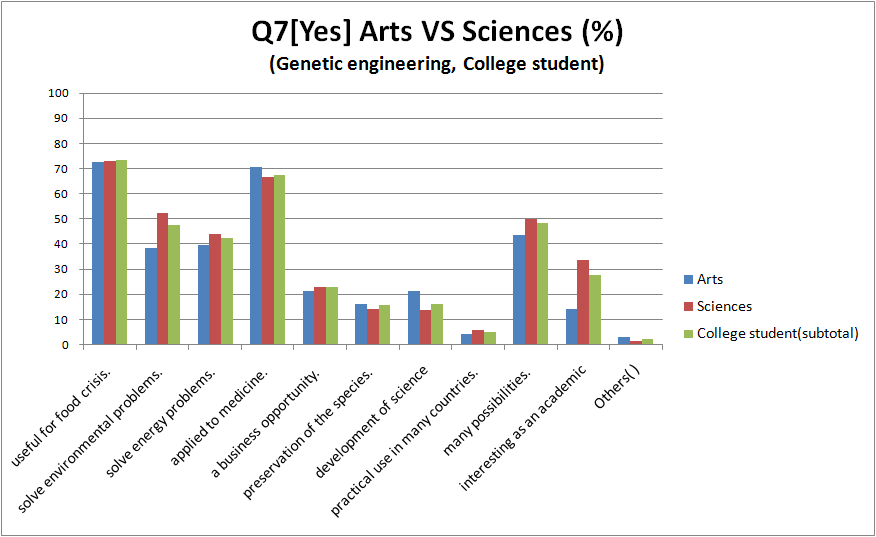
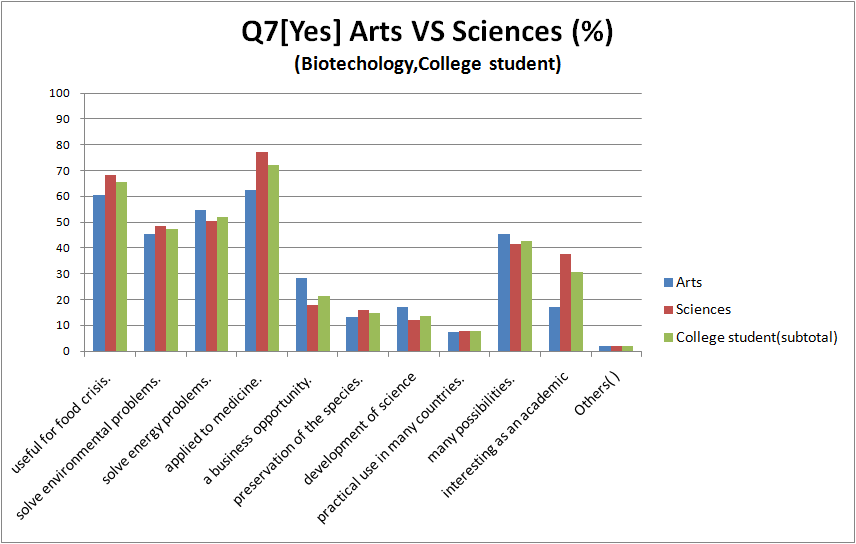
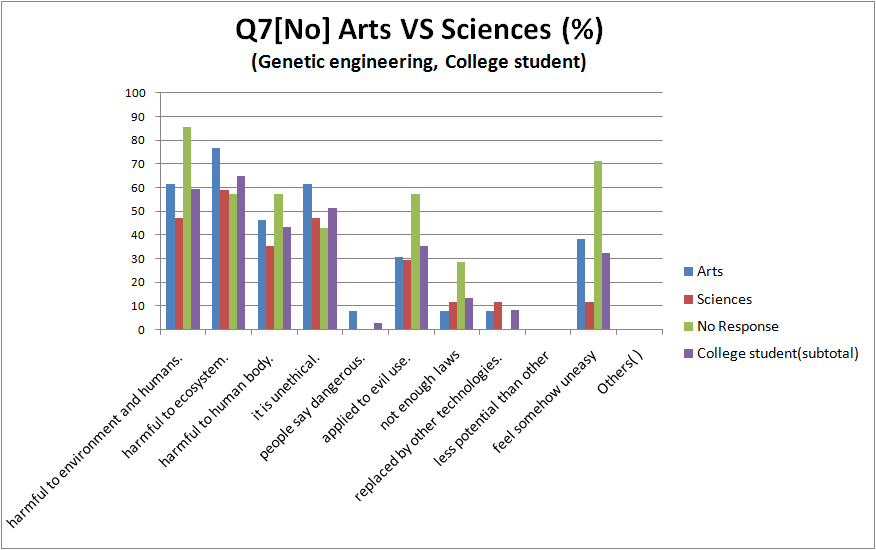
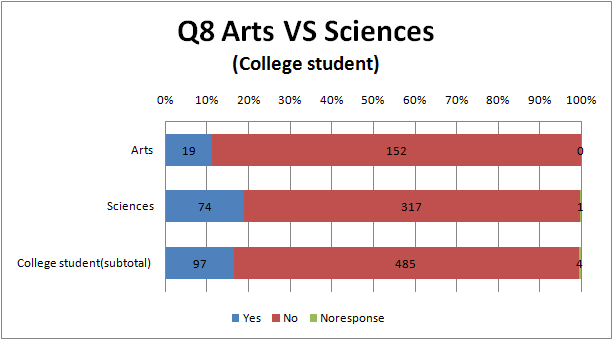
- compare between arts and science(*) in college student
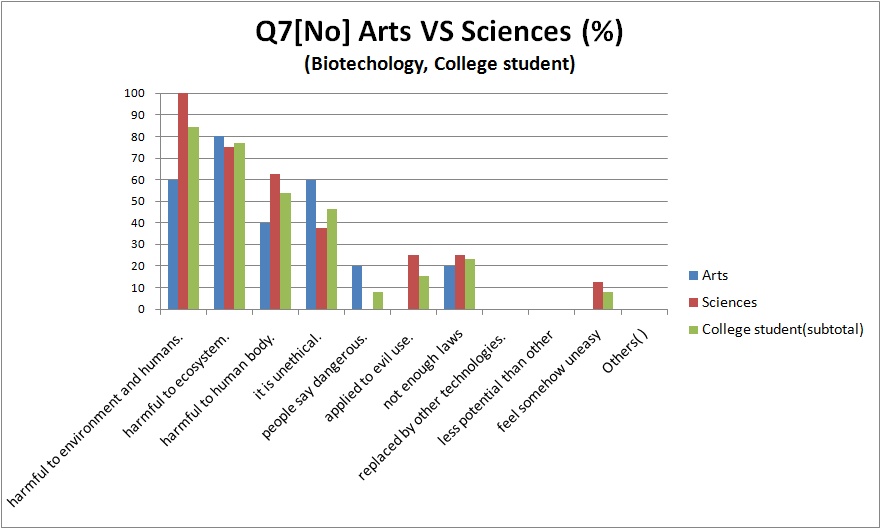
- compare with "genetic engineering" and "biotechnology"
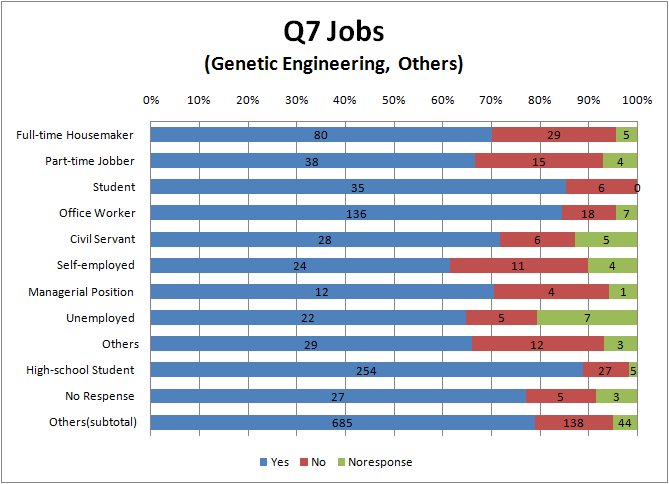
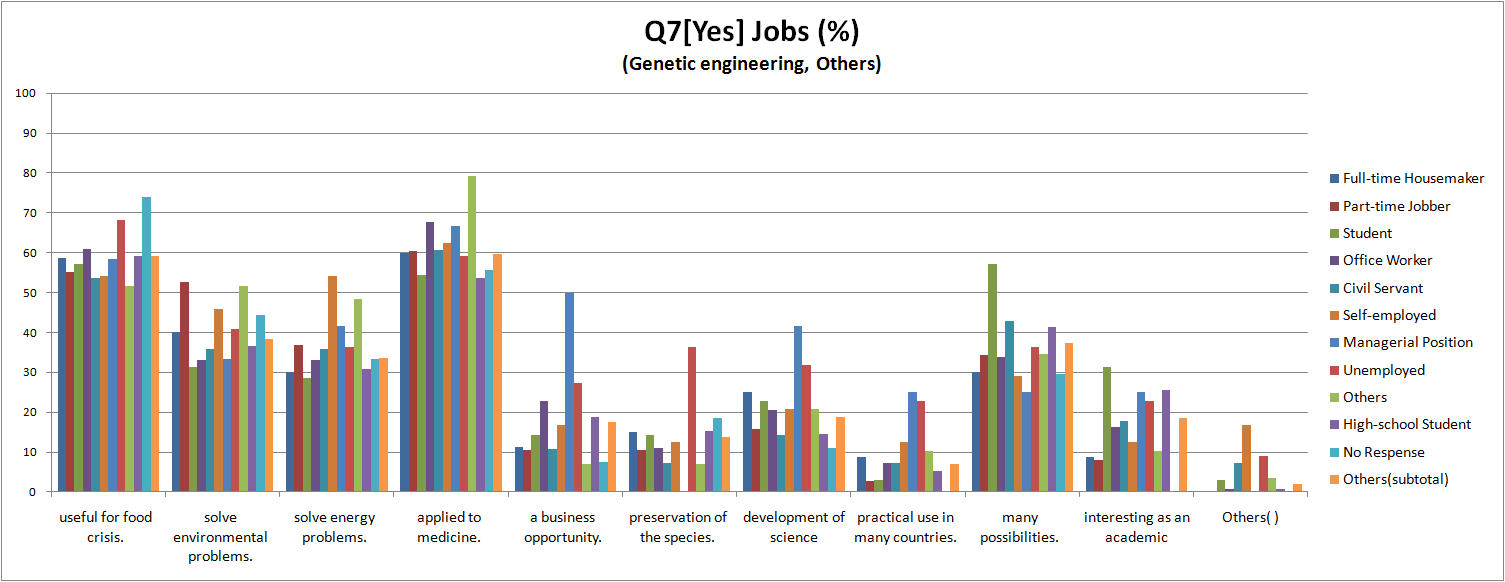
