|
Motivation
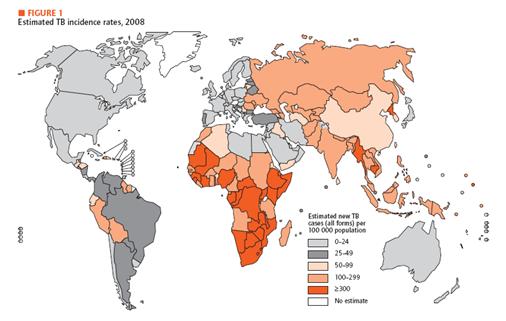
We are suffering from various kinds of diseases. Three most prevalent ones would be malaria, HIV and tuberculosis. Malaria is transmitted from human to human by mosquitoes. Each year, malaria causes nearly one million deaths, and the majority of casualties occur in Africa. Furthermore, disease is high-risk in children, pregnant women, travelers, refugees, displaced persons, and laborers entering endemic areas. In the case of HIV, there are 33 million infected people in the world and 95 percent of them are living in developing countries. Last but not least, there is tuberculosis, which is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis, affecting lungs most. Until now, more than 2 billion people are infected with tuberculosis bacilli and 90 percent of them live in developing countries. As we can see, all of these diseases are especially problematic in developing country.
Fig 1. Estimated TB incidence rates, 2008
In developing country, economic is unstable, and development in medical technology is not a priority. Unfortunately, basic medical examination like blood tests, biopsy and others need certain foundation of medical technology. In addition, some areas in developing countries do not offer electricity or access to high-tech equipments. Therefore, we need new and affordable diagnosis system especially for the diseases mentioned above. For our system, we choose TB as a target. In recent decades, diagnosis and treatment of TB have been developed. Diagnostic methods include Tuberculin Skin Test, X-ray Test for its activation and examination of the sputum. In addition, people take a blood test that involves ESR, white blood cell, CRP status checking. If necessary, CT scan and endoscopy can be performed. Most of these tests, however, require high technology and proper machines. Therefore, in developing countries, these tests are not really options. As an alternative, we introduce DiscoverY.
Fig 2. People suffering from malaria and TB Fig 3. Researching disease
We suggest a system using antigen-antibody reaction. Actually, antibody cannot release perceivable signals by antigen-antibody reaction alone, so we thought of fusion antibody-receptor as the solution. Fusion antibody-receptor is a receptor which is fused with other functional protein, antibody. In this way, we can get result by gene expression which would generate GFP expression after our system is triggered by target antigens. As the result, we may develop universal sensor by changing only target antigen’s antibody in fusion antibody-receptor. It will provide relatively simple and direct way of diagnosis.
