Team:Stockholm/12 August 2010
From 2010.igem.org
NinaSchiller (Talk | contribs) (/* Map from String database [http://string.embl.de/version_8_3/newstring_cgi/show_network_section.pl?identifiers=9606.ENSP00000347190%250D9606.ENSP00000226877%250D9606.ENSP00000368424%250D9606.ENSP00000264498%250D9606.ENSP00000269280%250D9606.ENSP000) |
NinaSchiller (Talk | contribs) (→Nina) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
==Nina== | ==Nina== | ||
| - | + | ||
==Mini prep on protein A (ZZ domain)== | ==Mini prep on protein A (ZZ domain)== | ||
Revision as of 22:55, 13 August 2010
Contents |
Hassan
Map from [http://string.embl.de String database] [http://string.embl.de/version_8_3/newstring_cgi/show_network_section.pl?identifiers=9606.ENSP00000347190%250D9606.ENSP00000226877%250D9606.ENSP00000368424%250D9606.ENSP00000264498%250D9606.ENSP00000269280%250D9606.ENSP00000228280%250D9606.ENSP00000295600%250D9606.ENSP00000241052%250D9606.ENSP00000360157%250D9606.ENSP00000302777%250D9606.ENSP00000373571%250D9606.ENSP00000267082%250D9606.ENSP00000281043%250D9606.ENSP00000343052%250D9606.ENSP00000364094%250D9606.ENSP00000257880&channel1=off&channel2=off&channel3=off&channel4=on&channel5=on&channel6=on&channel7=on&interactive=yes&limit=0&network_flavor=actions&targetmode=proteins]
- SOD3 Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] precursor (EC 1.15.1.1) (EC-SOD); Protect the extracellular space from toxic effect of reactive oxygen intermediates by converting superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen (240 aa)
- KITLG Kit ligand precursor (C-kit ligand) (Stem cell factor) (SCF) (Mast cell growth factor) (MGF); Stimulates the proliferation of mast cells. Able to augment the proliferation of both myeloid and lymphoid hematopoietic progenitors in bone marrow culture. Mediates also cell-cell adhesion. Acts synergistically with other cytokines, probably interleukins (273 aa)
- CAT Catalase (EC 1.11.1.6); Occurs in almost all aerobically respiring organisms and serves to protect cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide. Promotes growth of cells including T-cells, B-cells, myeloid leukemia cells, melanoma cells, mastocytoma cells and normal and transformed fibroblast cells (527 aa)
- ITGA7 Integrin alpha-7 precursor [Contains- Integrin alpha-7 heavy chain; Integrin alpha-7 light chain]; Integrin alpha-7/beta-1 is the primary laminin receptor on skeletal myoblasts and adult myofibers. During myogenic differentiation, it may induce changes in the shape and mobility of myoblasts, and facilitate their localization at laminin-rich sites of secondary fiber formation. It is involved in the maintenance of the myofibers cytoarchitecture as well as for their anchorage, viability and functional integrity. Isoform Alpha-7X2B and isoform Alpha-7X1B promote myoblast migration on lamin [...] (1162 aa)
- FGF2 Heparin-binding growth factor 2 precursor (HBGF-2) (Basic fibroblast growth factor) (BFGF) (Prostatropin); The heparin-binding growth factors are angiogenic agents in vivo and are potent mitogens for a variety of cell types in vitro. There are differences in the tissue distribution and concentration of these 2 growth factors (288 aa)
- ITGB7 Integrin beta-7 precursor; Integrin alpha-4/beta-7 (Peyer patches-specific homing receptor LPAM-1) is an adhesion molecule that mediates lymphocyte migration and homing to gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). Integrin alpha-4/beta-7 interacts with the cell surface adhesion molecules MADCAM1 which is normally expressed by the vascular endothelium of the gastrointestinal tract. Interacts also with VCAM1 and fibronectin, an extracellular matrix component. It recognizes one or more domains within the alternatively spliced CS-1 region of fibronectin. Interactions involves the tripeptide L [...] (798 aa)
- NLRP1 NACHT, LRR and PYD-containing protein 1 (Death effector filament- forming ced-4-like apoptosis protein) (Nucleotide-binding domain and caspase recruitment domain) (Caspase recruitment domain protein 7); Able to form cytoplasmic structures termed death effector filaments. Enhances APAF1 and cytochrome c-dependent activation of pro-caspase-9 and consecutive apoptosis. Stimulates apoptosis through activation of caspase-3. Involved in activation of caspase-1 and caspase-5 as part of the NALP1 inflammasome complex which leads to processing and release of IL1B and IL18. Binds ATP (1477 aa)