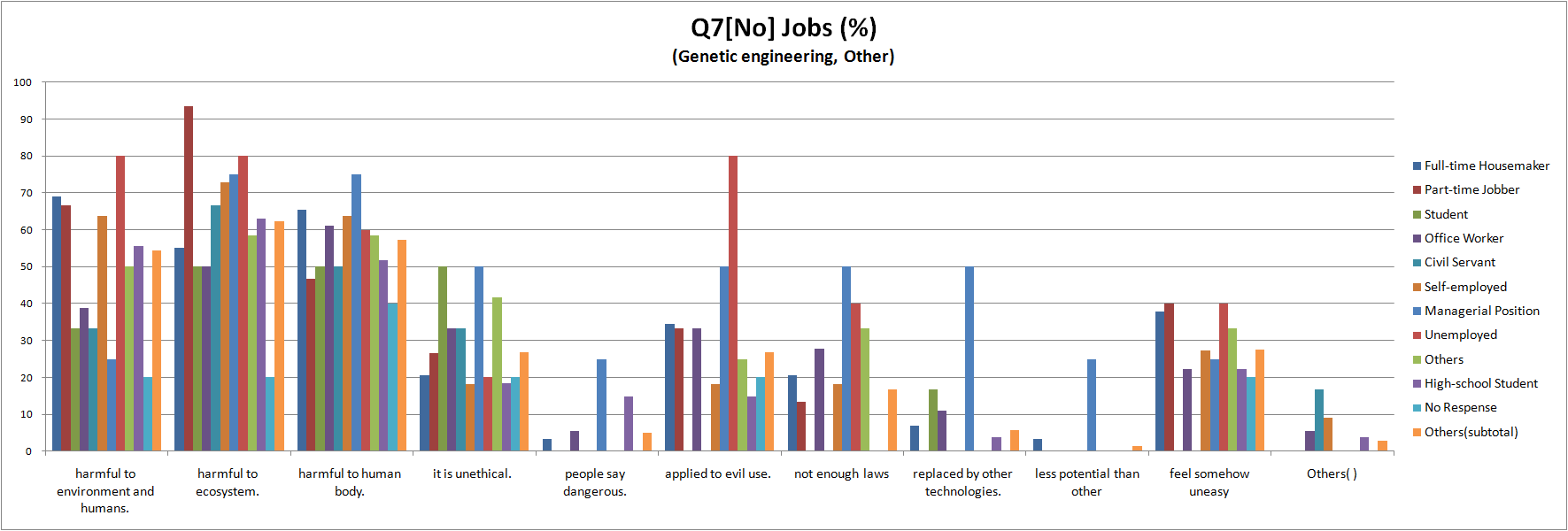
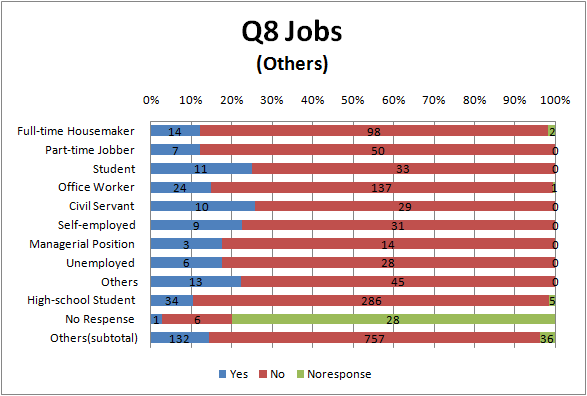
- compare in job
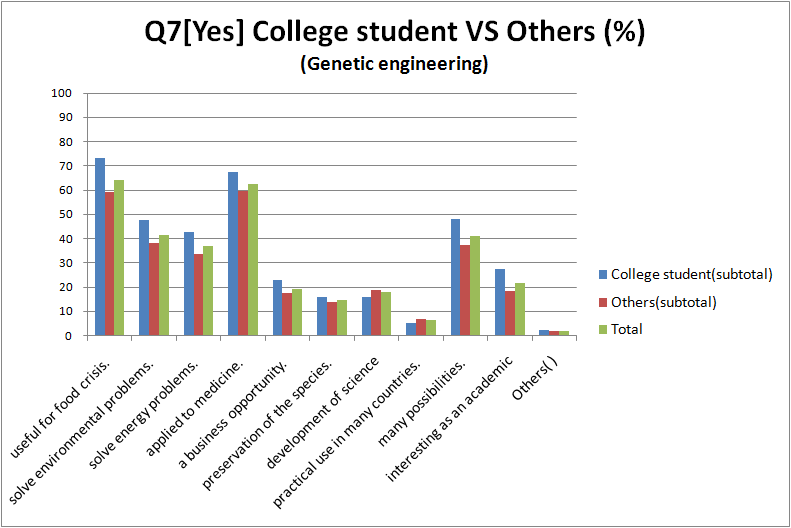
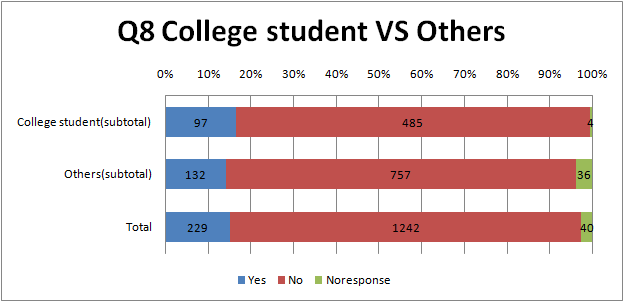
- compare between college student and the other
(*)In Japan, classification of arts and science is important. Most Japanese students study different subjects since high school due to the classification, because it is a big factor to decide the subjects required in the entrance examination for universities or colleges. This is the reason we predicted that there might be some differences between arts and science.
Scale
Following is the scale of our survey(whole iGEM Japan.)
| College Student | ||||
| No. | Arts or Science | Genetic Engineering | Biotechnology | Subtotal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arts | 113 | 58 | 171 |