Fig 4. Antibody
Whole Pathway
|
DiscoverY pathway
|
|
1. 'DiscoverY' is spread on the sample. |
|
2. 'DiscoverY’s antibody combines with the antigen on the Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
|
3. The tyrosine kinase receptor FGFR bind to the cytokine receptor integral to membrane. |
|
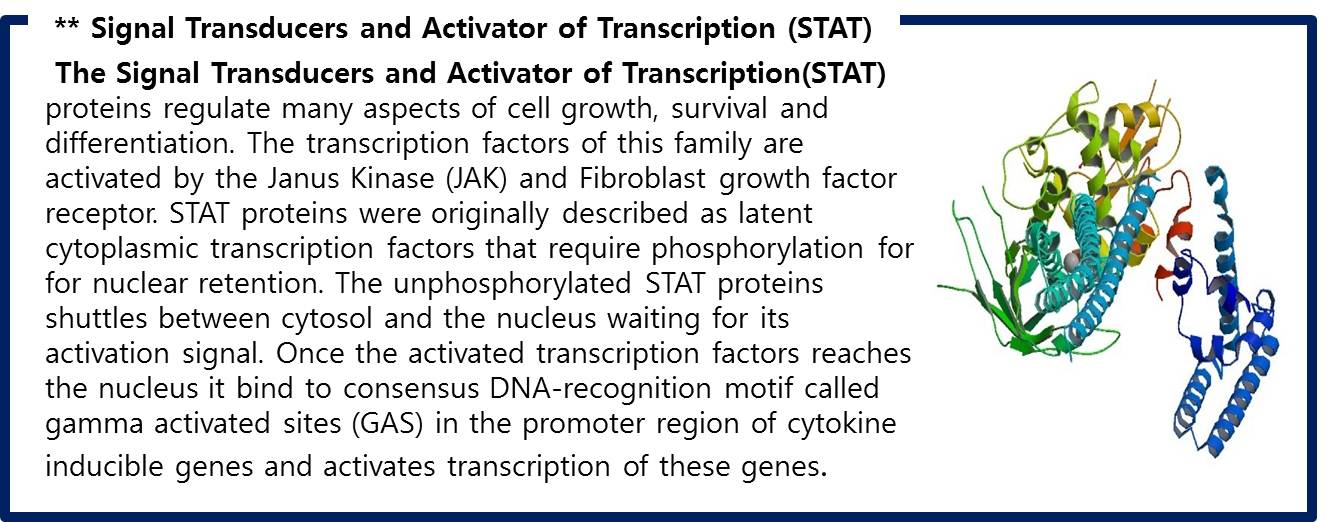
4. FGFR autophosphorylation activates transcription factors called STAT1. |
|
5. The activated STAT1 dissociate from the receptor. |
|
6. The activated STAT1 form dimers. |
|
7. The STAT1 dimer go into nucleus and regulates GFP gene that attached to GAS elements of promoter. |
|
8. 'DiscoverY' expresse GFP. |
Antibodies for Detecting
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
The major problem of Tuberculosis is including the prevalence of multi-drug-resistant strains and co-infection with human immunodeficiency virus. We found a report, and that is written that MPT51 is over-expressed on the tuberculosis cell membrane. So, we thought that we can use MPT51 as a antigen to detect tuberculosis. The reason why we selected these proteins is that they are differently over-expressed. Also, other normal human cell in our body does not have MPT51 protein on a cell. Therefore, if we can detect the existence of MPT51 on a cell, we could know that someone has tuberculosis or not. So, we will make fusion antibody that can cognize MPT51 as an antigen, and put it into yeast.
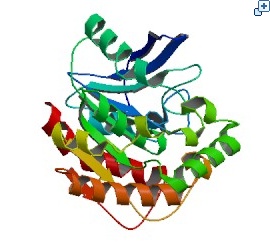 Fig. 5 The crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis MPT51
Fig. 5 The crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis MPT51
Making Biosensor – Yeast Detector
Biosensor
A biosensor is a device for the detection of an analyst that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector component.[1] In order to make biosensor with genetically engineered organism, we should consider the following basic sensing process.
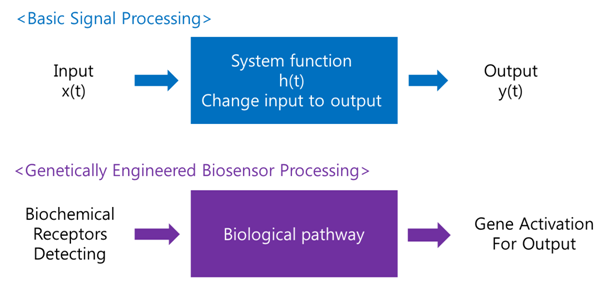
Receive input -> Process -> Extract output
The ‘Receive input’ part can be alternated by represented receptor, the ‘Process’ part can be signaling pathway which changes input to output, and the ‘Extract output’ part can be something easily detectable by human. Nowadays, pigments or fluorescence proteins are usually used for output, and in order to express these substances, gene expression is made constant use in genetically modified organism. Thus, all engineered biosensors with organisms should be modeled on (consist of) 1) biochemical receptors which can activate gene expression, 2) biological pathway, and 3) gene activation for output.
Organism Decision : Why Yeast?
Why we use ‘Yeast’ instead of ‘E. coli’?