- MYCN N-myc proto-oncogene protein; May function as a transcription factor (464 aa)
- MITF Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; Transcription factor for tyrosinase and tyrosinase- related protein 1. Binds to a symmetrical DNA sequence (E-boxes) (5'-CACGTG-3') found in the tyrosinase promoter. Plays a critical role in the differentiation of various cell types as neural crest- derived melanocytes, mast cells, osteoclasts and optic cup-derived retinal pigment epithelium (526 aa)
- PAX3 Paired box protein Pax-3 (HUP2); Probable transcription factor associated with development of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (505 aa)
- CTNNA1 Catenin alpha-1 (Cadherin-associated protein) (Alpha E-catenin) (NY- REN-13 antigen); Associates with the cytoplasmic domain of a variety of cadherins. The association of catenins to cadherins produces a complex which is linked to the actin filament network, and which seems to be of primary importance for cadherins cell-adhesion properties. May play a crucial role in cell differentiation (929 aa)
- FOXD3 Forkhead box protein D3 (HNF3/FH transcription factor genesis); Binds to the consensus sequence 5'-A[AT]T[AG]TTTGTTT-3' and acts as a transcriptional repressor. Also acts as a transcriptional activator. Promotes development of neural crest cells from neural tube progenitors. Restricts neural progenitor cells to the neural crest lineage while suppressing interneuron differentiation. Required for maintenance of pluripotent cells in the pre-implantation and peri-implantation stages of embryogenesis (478 aa)
- ITGB1 Integrin beta-1 precursor (Fibronectin receptor subunit beta) (Integrin VLA-4 subunit beta) (CD29 antigen); Integrins alpha-1/beta-1, alpha-2/beta-1, alpha-10/beta- 1 and alpha-11/beta-1 are receptors for collagen. Integrins alpha- 1/beta-1 and alpha-2/beta-2 recognize the proline-hydroxylated sequence G-F-P-G-E-R in collagen. Integrins alpha-2/beta-1, alpha- 3/beta-1, alpha-4/beta-1, alpha-5/beta-1, alpha-8/beta-1, alpha- 10/beta-1, alpha-11/beta-1 and alpha-V/beta-1 are receptors for fibronectin. Alpha-4/beta-1 recognizes one or more domains within the alternatively spliced CS-1 and [...] (825 aa)
- PAX6 Paired box protein Pax-6 (Oculorhombin) (Aniridia type II protein); Transcription factor with important functions in the development of the eye, nose, central nervous system and pancreas. Required for the differentiation of pancreatic islet alpha cells (By similarity). Competes with PAX4 in binding to a common element in the glucagon, insulin and somatostatin promoters. Regulates specification of the ventral neuron subtypes by establishing the correct progenitor domains (By similarity). Isoform 5a appears to function as a molecular switch that specifies target genes (436 aa)
- TYRP1 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid oxidase precursor (EC 1.14.18.-) (DHICA oxidase) (Tyrosinase-related protein 1) (TRP-1) (TRP1) (TRP) (Catalase B) (Glycoprotein 75) (Melanoma antigen gp75); Oxidation of 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) into indole-5,6-quinone-2-carboxylic acid. May regulate or influence the type of melanin synthesized (537 aa)
- MC1R Tubulin beta-3 chain (Tubulin beta-III) (Tubulin beta-4); Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha-chain (By similarity) (797 aa)
Nina
Mini prep on protein A (ZZ domain)
I performed a mini prep on the three inoculated protein A ZZ domain in the bank vector C samples from colony # 5. The method was according to the procedure described under Protocols. The samples in each tube were collected in a single epp tube.
spectrophotometer: 400 ng/ul
- λ260: 0.070
- λ280: 0.039
- λ315: 0.008
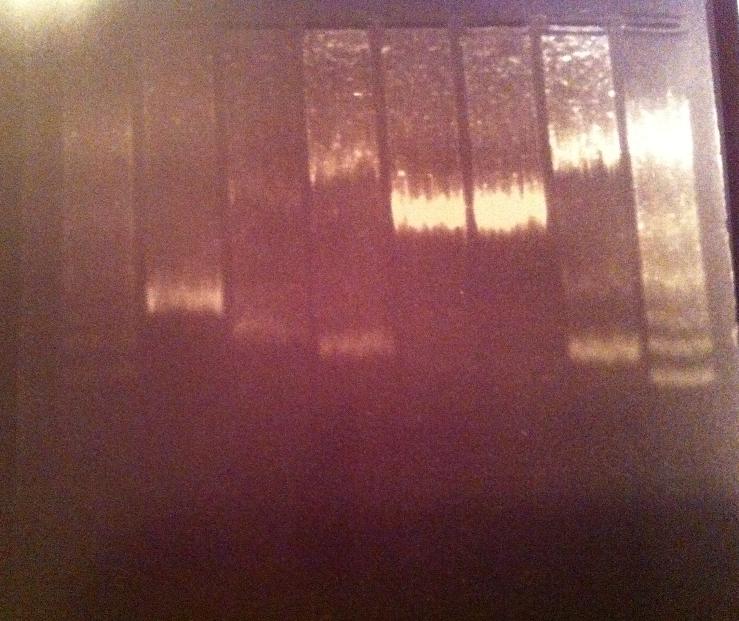
PCR on protein A (ZZ domain) and IgG protease
I ran a PCR on protein A ZZ domain in the bank vector C, protein A in original vector from 21/7, IgG protease in bank vector A, C and K and also an IgG protease control from miniprep #17 from 1/7.