| 2 | Science | 282 | 110 | 392 |
| 0 | No response | 23 | 1 | 24 |
| - | Total | 418 | 169 | 587 |
| Other | ||||
| No. | Job | Genetic Engineering | Biotechnology | Subtotal |
| 1 | Full-time House maker | 114 | 0 | 114 |
| 2 | Part-time Jobber | 57 | 0 | 57 |
| 3 | Student | 41 | 3 | 44 |
| 4 | Office Worker | 161 | 1 | 162 |
| 5 | Civil Servant | 39 | 0 | 39 |
| 6 | Self-employed | 39 | 1 | 40 |
| 7 | Managerial Position | 17 | 0 | 17 |
| 8 | Unemployed | 34 | 0 | 34 |
| 9 | Other | 44 | 14 | 58 |
| 10 | High-school Student | 286 | 39 | 325 |
| 0 | No Response | 35 | 0 | 35 |
| - | Subtotal | 866 | 58 | 924 |
| - | Total | 1284 | 227 | 1511 |
| Male | 771 |
| Female | 702 |
| No Response | 38 |
| Total | 1511 |
Graph
1. When shopping, do you buy "not genetically modified food”?
- [ Always buy / Tend to buy / Hardly mind / Not mind / I have never seen such an indication ]
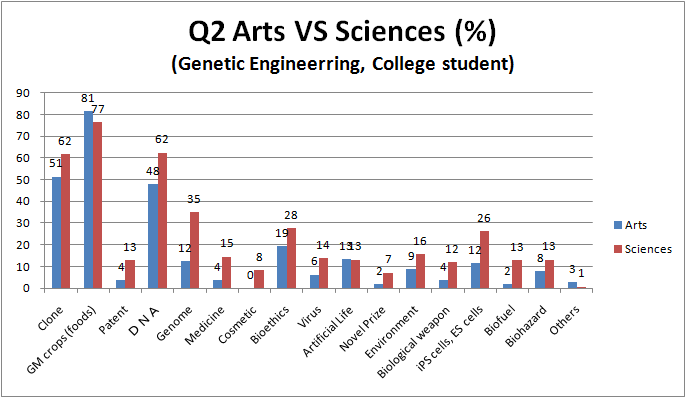
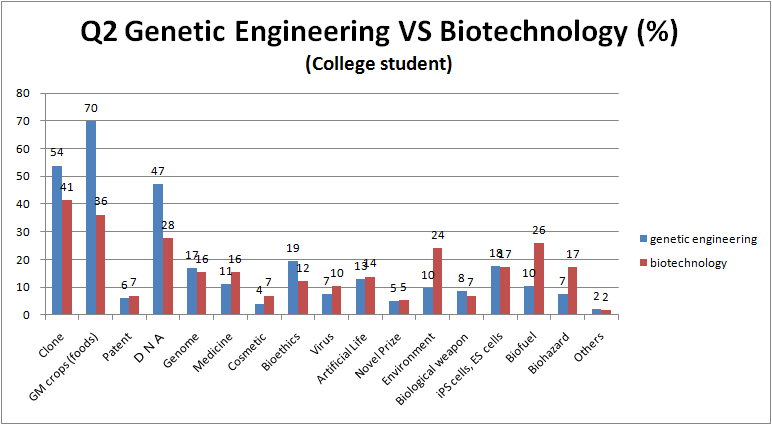
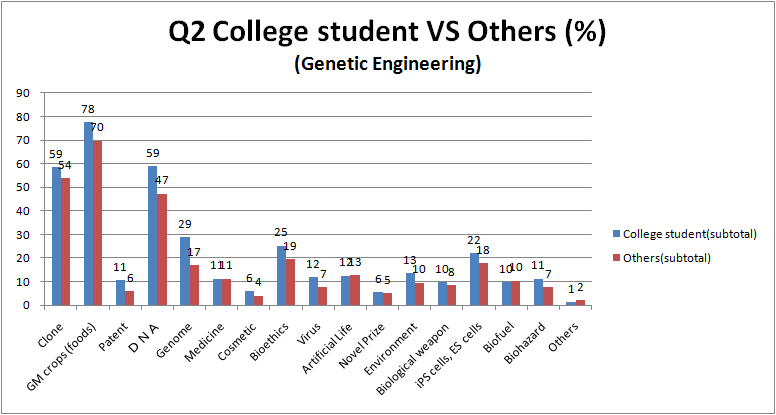
2. What do you associate with ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )? (※Please circle all that apply)
- [ Clone / GM crops (foods) / Patent / DNA / Genome / Medicine / Cosmetic / Bioethics / Virus / Artificial Life / Novel Prize / Environment / Biological weapon / iPS cells, ES cells / Biofuel / Biohazard / Others( ) ]
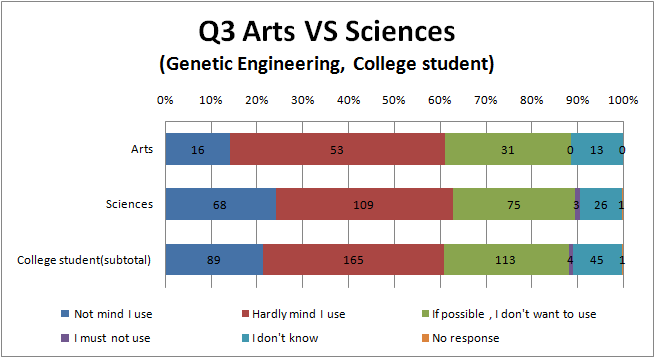
3. If there is no difference in effectiveness, what do you think about using the drugs manufactured by ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )?
- [ Not mind I use / Hardly mind I use / If possible, I don't want to use / I must not use / I don't know ]
4. What do you think of the artificial genetic mutation by ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )?
- [ Bad / Little bad / Little good / Good ]
5. Which trend of information about ( genetic engineering or biotechnology ) is major, negative or positive?
- [ Negative / About the same degree / Positive / No idea ]
6. Do you think Japan actively tackles on ( genetic engineering or biotechnology )?
- [ Yes / Partly yes / Not so much / No ]
7 Do you think the research on ( genetic engineering or biotechnology ) should continue?
- [ Yes / No ]
- If you answered [Yes], please circle every fit reason from below.
- Because it may be useful for food crisis.
- Because it may solve environmental problems.
- Because it may solve energy problems.
- Because it may be applied to medicine.
- Because it may be a new business.
- Because it can use preservation of the species.
- Because it symbolizes the development of science and technology.
- Because it has already been put to practical use in many countries.
- Because it has potential.
- Because it is interesting as academic.
- Others( )
- If you answered [No], please circle every reason from below.
- Because it can create evil things harmful to environment and humans.
- Because products of it can be harmful to ecosystem.
- Because products of it can be harmful to human body.
- Because I can't approve it ethically.
- Because people say it is dangerous.
- Because it can be applied to evil use.
- Because there are not enough laws governing it.
- Because it can be replaced by other technologies.
- Because it seems to have less potential than other technologies.
- Because I feel somehow uneasy.