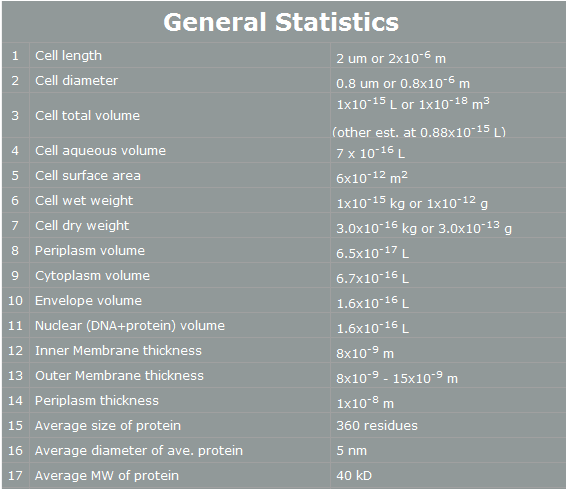
E. coli control is easier than Yeast control. E. coli has faster cell cycle than Yeast. Moreover, there are many E. coli templates. But, although E. coli has many profits, we choose Yeast. Why? The following table is E. coli properties.[2]
Fig 6. E.coli statistics
According to the table, we can find easily some reasons that E. coli cannot work human pathway well.
First, the periplasm’s thickness of E. coli is the very small as 10nm. In our project, we have to use human proteins. Almost human proteins are much bigger than E. coli’s proteins. (They are over 10nm*10nm*10nm.) Furthermore, in our project, FGFR has 20nm height. Therefore, this protein cannot be in periplasm, and our pathway cannot work completely.[3]
Second, the average E. coli protein has only 360 residues, 5nm diameter, and 40kD MW. As we mentioned, our project’s proteins have over 1000residues, 10nm diameter and 50kD MW. Thus, the possibility that E. coli have our pathway is very low.
However, Yeast has big volume size from 3~4 µm to 40 µm. [4] And Yeast is a eukaryotic, so it is more similar to human cell than E. coli. There is no physical problem of using human protein in yeast. And has more possibility to do our pathway. Therefore, we use Yeast instead of E. coli.
Organism Decision : Minimal genome fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe
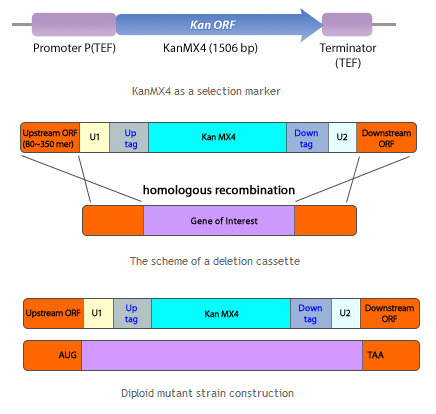
Porting of cell signal transduction pathway is not easy for wild type organism. Most important reason is unwanted protein degradation. For wild type organism, unfamiliar protein can be harmful because it may be fragmented or misfolded proteins which disturb cellular pathway or viral proteins which may infect organisms. So wild type organism degrade unfamiliar proteins whether it is really harmful or not. And even degradation of at least one element of signal transduction pathway can disconnect whole pathway. So for successful porting of cell signal transduction pathway, inhibition of protease is important. Another problem is signal confusion. Basically, cellular signal transduction pathway is based on the protein-protein interaction(PPI). So unwanted PPI with elements of ported signal transduction pathway can confuse the signal. Of course if origin species of ported pathway is far enough from target species, we can exclude predictable unwanted PPI to avoid homologous proteins. But there are many unpredictable PPIs which can confuse the pathway. To avoid this problems, deletion of unnecessary proteins is required. And fission with minimal genome is made[5]. This yeast have only 1033 necessary genes of 5776 genes from wild type. So it may be useful to port cell signal transduction pathway from other organism(Human) without unwanted protein degradation or signal confusion.
