Team:USTC Software/demo
From 2010.igem.org
Using C-N Model we can model systems with great complexity
The simplest example with only E.coli cell
introduction
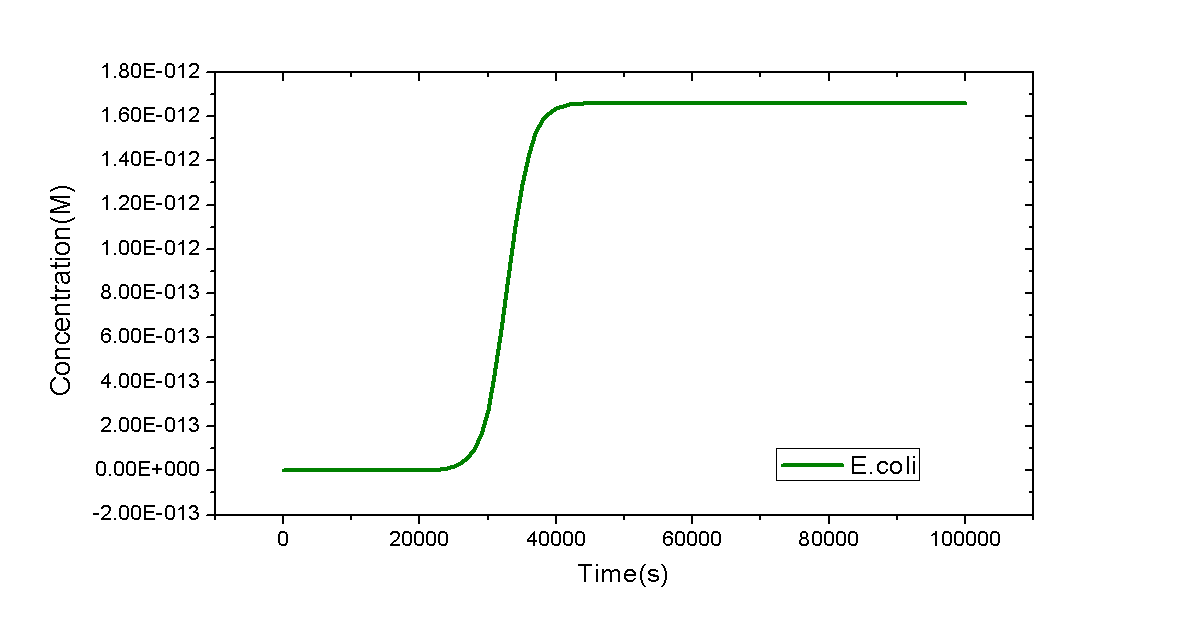
As the simplest example, a model of a flask with only E.coli cells inside will be shown. Only one reaction will be considered: the replication of E.coli. However, it is not trivial. MoDeL enables users to add such an auto-catalytic replication reaction easily and conveniently. The minimal database used for this model could be download here.
database construction
We only provide key points regarded with construction of this minimal database. To add the auto-catalytic reaction in the Reaction container, a species with only part E.coli is required. It has the simplest Chain-Node model format: only one chain with one part and no trees. The auto-catalytic reaction has one modifier and one product and they are both referred to E.coli defined in Species container. Since they are compartment-type species (species representing a compartment), attribute itself of compartmentLabel node in modifiers and products definitions should be set the same with label of the compartment they represent in the compartments definition. It ensures that the product and the modifier are the same, avoiding wrong mismatch of the product which is different with the modifier. Since number of E.coli cells will reach a stable level in a long time course, we use <math>k_{g}(1-C_{E.coli}/C_{max})C_{E.coli}V_{Flask}</math> as the reaction rate, where <math>k_{g}</math> is the growth rate of E.coli, <math>V_{Flask}</math> represents the size of E.coli, and <math>C_{E.coli}</math> and <math> C_{max}</math> are concentration of E.coli and its max concentration in the flask, respectively. The negative sign in the rate equation indicates self-repression of E.coli cells.
modelling and simulation
Model written in SBML format is shown below. The dynamic curve of E.coli replication is plotted by time course simulation. Exactly speaking, dynamic behaviors of biological system are meaningless after 4000s because of termination of reproduction of E.coli. However, the curve is in qualitative agreement with that from experiments in the first and second stage of reproduction of E.coli.