8. Have you ever heard the word, "Synthetic biology"?
- [ Yes / No ]
[ This is the common Result article of participating universities of “iGEM Japan Human Practice”(KIT-Kyoto, Kyoto, Osaka, Tokyo_Metropolitan, and UT-Tokyo).iGEM Kyoto has the responsibility for the wording. ]
Discussion
Q1
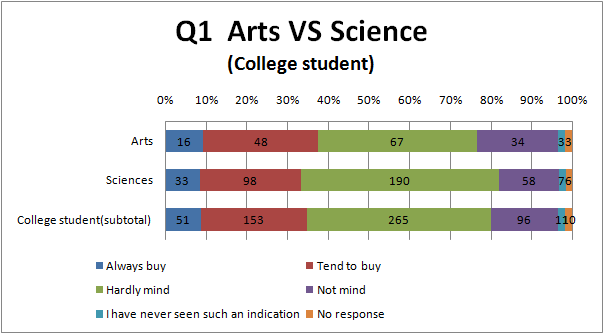
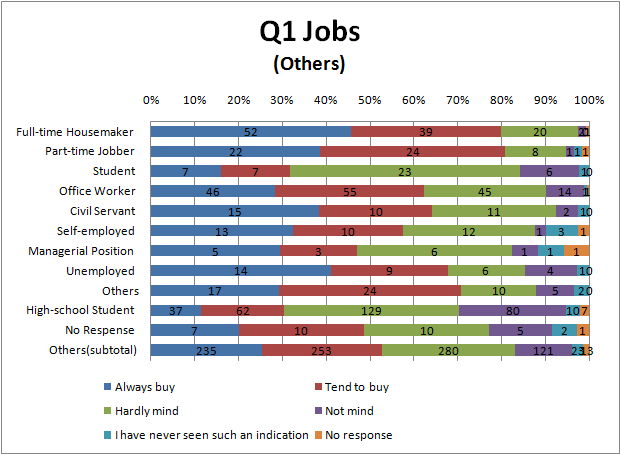
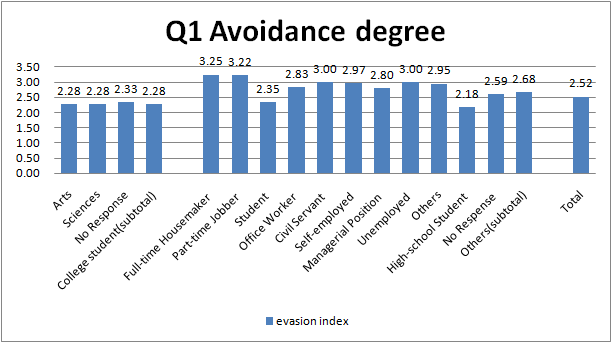
- To see Fig.1.3, avoidance degree of Full-time House maker and part-time jobber is higher than others, and one of college student and High school student is lower.
- This result suggests that Full-time House maker and part-time jobber tend to have concerns about food labeling because they have more opportunities of purchasing foods than other occupations.
- It may be because “students are less conscious of food”, ”students put a higher value on other heads such as price rather than food safety ” or ”students apply to GM foods”
- about ”students apply to GM foods”, contemporary students have had a debate on GM foods at least once in high school or junior high school. So they may tend to have positive opinions because they probably have more intelligence and opinions on GM foods than people
Q2
- The phrases “Cloning”, ”GM foods” and ”DNA” are highly responded by people.
- Because, speaking of genes or biotechnology, people especially has a strong impression about DNA, many people may have chosen “DNA”.
- When questionnaire sheets title is “genetic modification”, the phrase ”GM foods” was highly responded. More than half of people respond.
- When questionnaire sheets title is “biotechnology”, the phrases ”environment”, “biofuel” and “biohazard” was highly responded, related to genetic modification sheets.
- Moreover, because biotechnology survey include the word “bio”, the phrases ”biofuel” and ”biohazard” was responded more higher than “genetic modification” sheets.
- The result may suggest that the word ”genome” was lower acknowledged by people.
- The tendency of answer shows that this is accurate information in terms of association, since figures of graphs are same as a whole.
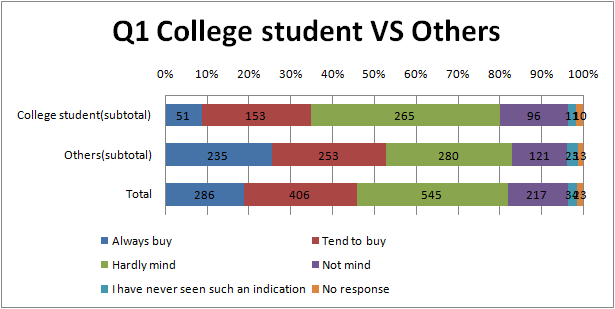
- Comparison between Arts and Science, between College student and the Other.
- Science is more familiar to Academic term than Arts and the Other.
- Science and the Other is more familiar to a term connected with life than Arts.
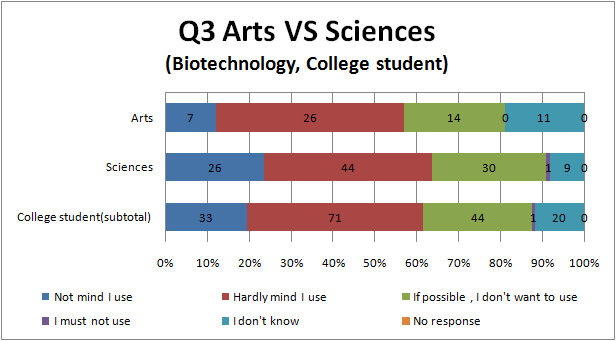
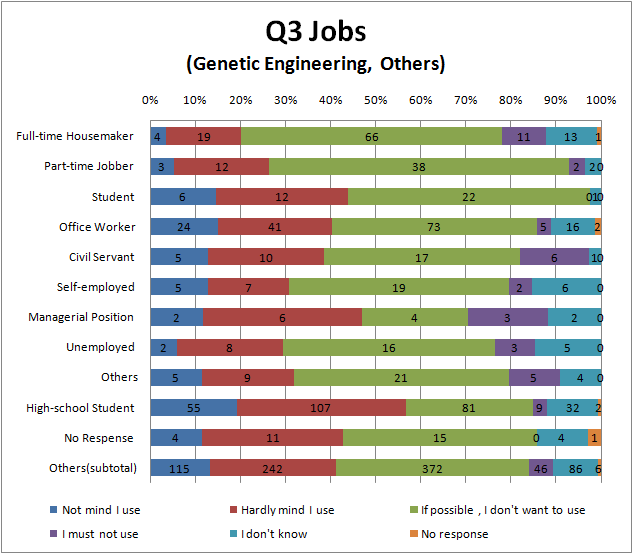
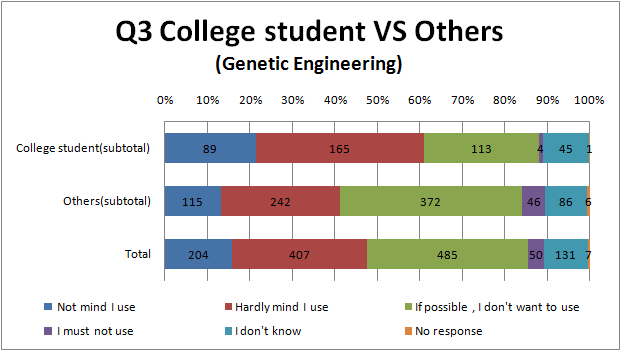
Q3
- To see Fig.3.3 and Fig.3.4, there seems to be the same tendency as Question 1. That is Full-time House maker and part-time jobber relatively avoid genetic engineering or biotechnology, and college student and High school student relatively accept it.