Fig 7. Schizosaccharomyces pombe homologus recombinant
Schizosaccharomyces pombe (S. pombe) Deletion Mutant Library Sets were created by Dr. Kwang-Lae Hoe at KRIBB (Korea Research Institute of Biotechnology and Bioscience, Korea) through collaboration with Sir Paul Nurse at CRC (Cancer Research Center, UK, currently at the Rockefeller University in USA) and Bioneer based on the genome sequences of the S. pombe provided by the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. This genome-wide S. pombe deletion collection covers more than 98% of genome consisting of 4,914 genes. As each deletion strain has its distinct tags, functional analysis can be performed both in a gene-specific manner and a genome-wide scale. Two different sets of mutant collections are available: h+ haploids and h+/ h+ diploids.
Biochemical Receptors Selection
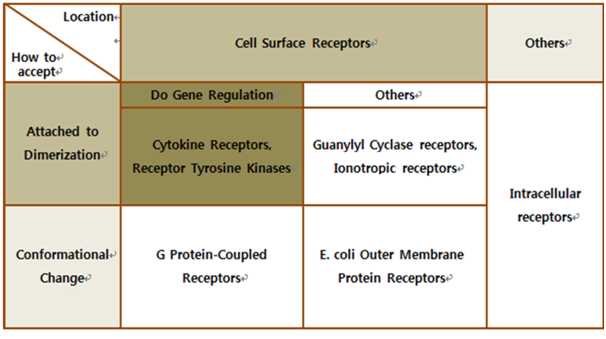
The upper table represents classification of all biological receptors. First of all, since our genetically engineered machine has to detect on mycobacteria directly, we should select cell surface receptors. Next, we should consider using fusion-antibody-receptors. We used gene combination simply (add antibody to biological receptor without original receipt part). If the receptor has conformational change property when it accepts input signal, we guess that our fusion antibody receptor cannot operate well because antibodies characteristics (antigen size, antibody size, etc.) are different. They don’t have special receipt part in a whole receptor, of course, so whole receptor is important receipt part; we cannot create fusion-antibody-receptor with this protein