PCR master mix for 6 tubes:
- MgCl2 6 ul
- Buffer phusion 5X 60 ul
- dNTP 10 uM 6ul
- primer VR 10 uM 18 ul
- polymerase PjuX7 6 ul
- H2O 180 ul
Aliquate 46 ul in each pcr tube. Add 1 ul DNA template and 3 ul protein A ZZ domain forward primer to the protein A ZZ domain samples and 3 ul igG protease forward primer to the IgG protease samples.
I ran 5 ul of the PCR products with 1 ul 6X loading dye on an 1 % agarose gel 120 V.
Ladder: GeneRuler™ DNA Ladder Mix, ready-to-use, 100-10,000 bp Fermentas
Unfortunately the gel looks very blurry, this might have occured by not dissolving the agarose well in the TAE 1X buffer. I don't think the problem lays in the amount of sample loaded in the gel nor the high voltage since even the ladder looks blurry.
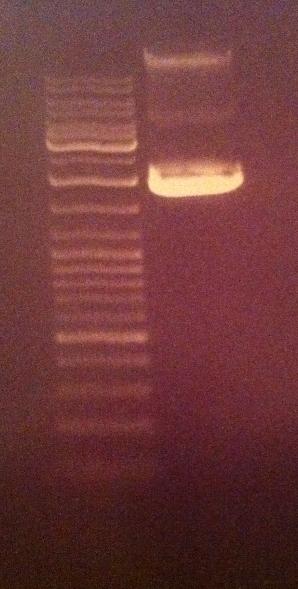
Gel verification of undigested tyrosinase
I ran 5 ul of the undigested tyrosinase from tube 4/8-2010 with 1 ul 6X loading dye in an agarose 1 % gel 80 V.
Ladder: GeneRuler™ DNA Ladder Mix, ready-to-use, 100-10,000 bp Fermentas
This undigested sample looks compared to the NgoMIV digested tyrosinase vector control from yesterday to have travelled further down, meaning that the digested tyrosinase has indeed become cut. A circular vector travels further in an agarose gel compared to a cut linjerized vector.
Andreas
IgG protease cloning
In order to identify the problems with cloning IgGp into pSB1C3, the previously digested samples (pSB1A3.IgGp & pSB1C3.BBa_J04450) were run on a gel to identify correct bands. Also, a PCR verification was prepared from both samples.
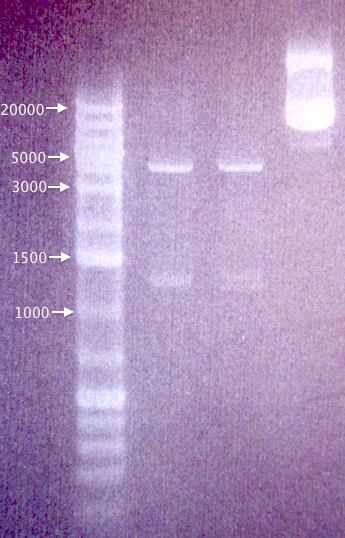
Gel verification of digested samples
Undigested and digested samples of pSB1A3.IgGp and pSB1C3.BBa_J04450, as well as an additional clone of pSB1C3.BBa_J04450 (4), in case the originally used (3) was defective; both samples from 3/8.
Results
Correct-sized bands for undigested (≈3100 bp) and digested (≈2100 bp, ≈1100 bp) pSB1C3.BBa_J04450.
Very strange-sized bands for undigested and digested pSB1A3.IgGp, not corresponding to what was expected (Undig.: ≈3100 bp; Dig.: ≈2160 bp, ≈990 bp).
Plasmid PCR verification
Ran a PCR with pSB verification primers (VF2 and VR) to verify the DNA from each of the two samples used for digestion/ligation (pSB1A3.IgGp & pSB1C3.BBa_J04450).
Procedures
As described in the colony PCR protocol in our Protocols page.
Gel verification
1 %, 100 V, 40 min
Results
Correct band (1400 bp) for pSB1C3.BBa_J04450.
A strong incorrectly sized band at ≈2500 bp for pSB1A3.IgGp, and a weak correct-sized band (1260 bp).
Seems like the IgGp sample is contaminated, resulting in more than one digestion and (colony) PCR amplification product. Sample returned to Nina who will take over the IgGp cloning.
MITF troubleshooting
Re-ran three samples for Mimmi to get a better gel result.
Results
Bands corresponding to pRc/CMV vector lacking the MITF insert (Mimmi's calculations). Possible that we have received an empty vector, which would explain our failed PCR amplifications of the MITF gene.
 "
"