- we think that it is similar reason to Q1 why there is the tendency like this.
- There are hardly difference between the result of genetic engineering and biotechnology.
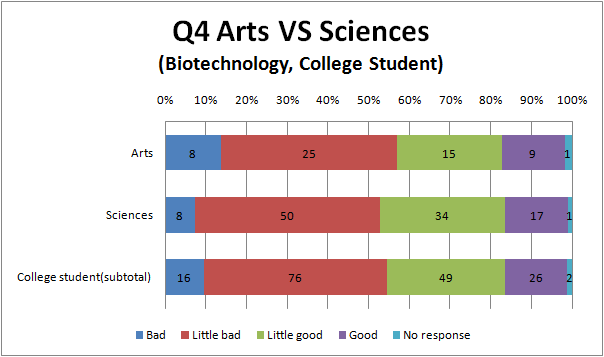
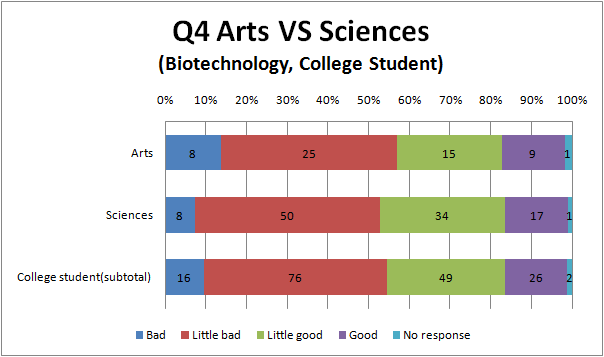
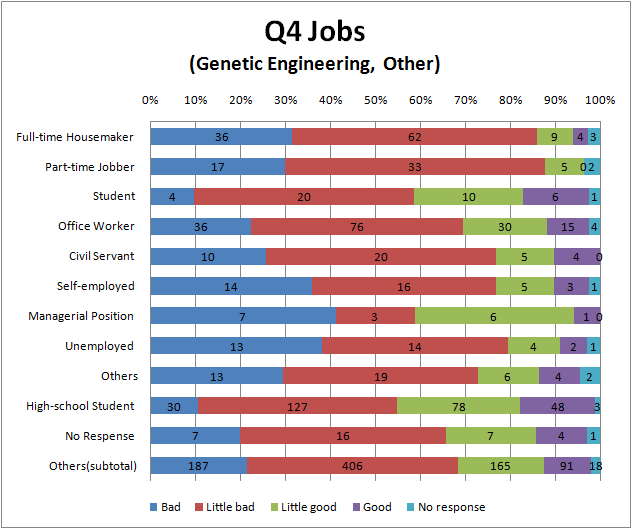
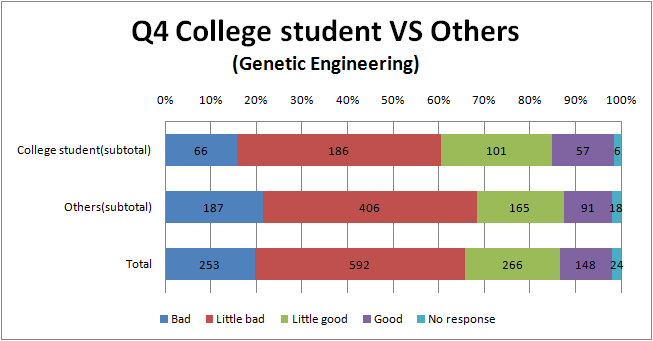
Q4
- College student and high school student think that we can do than the other.
- In addition, we find out that less Arts than Science feel genetic engineering bad.
- we think that it is similar reason to Q1 and Q3 why there is the tendency like this.
- There are hardly difference between the result of genetic engineering and biotechnology.
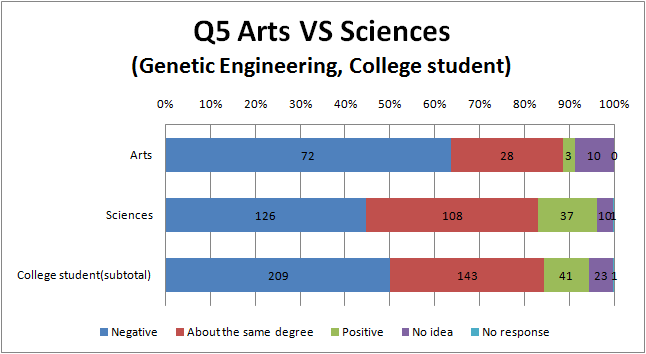
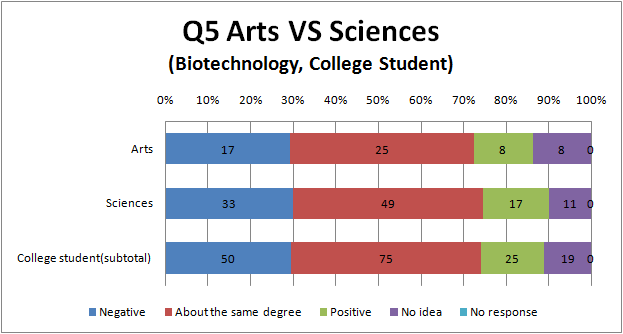
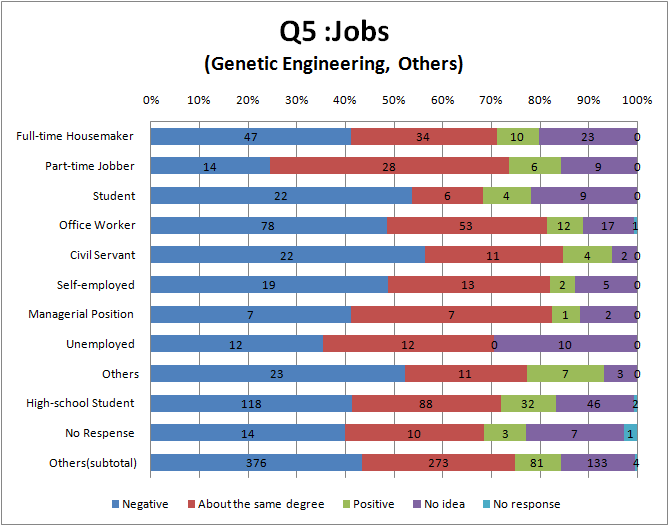
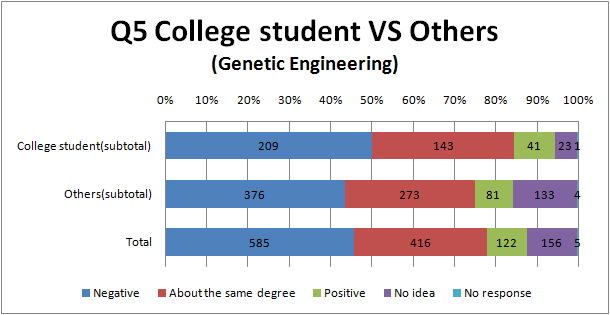
Q5
- More people answering survey of genetic engineering than that of biotechnology think that negative information is major.