anyway. Therefore, we choose ‘Dimerization’ receptor. Most of these receptors have Immunoglobulin-like receptor part which can be alternated by antibodies easily. Also, since biosensors should activate gene expression, we selected gene-regulation related receptors.
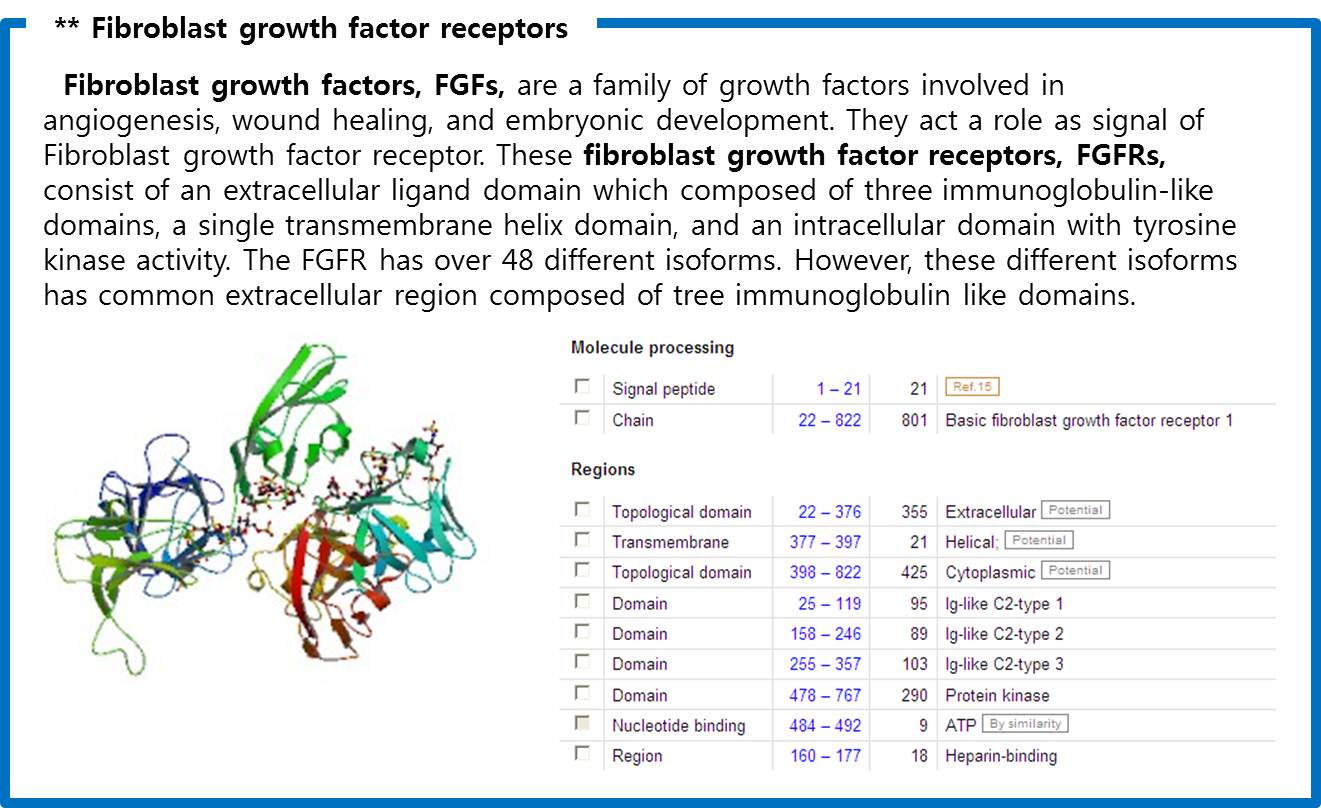
Finally we choose cytokine receptors and receptor tyrosine kinases. Among them, Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR) in receptor tyrosine kinases was selected.
Fig 8. Crystal structure of a ternary FGF-FGFR-heparin complex
Fusion Antibody Receptor Making
The Fusion Antibody-Receptor is a protein which receptor genetically combines with a specific antibody. The following figures show what the fusion antibody-receptor is for details.
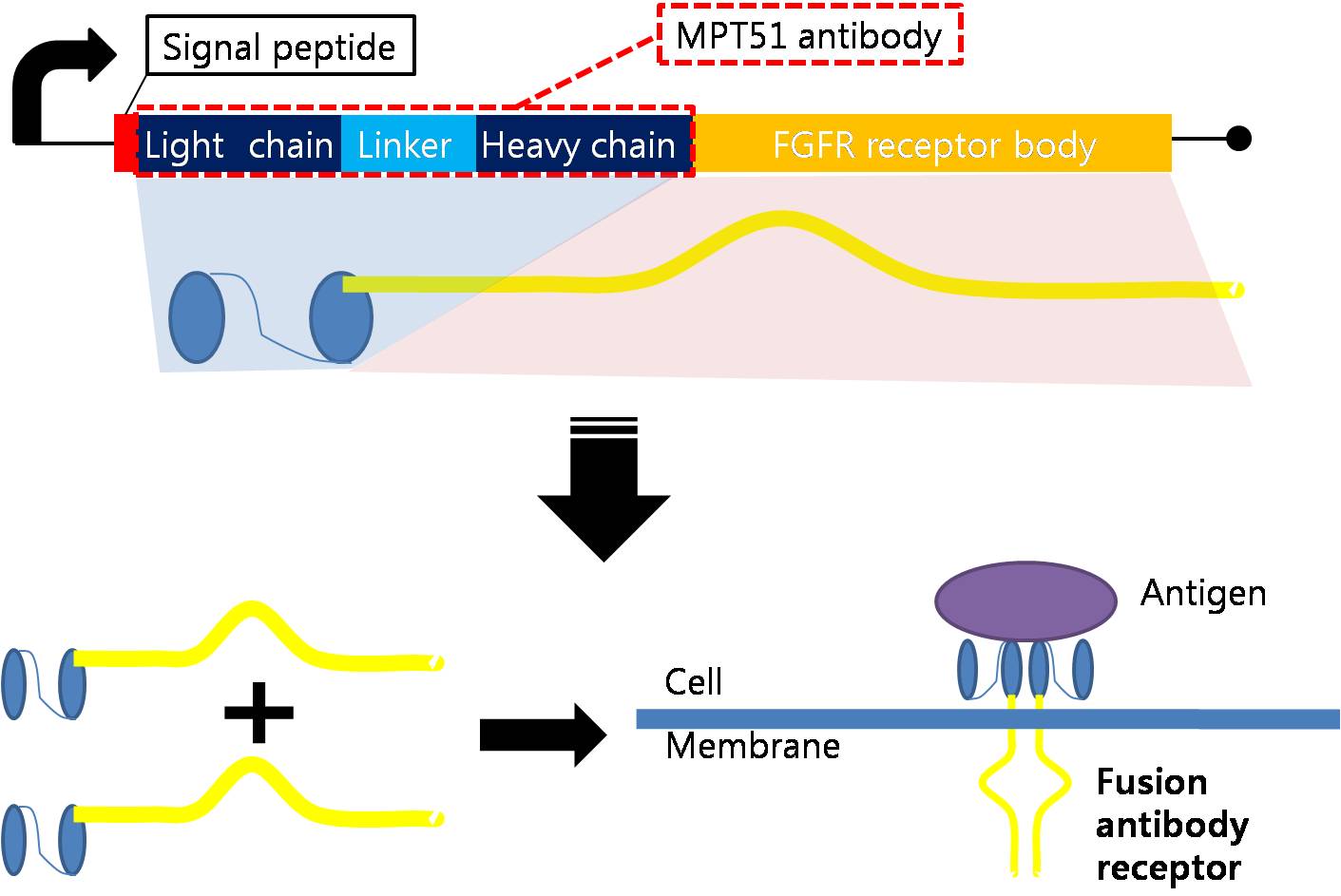
The fusion antibody-receptor is designed by simple gene modification. We altered the Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen detectable antibody single chain instead of the FGFR receptor’s antigen acceptable part (Immunoglobulin-like parts). Light chain part of the antibody – Linker – Heavy chain part of antibody is enough. (There are some evidences to success making fusion antibody-receptor with this method in some experiments. [4]) Then in order to express the receptor on cell surface membrane of Schizosaccharomyces pombe, we change the original signal peptide to outer membrane signal peptide of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Surely the receptor should satisfy our standard for biosensor.
|
|
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Signal peptide for cell surface from Cell wall integrity and stress response component 1
