|
|
Proteins
Superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1)
Human soluble Superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) is a soluble cytoplasmic protein functional as a homodimer that binds copper and zink ions. SOD1 catalyzes the reaction O-2 + O-2 + 2H+ → H2O2 + O2, protecting the cell from oxidative damage. SOD1 was first cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli by [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3889846 Hallewell et al., (1985)].
| Gene (cDNA)
| 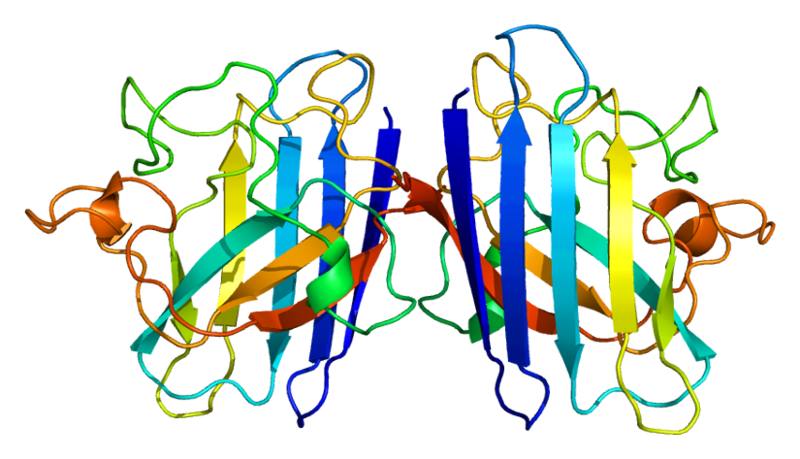
3D structure of human SOD1 in its dimeric form. Primary citation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20822138 Leinartaite et al. (2010)]
|
| Length
| 465 bp
|
| Edited nucleotide(s)
| nt331 A → G
|
| Removed restr. site(s)
| PfeI
|
| GenBank
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/38489879?report=genbank&log$=nucltop&blast_rank=22&RID=CAM83NYN01S AY450286.1]
|
| Protein
|
| Length
| 154 aa
|
| Size
| 15,936 Da
|
| Fasta
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/49456443?report=fasta SOD1]
|
| First reported by [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3889846 Hallewell et al., (1985)].
|
Yeast copper chaperon (yCCS)
Yeast copper chaperon protein (yCCS) is a helper chaperon specific for copper/zinc superoxide dismutase located to the cytoplasm. yCCS generates fully metallized, active SOD1 proteins that in turn protects the cell from oxidative damage.
yCCS has been shown to successfully mediate the delivery of copper ions to human SOD1 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15358352 Ahl et al. 2003]). Co-expression of SOD1 and yCCS yields proteins with higher copper contents, leading to increased activity and more stable proteins.
| Gene (cDNA)
| 
3D structure of yCCS interacting with yeast superoxide dismutase (ySOD) in it's monomeric form. Ions indicated as gray orbs. Primary citation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11524675 Lamb et al. 2001]
|
| Length
| 750 bp
|
| Edited nucleotide(s)
| nt257 T → C
|
| Removed restr. site(s)
| EcoRI
|
| GenBank
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_001182535.1?report=genbank&log$=seqview NM_001182535.1]
|
| Protein
|
| Length
| 249 aa
|
| Size
| 27,330 Da
|
| Fasta
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/596088?report=fasta yCCS]
|
First reported by [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9295278 Culotta et al. (1997)].
|
Human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)
| Gene (cDNA)
| 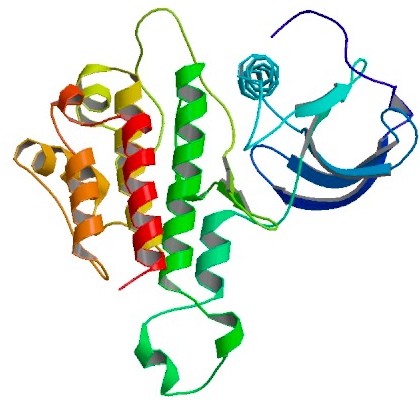
3D structure of bFGF. Primary citation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20133753 Bae et al. 2010]
|
| Length
| 468 bp
|
| Edited nucleotide(s)
| nt341 C → T
|
| Removed restr. site(s)
| AgeI
|
| GenBank
|
|
| Protein
|
| Length
| 155 aa
|
| Size
| 17,353 Da
|
| Fasta
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/153285461?report=fasta bFGF]
|
First reported by <unknown>
|
Protein A, z domain
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K380009 Part:BBa_K380009]
[[Image:|300px|thumb|right|]]
| Genepart
|
|
| length
| 174 bp
|
| removed restriction sites
| -
|
| exchanged nt
| -
|
| Protein
|
|
| length
| 58 aa
|
| size
|
|
| Fasta
|
|
GenBank:
First reported by:
IgG protease, IdeS
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K380010 Part:BBa_K380010]
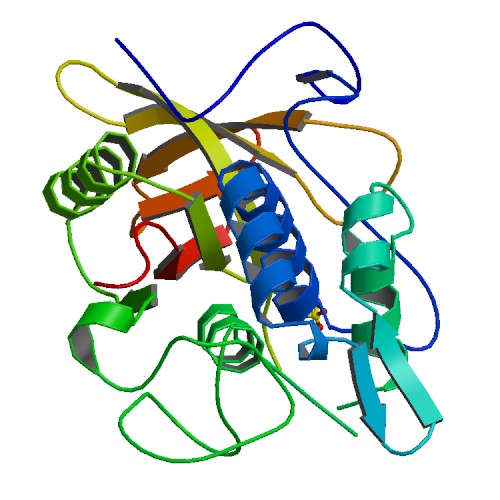 3D structure of IdeS. Primary citation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15574492 Wenig et al. 2004]
| Gene (cDNA)
|
|
| length
| 930 bp
|
| removed restriction sites
| -
|
| exchanged nt
| -
|
| Protein
|
|
| length
| 339 aa
|
| size
| 37,977 Da
|
| Fasta
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/209559219?report=fasta IdeS]
|
GenBank:
First reported by:
|















