Team:EPF Lausanne/Project droso
From 2010.igem.org


Contents |
Experiments on Drosophilia
The final goal of our project is for our modified Asaia to survive and produce proteins in the mosquito's gut. Working with mosquitoes however requires special equipment that we do not have at EPFL, and we wondered if we could work on another insect which is less demanding. We therefore turned towards Drosophila, commonly known as the fruit fly, which is much easier to work with.
Considering the fact that bacteria that live in the guts of insects are not very common, we assumed that there was a fair chance that Asaia could persist in Drosophila and that we could use the it as an alternative to mosquitos for our basic experiments.
Using Drosophila melanogaster we aimed to address two questions: </br> i) Is Asaia pathogenic for Drosophila? </br> ii) Is Asaia able to colonize the Drosophila gut and persist?
Our main results
1) Asaia is not toxic for Drosophila
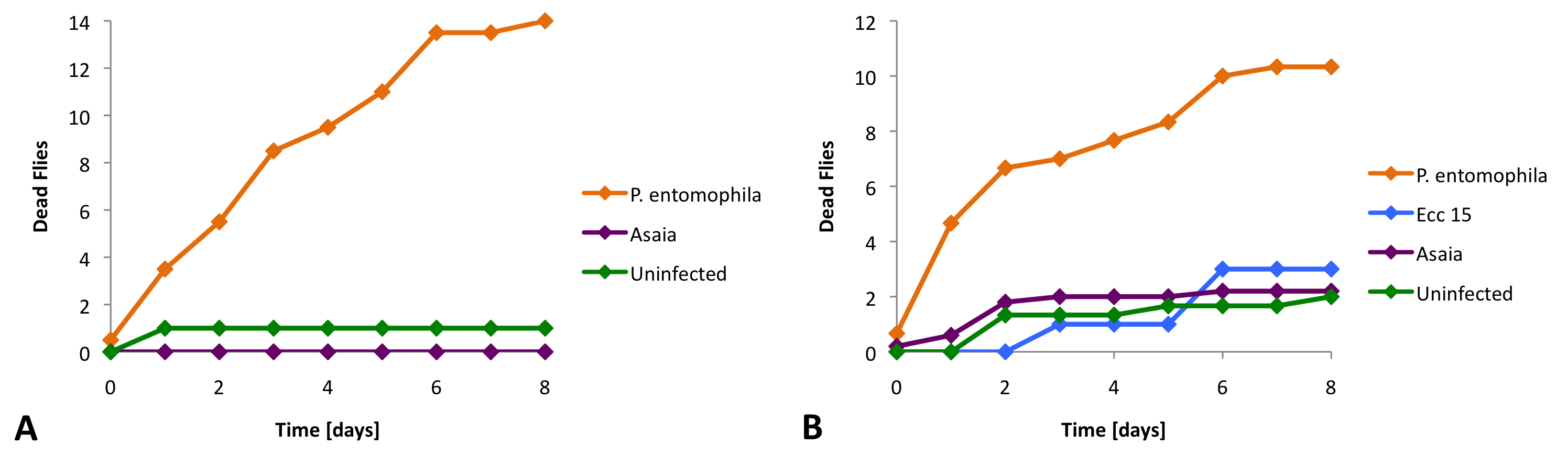
To find out if Asaia is toxic for Drosophila and if it can persist, we fed Asaia to flies. If we fed Asaia that expressed GFP to our flies, we could observe the fluorescent bacteria in the gut of the flies (Figure 1).
Then we moved on to find out more quantitatively if Asaia was toxic for our flies. We infected Drosophila with different bacterial strains, a pathogenic control starin (P. entomophila), a non-pathogenic control strain (Ecc 15) and our Asaia bacteria. For these experiments we used two different fly strains (Oregon and Relish). The strain Relish does not have an immune system. We found that Asaia does not cause significantly more deaths than the non-pathogenic bacteria or in the uninfected control (Figure 2).
2) Asaia is not persistant in Drosophila
With this last experiment we wanted to ascertain wether asaia persisted in drosophila and quantize how many asaia were present in the drosophila’s gut after 3h, 24h and 48h.
To be able to “count” the number of asaia at these three different periods of time, we had to retrieve the bacteria inside the flies, plate them and after incubation count the number of colonies present.
To do this we disinfected the exterior of the flies by washing them with ethanol (for less than five seconds) and then rinsing them with water. The flies were then crushed in the medium corresponding to the bacteria we were interested in (i.e: Gly+LB for asaia, LB for Pe, etc). We then did a serial dilution eleven times with a factor of ten with the crushed flies, and plated each dilution with antibiotics to specifically select the bacteria we were interested in.

 "
"