Protein sequence:
MVFLNSSPFKGRLLFFVYLLIISTRLVAA
mRNA sequece:
atggtgtttctgaacagcagcccgtttaaaggccgcctgctgttttttgtgtatctgctgattattagcacccgcctggtggcggcg
|
Signaling Pathway Research
There are many signal pathways from plasma membrane receptor to the gene regulation. Here is an famous example of these pathways, MAP kinase pathway linked with RAS pathway. In this pathway,
- With existence of signal molecule, receptor kinases dimerize themselves and phosphorylate each other.
- This phosphorylated receptor dimer is cognized by Grb2 and recruit SOS protein, the Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor(GEP)
- Recruited SOS protein substitute as GDP of Ras protein with GTP.
- Ras protein with GTP changes its conformation and activate its own kinase activity(Ras pathway so far)
- Ras kinase activate the MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP KKK(also called as Raf protein) with phosphorylation
- MAP KKK activates the MAP kinase kinase, MAP KK(also called as Mek) with phosphorylation
- MAP KK activates the MAP kinase, MAP K(also called as Erk) with phosphorylation
- Activated MAP Kinase phosphorylates many cytosol proteins.
- For example, if Jun TF is phosphorylated by MAP K, phosphorylated Jun go inside of nucleus and activate the transcription to bind to DNA. (MAP pathway so far)
But to port this signal pathway into the Yeast is not easy because this pathway is related with too many new proteins, so we should have found the simplest pathway. The followings are our history of the change in pathways. You can see the details 'Memo-etc page' in our wiki
(1) Interleukin-1 pathways (8 proteins are required.)