- Now, Japanese trends to impress the word ‘genetic engineering’ as bad one. On the other hand Japanese does not feel biotechnology so bad.
- There are hardly a difference between the result of university students and the others.
- Most Arts among all groups think that negative information is major.
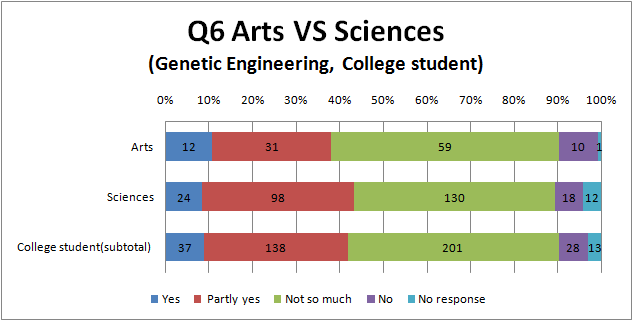
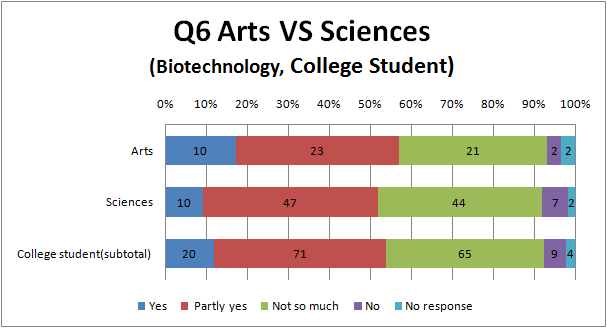
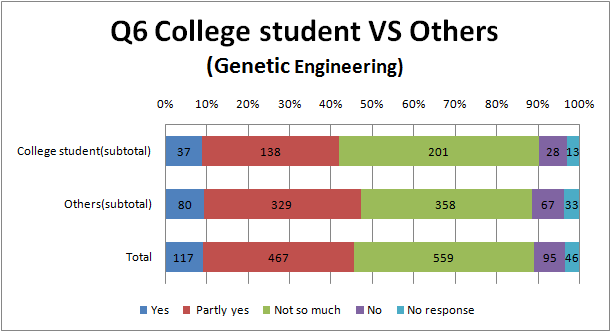
Q6
- Surprisingly, there are hardly a difference between the result of university students and the others.
- comparing between Fig6.1 and Fig.6.2, There are a little more people answering ‘Yes’ in the survey of biotechnology than that of genetic engineering.
- It also suggests biotechnology has more positive impression than genetic engineering to Japanese.
- Although Japanese iPS cell study becomes big news, there are hardly a difference between the result of ‘Yes’ and ‘No’, and this situation is dangerous.
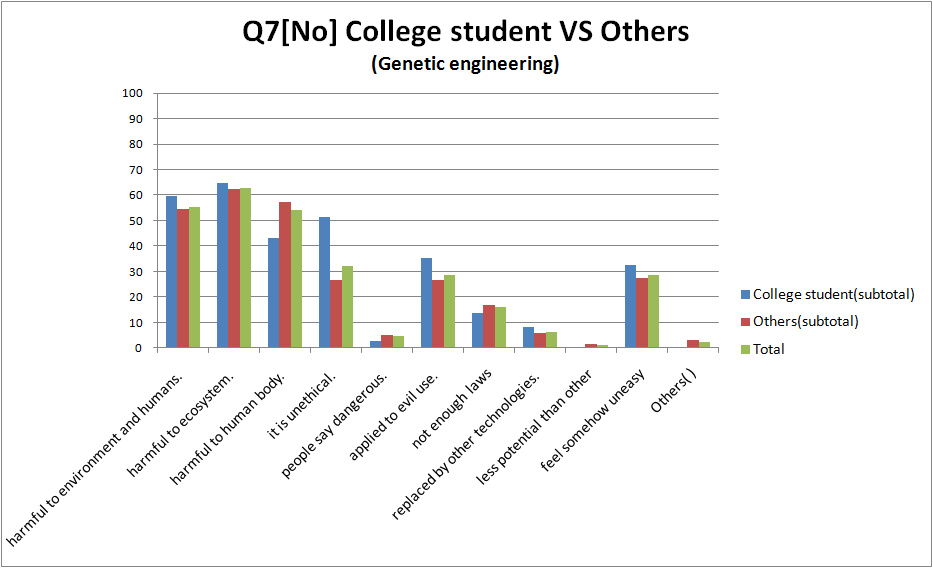
Q7
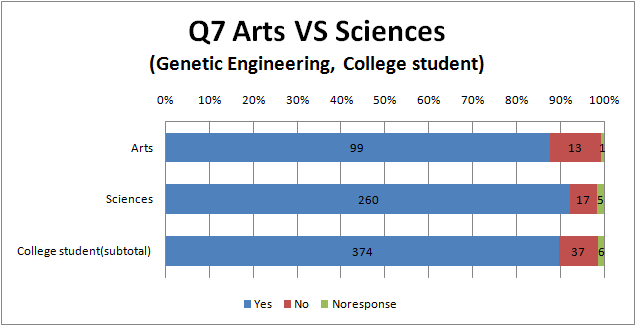
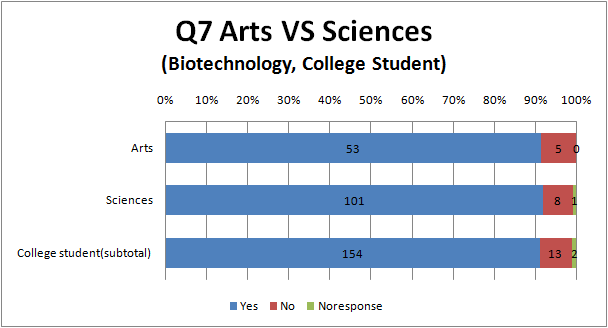
The rate of “continue” to “stop”
- The overwhelming majority responded to “yes”.
