Team:Berkeley/Results
From 2010.igem.org
- Home
- Project
- Parts
- Self-Lysis
- Vesicle-Buster
- Payload
- [http://partsregistry.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2010&group=Berkeley Parts Submitted]
- Results
- Judging
- Clotho
- Human Practices
- Team Resources
- Who We Are
- Notebooks:
- [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/Berk2010-Daniela Daniela's Notebook]
- [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/Berk2010-Christoph Christoph's Notebook]
- [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/Berk2010-Amy Amy's Notebook]
- [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/Berk2010-Tahoura Tahoura's Notebook]
- [http://www.openwetware.org/wiki/Berk2010-Conor Conor's Notebook]
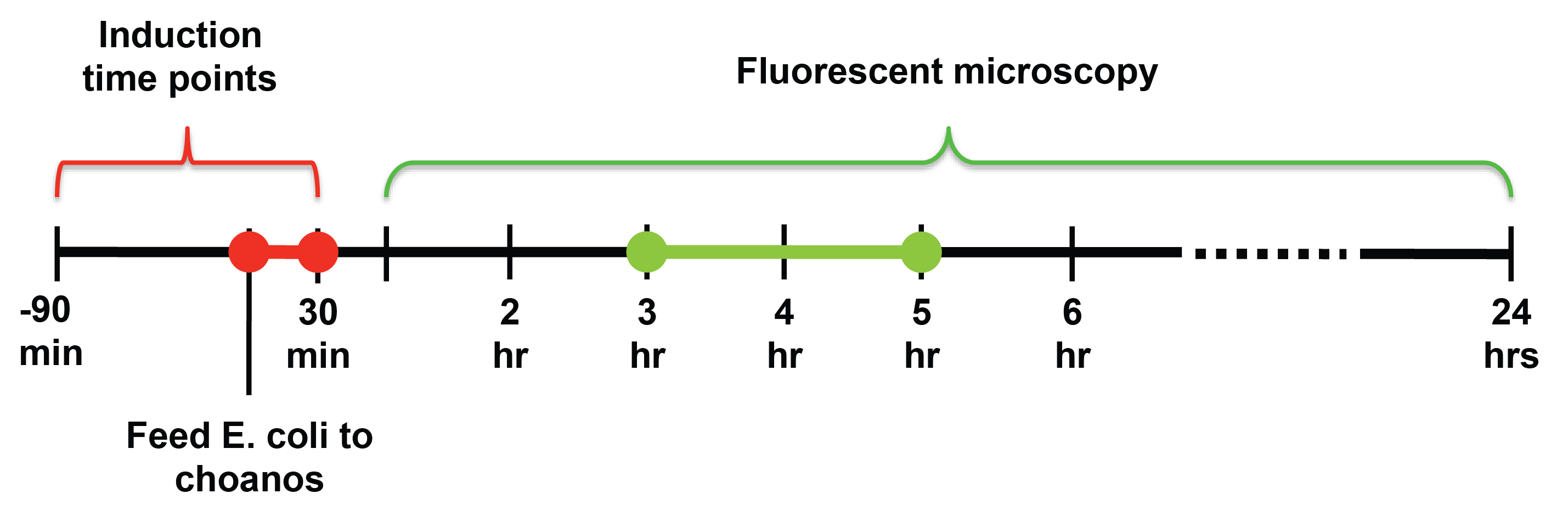
General Experimental Set Up
Our payload delivery assay involves the following steps:
- Feed the payload bacteria to the choanos and induce self-lysis with arabinose. Induction of self lysis and feeding are not necessarily at the same time.
- Use fluorescent microscopy to detect delivery of our GFP payload.
Challenges
One of the challenges we faced in assaying for payload delivery was finding a media that the Choanoflagellates liked and that accomodated lysis. After assaying several different media formulations, including CGM, LB, TB, ASW and four different mixtures of ASW and LB, we found that CGM media was the best media for Choano viability, E. Coli lysis, and protein delivery. For more details, see our characterization of the self-lysis device.
The major challenge we faced when assaying for payload delivery was determining when to induce self-lysis and when to look at the choanos under the microscope.
For induction of self lysis, we tested timepoints from 90 minutes to 30 minutes after feeding the choanos (-90 to +30 minutes), with 15 minute intervals. For looking at the choanos under the microscope, we tested timepoints from 1 hour after feeding to 24 hours after feeding.
From our experiments, we found that induction at the same time as feeding, or 15 or 30 minutes after feeding yielded the most delivery events. For timepoints before -15 minute, delivery events were undetectable or happened extremely infrequently.
We also observed that choanos seem to eat and digest bacteria with 1-2 hours after feeding, and that the best time to look for successful delivery was between 3 and 5 hours after feeding.
