Team:Michigan/Project
From 2010.igem.org
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Hy-Bi: Pili Hyperexpression == | == Hy-Bi: Pili Hyperexpression == | ||
| - | [[Image:Michigan-Pili2.png|350px|thumb|left|Fig. 1]] | + | [[Image:Michigan-Pili2.png|350px|thumb|left|Fig. 1 An electron micrograph view of E. coli, with a close-up of the pili in the inset.]] |
Type 1 pili (also known as fimbriae) are proteinaceous adhesins that are found on the surface of E. coli. One cell can contain up to 100 pili, which can form up to 2 um long (Fig. 1)[1]. The pili help E. coli. form biofilms, and can also be involved in urinary tract infections. However, the strains of E. coli that our team worked with were strictly nonpathogenic. | Type 1 pili (also known as fimbriae) are proteinaceous adhesins that are found on the surface of E. coli. One cell can contain up to 100 pili, which can form up to 2 um long (Fig. 1)[1]. The pili help E. coli. form biofilms, and can also be involved in urinary tract infections. However, the strains of E. coli that our team worked with were strictly nonpathogenic. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<br style="clear: both" /> | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
[[Image:Michigan-Pili.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig. 2 A representation of a single pilus and how the different genes in the fim operon function.]] | [[Image:Michigan-Pili.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig. 2 A representation of a single pilus and how the different genes in the fim operon function.]] | ||
| - | [[Image:Michigan-PiliReg.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig. 3 The recombinases FimB and FimE | + | [[Image:Michigan-PiliReg.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig. 3 The recombinases FimB and FimE regulate the fim operon via an invertible segment of DNA.]] |
| - | [[Image:Michigan-PiliReg2.png|200px|thumb|left|Fig. 4 ]] | + | [[Image:Michigan-PiliReg2.png|200px|thumb|left|Fig. 4 A model that illustrates the different states of the regulatory system.]] |
<br style="clear: both" /> | <br style="clear: both" /> | ||
Revision as of 22:40, 21 September 2010
Overall project
Our team decided to work on two projects simultaneously this year. The first involves making an efficient microalgae bioflocculant out of E. coli to improve oil harvesting from algae. For this project, we will be over-expressing type I pili and their associated adhesion protein, making a hyper-piliated, hyper-adhesive strain of E. coli. We hope that the extreme stickiness of the E. coli will turn them into an excellent bioflocculant- termed EcoGlue. In addition, we will also be expressing a virus protein which specifically binds to the algal species Chlorella vulgaris, a species of interest for harvesting algae oil. This protein will provide additional flocculation ability and specificity for this species. We hope that such a bioflocculant can provide a cheaper, safer alternative to chemical flocculants.
Our second project is working on the oil sands initiative, where we will be trying to reduce the reclamation time of tailings water, which must generally be retained for over 10 years. These waters are tainted with toxic naphthenic acids (NAs), and we will be trying to indirectly improve the natural degradation abilities of two Pseudomonas species, which were previously isolated from tailings pond sediment and found to degrade NAs. Since little to nothing is known about the degradation pathway itself, it is difficult to manipulate the pathway, however, these two species have a synergistic metabolism, and the efficiency of degradation is drastically increased when they are co-cultured. So we will be introducing a self-dimerizing surface protein into the two species, in order to ensure that they stick together, and also potentially increase their flocculation abilities, as we have seen that Pseudomonas to not make biofilms at the high pH levels seen in tailings waters. We want these bacteria to be in a biofilm in hopes that it will increase the efficiency and rate of their NA degradation. We will also be cloning a gene into both species that triggers dense, thick biofilms when over-expressed. This gene also prevents biofilm dispersal under carbon starvation, ensuring that a biofilm will stick around in one place even as NA levels diminish, ensuring degradation to the lowest level possible.
We also decided to split our team into multiple modules that will be working in parallel in order to increase our own efficiency. The work of each module is described in more depth below.
Hy-Bi: Pili Hyperexpression
Type 1 pili (also known as fimbriae) are proteinaceous adhesins that are found on the surface of E. coli. One cell can contain up to 100 pili, which can form up to 2 um long (Fig. 1)[1]. The pili help E. coli. form biofilms, and can also be involved in urinary tract infections. However, the strains of E. coli that our team worked with were strictly nonpathogenic.
The pili are controlled by the fim operon. This operon consists of several genes, FimA-H. The pili themselves are composed of several thousand subunits of FimA. The tip of each pili consists of the genes FimF, FimG, and FimH. FimH is an adhesin and is linked to FimA through FimF and FimG. Inside the cell, FimC carries proteins to the structural platform, FimD, which then assembles the pilus rod (Fig. 2)[2]. This whole process is regulated by the recombinases FimB and FimE. These genes control an invertible DNA sequence, which, when in the "on" position, promotes the production of pili (Fig 3).