- Although people(especially the public) don’t have a good impression about GM foods and genetic recombination at previous question more than eight-tenth of people respond to ”continue research ” here. This means that whether people agree or not depends on research content.
- College student respond to much more “continue” than the rest.
- There is hardly difference between “biotechnology” and “genetic modification”.
The reason that the research should continue
- There are hardly differences between College student and the Other..All have almost same tendency.
- Quite people answered “useful for food crisis”, ‘solve environmental problems”, “applied to medicine” or “it has potential”.
- People expected genetic engineering and biotechnology in the future.
The reason that the research shouldn't continue
- Quite people chose “harmful to environment and humans”, “can be harmful to ecosystem” and “harmful to human body”
- There are no big differences between biotechnology and genetic engineering.
Summarization of Question 7
- Solution to food, energy, environmental issues and medical treatments is expected.
- Many people worry about harmful effects on the environment or on us. It is Some people say they are against their moral values.
- Some of these worry may come from ignorance about genetic engineering and biotechnology. We hope we can relieve their worries if we explain more in detail.
Q8
- The result that only 10~20 percent of whole knows this term, shows that this term have hardly spread to people.
- We think that the most contribution of this questionnaire is that 1242 person know this term.
- There isn’t a large difference between university students and the Other
Conclusion
Overall tendency
The big difference in Japanese is caused by student (including college and high school) or not. This difference might come from following some reason.
- It comes from difference of generation. For example, when college student or high school student were childhood, Dolly was already born (1996).
- It comes from difference of education. Contemporary students are taught about genetic engineering and biotechnology in school. They probably have more intelligence about genetic engineering and biotechnology.
- It comes from the amount of chance of household chores, especially shopping. Students do household chore less than house maker.
According to the results of the questionnaire about both genetic engineering and biotechnology, over half of the subjects said that "the research should continue" in Q7, while most subjects have "a negative image" (Q1, Q3, Q4, Q5). It seems that people only have abstract and unclear image to this 'professional' technique. Genetic engineering is not still so common in Japan. And many people worry about safety. So engineers are desired to develop safety of biotechnology and spread knowledge about biotechnology.
Future work
We revealed the tendency of impressions on genetic engineering through comparison in Japanese. We found that Students think that genetic engineering and biotechnology is not so negative as Other people. So we should inform not only students but also public about biotechnology. In fact, focus of our action should be public. But we, college students, can do few approaches for public. To solve this problem, we can use iGEM networks! In our case, iGEM Japan attracted some media and we get a chance to be known by public. If iGEM team of only one university asked for media does an interview to us, it might be refused. So we want to continue iGEM Japan project, and to make this project bigger.
co-operate with other iGEM teams
Reference
- Darryl R. J. Macer, Ph.D., [http://www.eubios.info/AGE.htm Attitudes to Genetic Engineering: Japanese and International Comparisons], Eubios Ethics Institute 1992
- Masakazu Inaba and Darryl Macer, [http://www.eubios.info/EJ133/ej133b.htm Attitudes to biotechnology in Japan in 2003], Eubios Journal of Asian and International Bioethics 13 (2003), 78-90.
- Macer, D.R.J., Bezar, H., Harman, N., Kamada, H. & Macer, N., [http://www.eubios.info/EJ75/ej75h.htm Attitudes to Biotechnology in Japan and New Zealand in 1997, with International Comparisons], Eubios Journal of Asian and International Bioethics 7 (1997), 137-151.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10973213 PMID: 10973213] Macer D, Ng MA., Changing attitudes to biotechnology in Japan., Nat Biotechnol. 2000 Sep;18(9):945-7.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7765227 PMID: 7765227] Zechendorf B., What the public thinks about biotechnology., Biotechnology (N Y). 1994 Sep;12(9):870-1, 873-5.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16273712 PMID: 16273712] Ng MA, Takeda C, Watanabe T, Macer D., Attitudes of the public and scientists to biotechnology in Japan at the start of 2000., Eubios J Asian Int Bioeth. 2000 Jul;10(4):106-13.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11654983 PMID: 11654983] Asada Y, Tsuzuki M, Akiyama S, Macer NY, Macer DR., High school teaching of bioethics in New Zealand, Australia and Japan., J Moral Educ. 1996 Dec;25(4):401-20.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9062920 PMID: 9062920] Hoban TJ., Consumer acceptance of biotechnology: an international perspective., Nat Biotechnol. 1997 Mar;15(3):232-4.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9202112 PMID: 9202112] Europe ambivalent on biotechnology. Biotechnology and the European Public Concerted Action group., Nature. 1997 Jun 26;387(6636):845-7.
- [http://web.staff.or.jp/ STAFF] (2006)., Report of STAFF (in Japanese), available at: http://web.staff.or.jp/data/ivent/200603/20-2006032211531309821.pdf
- [http://www.cbijapan.com/ JMAR/CBI Japan] (2004)., "GMO" ni kansuru shohisha chosa (in Japanese), available at: http://www.cbijapan.com/d_investigation/2004.pdf
- iGEM 2009 - Team:Freiburg_bioware
- iGEM 2009 - Team:Valencia
 "
"