Basic example with pLac-LacI repression system
introduction
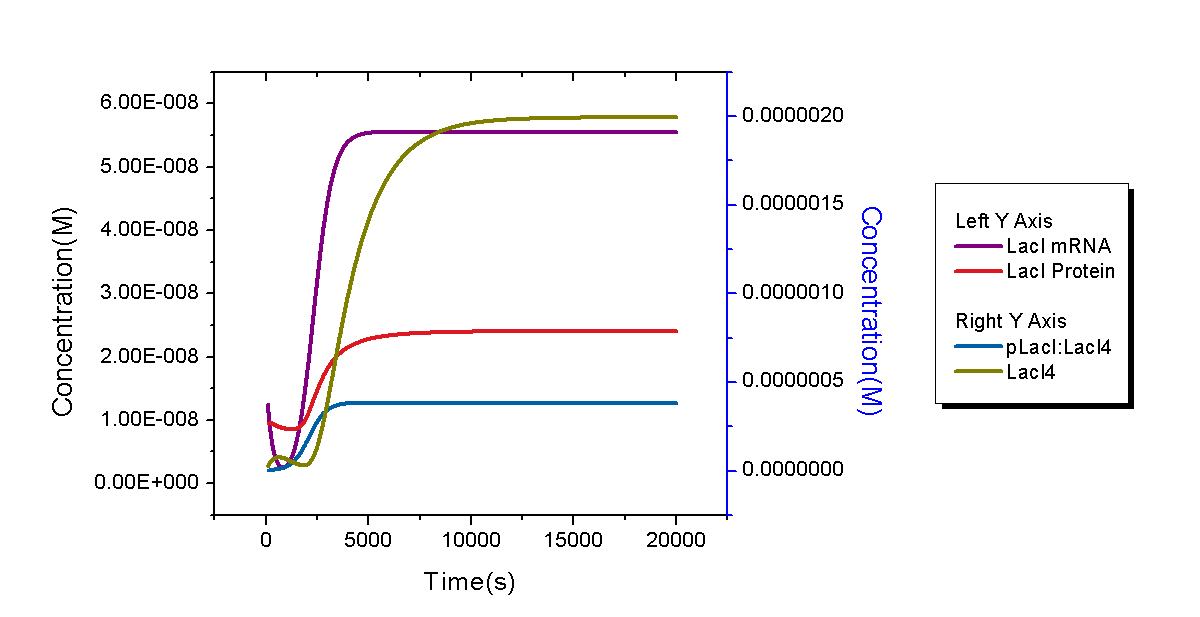
MoDeL provides poweful supports for description of interactions between two species. No interactions exist in the previous example. In this example, we will construct a plasmid backbone with promoter, rbs, coding sequence and terminator inserted in and transform it into E.coli. LacI repressor are produced after two steps of transcription and translation. It binds with itself to form a dimer and then a tetramer, which could bind with promoter LacI on the plasmid to repress the process of transcription. Besides, replication of E.coli cells, degradation of proteins and mRNAs, as well as dilution due to replication of cells, are also considered.
database construction
Actually, it is a complex molecular process and takes many steps to complete a transcription reaction. It includes binding and initiation, elongation, and termination. So does translation reactions. The first version of MoDeL DOES NOT support transcription and translation reaction templates and they will be handled by our core program of iGame and thus no need to write in the database.
All binding reactions in the database demo are modeled using law of mass action. They are dimerization of two LacI repressors and that of two LacI dimers. LacI tetramers will bind with promoter LacI in the plasmid and thus repressing the expression of plasmid DNAs. However, MoDeL enables any mathematical model form for species-species interactions and is not constrained within only law of mass action. Users could change the reactants, modifiers, products, as well as kinetic laws arbituarily and validate their models via output of dynamic curves.
Species reaction templates are worth mentioning to show features of our new language MoDeL. It is never a easy problem to calculate degradation rates of proteins since different parts in a fused protein may have different degradation rates and the overall rate is still unknown. What's more, a protein in MoDeL may have different protein chains and it is more complex to determine the overall rate. In the demo database, we assume all proteins with no parts in bound state have a uniform degradation rate. Proteins with more than one chains are considered stable and non-degradable. This idea could be applied easily by writing reaction templates in MoDeL format. The reactant is a general species template with only one substituent-type part (ANYUB) of type ForwardProtein (no reverse reactions happened here). It is similar for degradation of mRNA molecules. Only mRNAs with single chain degrades at the same rate.
For reactions of dilution due to reproduction of cells, quantities of species decrease in a similar way to degradation. The rate of dilution is also similar to the reproduction rate of E.coli:
<math>k_{g}(1-C_{E.coli}/C_{max})C_{species}V_{Flask}</math>
where we only replace the second <math>C_{E.coli}</math> with concentration of species in dilution. To apply this idea, we only need to construct a species with only one substituent-type part (ANY) of no specific type and it will be matched to all species. Among them, only species bound in compartment E.coli will be diluted.