The pili neural network has been characterized in several papers [1][2]. Essentially, the two recombinases FimB and FimE control an invertible DNA element that acts as a switch, known as FimS. When FimS is in the "on" position, the cell becomes fimbriated. It has been previously determined that the level of piliation depends on the ratio [FimE]/[FimB]. Fig 4 describes the pili regulatory system as a stochastic model. There is only one stable state, when FimB and FimE are both off. After FimB turns on, the cell starts to grow pili and accumulate FimE. When the cell reaches a critical amount of FimE, the cell stops producing pili and the system returns to the stable state. It has been shown that removing the FimE gene will cause the cell to constantly flocculate.
The reason we are so interested in the pili is their capability to flocculate. Several papers have shown that the pili bind to mannose through FimH. By overproducing the pili, we hope to increase flocculation. We plan to accomplish this goal by putting the FimB gene on a plasmid. You can find the pili team's lab notebook here.
Hy-Bi: Quorum Sensing
Our cells will use quorum sensing to determine when the flocculation will start. The cells will produce an inducer either AHL or AI-2. You can find their lab notebook here.
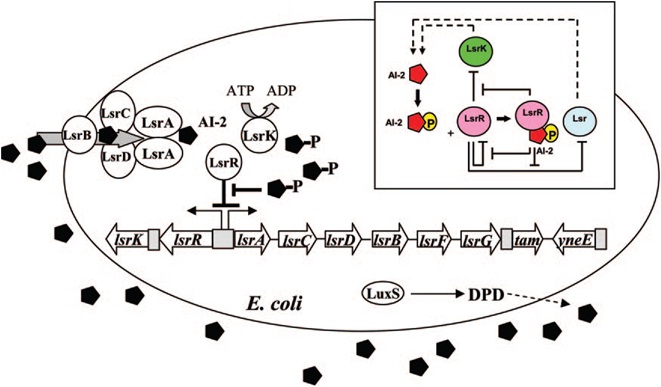
E. coli cells detect their population density by a method known as "quorum sensing." All cells produce a molecule known as Auto-Inducer 2 (AI-2) via the gene LuxS. AI-2 is actively imported via a complex of Lsr membrane proteins, after which it is phosphorylated and binds to the repressor LsrR. This binding relieves the Lsr operon from repression, increasing levels of both the AI-2 import and phosphorylation and of LsrR. The net effect is that cells respond to a threshold concentration of AI-2 (a threshold population density) by altering expression of many genes. E. coli, for example, tends to increase biofilm production in response to AI-2.
Certain species of microalgae useful for harvesting as biofuel, specifically Chlorella vulagris, have been characterized as releasing compounds that mimic the action of AI-2 or AHL, activating the quorum sensing circuits of many bacteria, including Vibrio harveyi, which responds to the same compound as E. coli, AI-2.
The goals of the quorum sensing team are two-fold: first to characterize the response of E. coli to the C. vulgaris AI-2 mimic (which may be actual AI-2), and second to engineer E. coli to flocculate in response to the presence of C. vulgaris. The first task will be accomplished by transforming a LuxS-mutant strain of E. coli (cannot produce its own AI-2) with an AI-2 reporter biobrick. We will then harvest supernatant from C. vulgaris, which should contain AI-2 or its mimic, and apply it to the reporter strain to test its response. The second task will be accomplished by ligating a gene that causes over-expression of pili (characterized by the pili team) to the Lsr promoter, which is derepressed in response to AI-2. By transforming this part into LuxS-mutant E. coli, we hope to create strain that will stick to algae and will flocculate only in the presence of C. vulgaris.
(Li, et. al.)
Hy-Bi: Virus Protein Surface Display
The idea is to express algae-binding proteins on the surface of E. Coli in order to cause flocculation.
Oil Sands: Ag43 Expression
Oil Sands: YhcK Over-Expression
References
1. Hahn, E., Wild,P., Hermanns, U., Sebbel, P., Glockshuber, R., Haner, M., Taschner, N., Burkhard, P., Aebi, U., A. Muller, S., Exploring the 3D Molecular Architecture of Escherichia coli Type 1 Pili, Journal of Molecular Biology 323 845-857 (2002)
2. Vetsch, M., Puorger, C., Pilus chaperones represent a new type of protein-folding catalyst. Nature 431, 329-332 (2004).
1. Kuwahara, H., Myers, C., Samoilov, M., Abstracted Stochastic Analysis of Type 1 Pili Expression in E. Coli.
3. Wolf, D., and Arkin, A., Fifteen Minutes of fim: Control of Type 1 Pili Expression in E. Coli. OMICS 6 2002
5. Schwan, W., Shibata, S., Aizawa, S., and Wolfe, A., The Two-Component Response Regulator RcsB Regulates Type 1 Piliation in Escherichia Coli Journal of Bacteriology 189 7159-7163 (2007)
3. Li, J., Atilla, C., Wang, L., Wood, T. K., Valdes, J. J., Bently, W. E. Quorum Sensing in Escherichia coli Is Signaled by AI-2/LsrR: Effects on Small RNA and Biofilm Architecture. Bacteriology. 189: 6011-6020 (2007).
 "
"