Controls
Our first step before assaying was to establish controls. Based on how our parts should work, and work done in the Anderson Lab in mammalian cells, we expected that a sucessful delivery event would consist of diffuse GFP fluorescence throughout a choano's cytoplasm. With this in mind, the controls we ran regarding the choanos were:
Payload cells with no payload delivery device
This control was to establish a baseline of what normal eating and digestion of bacteria in choanos looks like. We observed that choanos seem to eat with 3-5 minutes after feeding. During the first hour or so, one generally sees bacteria in food vesicles , either as rod shapes or circles (rod shaped bacteria 'head on'). They are very bright and have signifcant halos. Slowly, we end up seeing fluorescence in small circular objects.The fluorescent intensity is less than the initial bacteria in food vesicles, and we believe flourescent payload is in the food vacuole. Eventually, the fluorescence disappears altogther, degraded by the vacuole of the choano.
Payload cells with uninduced payload delivery device
This control was to ascertain that any delivery events we got were from induction with arabinose, and not just a normal phenotype exhibited when choanos eat cells with self-lysis, vesicle buster and payload.
Cells with payload and self lysis but no vesicle buster
This control was to confirm that the successful delivery phenotype we saw was due to self-lysis device and the vesicle buster, not just self-lysis alone. We wanted to make sure that the what we were seeing was payload that had escaped the food vesicle, not just payload in a food vesicle.
Cells with payload and vesicle buster, but no self-lysis
This control was once again to make sure that if we saw a successful delivery event, we could be certain that it was a phenotype unique to cells with induced self-lysis and vesicle buster.
Additionally, since all of these assays are microscopy based, we kept the settings on our microscopes constant and kept careful notes on exposure and magnification in order to avoid getting misleading results.
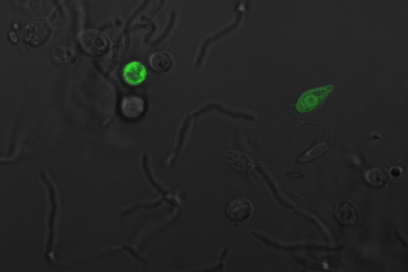
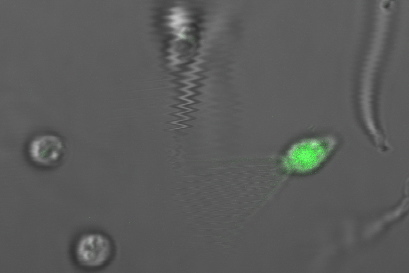
Payload Delivery
The following images are of successful payload delivery events. As the images of the control above showed, the phenotype of GFP throughout the cytoplasm shown below is unique to constructs with self-lysis and vesicle buster, and is consistent with what we'd expect to see based on the biology of our parts.
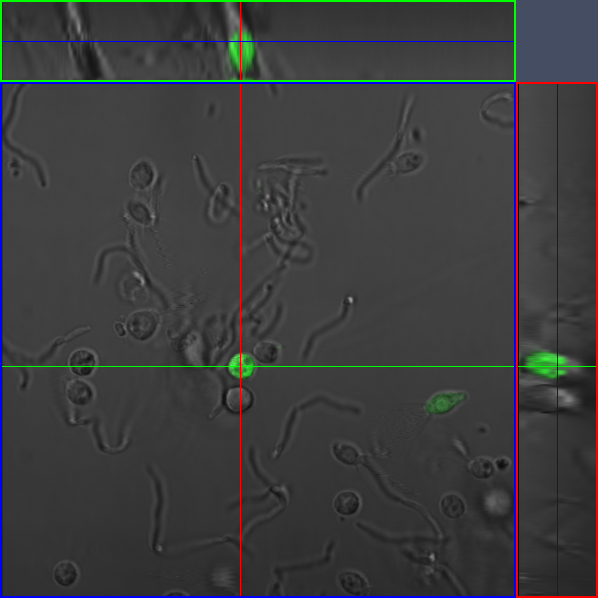
Confocal Imaging |
|
Efficiency of GFP Delivery: 7% (±2%)
We also used a hemocytometer to quantify the frequency of delivery. For an assay with self-lysis induction 15 minutes after feeding, an average of 7% (±2% standard deviation) of choanoflagellates experienced successful delivery of GFP - 1 out of every 16 choanos. In a culture at average density (10^6 cells per mL), we will have approximately 6.2x10^4 delivery events per mL of culture.
Specific Protocols
1. We generally keep our choanos in artificial sea water, so to prepare them for an assay, we aspirate the seawater off and replace it with CGM3. Since choanos naturally fix to the surface of the dish they are cultured in, aspirating is not a problem. 2. For induction time points before feeding, we induce self lysis with arabinose in a test tube, and then put it in a 37 incubator with shaking until it is time to feed the choanos. For induction time points after feeding, we add arabinose to the choanos and keep them incubating at 37 C without shaking until we assay. 3. At time 0, we feed the choanos bacteria from the different induction time points. Usually we feed 2 ul of bacteria per 500 ul of choanos. 4. We put the choanos and the bacteria back in the 37 C incubator for three hours. 5. We remove the choanos from the incubator, and put them in viewing wells 6. Look for delivery events on the microscope!
 "
"