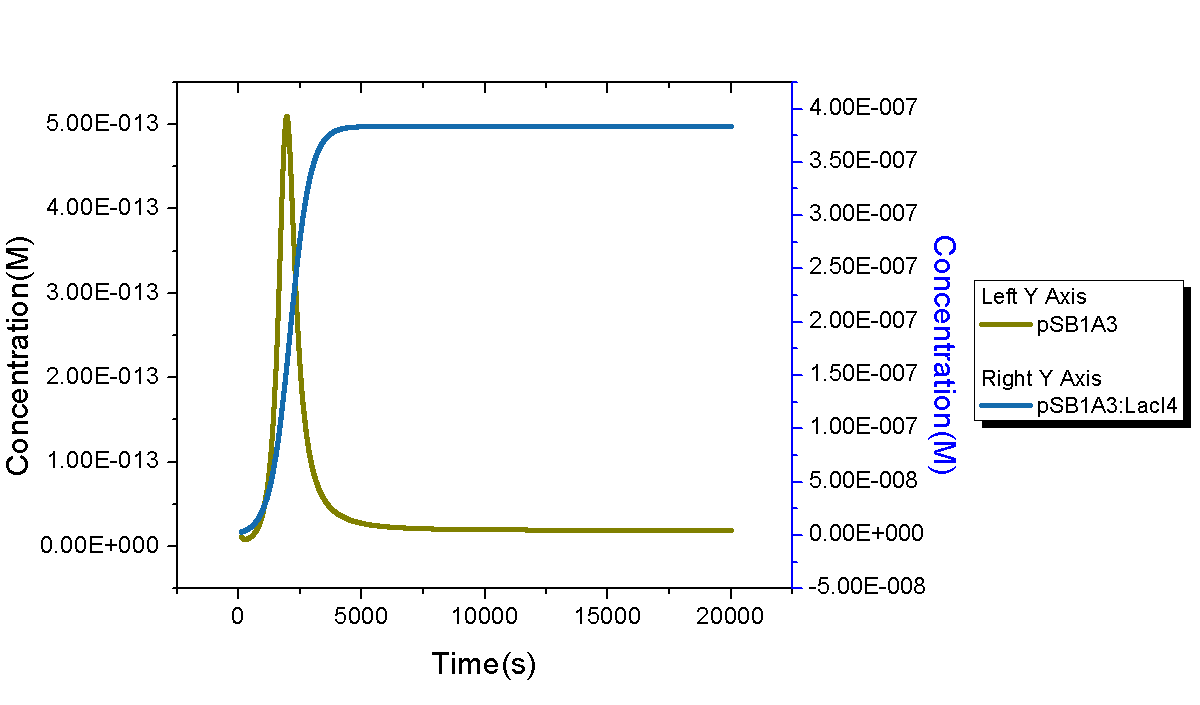
Replication of plasmid DNAs is not as easy as reproduction of living cells in two aspects: first, plasmid backbone with the same replication origin could be found in many species in the system because the original transformed plasmid backbone may bind with other compounds or proteins to form complex; second, the replication of original transformed plasmid DNA molecule tends to be repressed by all species including the same replication origin. However, E.coli cells do not have any effects on the reproduction of other E.coli cells. MoDeL language perfectly support this idea by separating the template reaction into replications and repressions. The first part describes the exponential amplification of plasmids with reaction rate <math>k_{g}C_{plasmid}V_{E.coli}</math>, where <math>k_{g}</math> is the replication rate of a certain plasmid, <math>C_{plasmid}</math> is the concentration of this plasmid, and <math>V_{E.coli}</math> is the volume of E.coli cell. The product may be different from the reactant. It is possible because the reactant may be a complex, such as complex of LacI tetramer and plasmid with promoter LacI (we call it pLacI:LacI4 below). Only the products of the replication reaction will be repressed with a certain rate. In this example, pLacI:LacI4 would not be repressed since it is not among the products of its replication. Via MoDeL language, we design a template reaction with no reactants, two modifiers and one product. The two modifiers are template species containing a certain plasmid backbone (say pSB1A3), and binding state is allowed for both. The product is also a template species containing pSB1A3, however, it has only one chain and no binding is permitted. Hence, modifiers have Chain-Node structure ANY--pSB1A3--ANY, while product has its structure ANYUB--pSB1A3--ANYUB. The listOfTransferTable makes parts transfer from part ANY of either modifier to its corresponding part ANYUB of the product. The reaction rate is <math>-k_{g}C_{mod1}C_{mod2}/C_{max}</math>, where <math>k_{g}</math> is the same as that defined in the replication reaction, <math>C_{max}</math> is the max concentration of plasmids containing pSB1A3 as backbone, and <math>C_{mod1}</math>, <math>C_{mod2}</math> are concentrations of modifier1 and modifier2, respectively. The negative sign in the rate law indicates a repressed effect to the replication of the product.
modelling and simulation
To give a reasonable dynamic curve of species in the biological system, parameters are obtained from experiments if they are available. Besides E.coli, there are 6 species: LacI mRNA (with RBS), LacI protein, LacI dimer, LacI tetramer, and complex of LacI tetramer and DNA1 (DNA
 "
"