(2) Interleukin-6 JAK-STAT pathways (6 proteins are required.)
(3) Fc Epsilon pathways (5 proteins are required.)
(4) FGFR AP-1 pathways (4 proteins are required.)
(5) FGFR STAT1 pathways (3 proteins are required.)
Finally, we selected FGF signaling pathway which is the easiest way. The signal transduction step of FGF signaling pathway pathway as follows.
Signaling Pathway Research : Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling Pathway
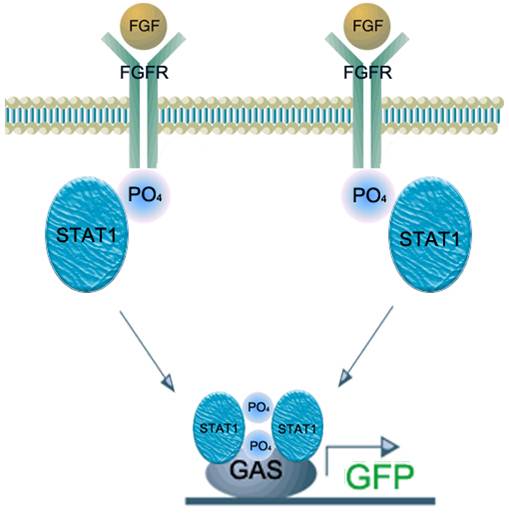
Fig.9 FGF signaling pathway
This figure show simple pathway of FGF(Fibroblast Growth Factor) and FGFR(Fibroblast Growth Factor).
FGF is a growth factor concerned with wound healing and embryonic development.
|
|
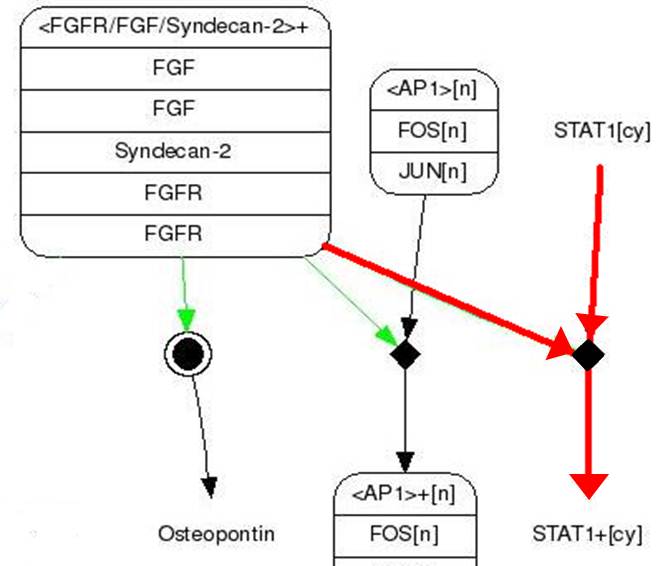
Fig.10 Unneccesary Syndecan-2 Function
|
- FGF binds to FGFR.(Syndecan-2 help in this process)
- STAT1 sticks to phosphorylating FGFR and then it gets phosphoryl group from FGFR(Phosphorylation)
- Two phosphorylating STAT1s attach each other and form dimer
- Dimer gets into nucleus and binds to GAS promoter
- Gene behind GAS promoter expresses.
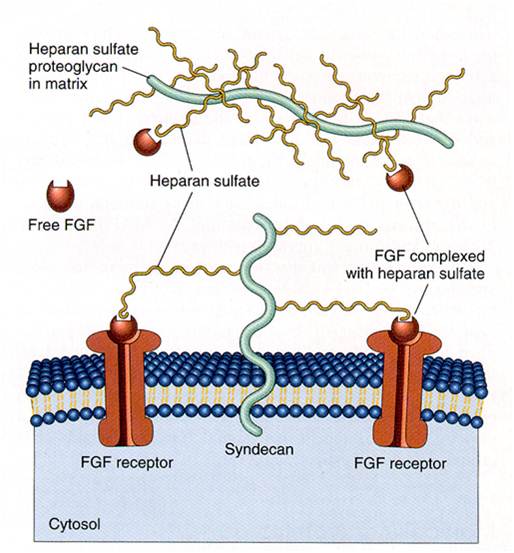
We applied this pathway to our project. Actually, Syndecan is a cell surface proteoglycan. Its core protein spans the plasma membrane and contains therr heparan sulfate chains and two chondroitin sulfate chains (not shown). The proteoglycans can codulate the activity of fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Free FGF binds poorly to the FGF receptor. Binding of FGF to the heparan sulfate chains like those on syndican allows FGF to bind efficiently its receptor. Binding of FGFto heparan sulfate in the ECM protects FGF and forms a reservoir of the growth factor. In addition we use antibody to detect tubercolusis antigen and GFP to confirm whether antigen is binded or not. Therefore, we don’t need Syndecan-2 because there is no FGF particle in this project.
Finally, we become to need only 3 genes (Fusion FGFR, STAT1, GFP with GAS promoter) in our project
Design Gene Activation For Output
Fig 11. Structural bases of unphosphorylated STAT1 association and receptor binding
STAT1 proteins with the formation of STAT1/1 dimers are confirmed using probe, namely the GAS probe. GAS probe(Gamma Activation Site probe) is the acute phase responsive element of the IL gene promoter and known to bind STAT1 dimer proteins. Using this pathway, we altered the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene instead of cytokine inducible genes. So, we could show GFP expression through the previous whole pathway.
Fig 12. Proteína fluorescente verde – história e perspectivas
For Success! Evidences of our project possibility
Fig 13. Success KAIST!
To successfully complete our project, we need 4 conditions work properly.
- FGFR should be expressed completely in yeast.
- FGFR and STAT1 should be located in appointed position in yeast.
- FGFR-STAT1 pathway should be operated normally to act normally as a transcription factor.
- Antibody fusion receptor should work properly to phosphorylate sub-pathway molecules, STAT1.
We have 4 papers which can prove our project works properly.
1. [Reconstitution of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Interactions in the Yeast Two Hybrid System] By Ronit A loni-Grinstein, Andrew Seddon, and Avner Yayon
>> This paper used yeast two hybrid system to show that FGFR interaction is possible in yeast. Through this paper, we knew that FGFR can be expressed completely in yeast without any functional disability and locate in outer cellular membrane.
2. [Jak2-Stat5 Interactions Analyzed in Yeast (Received for publication, January 30, 1998, and in revised form, March 2, 1998)] By Fariba Barahmand-Pour, Andreas Meinke, Bernd Groner, and Thomas Decker
>> This paper proves that JAK-STAT pathway is operated completely in yeast. The JAK in yeast phosphorylates STAT5 without any trouble. Since FGFR belongs to tyrosine kinase receptor family, same as JAK’s family, and STAT1 belongs to same protein family as STAT5 does, we could convince our signal delivery system. Consequently, we convinced that FGFR and STAT1 will be expressed completely to work as a signal pathway, and locate their appointed position properly.
3. [Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Induced Phosphorylation of STAT1 at the Golgi Apparatus Without Translocation to the Nucleus] By LUCI´A CITORES, LING BAI,2 VIGDIS SØRENSEN, AND SJUR OLSNES2
>> This paper shows that FGFR phosphorylate STAT1 at the golgi apparatus in human cell. The expressed FGFR at golgi apparatus phosphorylates STAT1, and the two phosphorylated STAT1 become dimerized to activate GAS promoter. The result of this study assures our FGFR-STAT1 pathway.
4. [Novel Recognition Motif on Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Mediates Direct Association and Activation of SNT Adapter Proteins](Received for publication, April 13, 1998) by Hong Xu, Kyung W. Lee, and Mitchell Goldfarb
>> In this paper, the researchers identified fusion FGFR, which combined with antigen called SNT, was phosphorylated itself automatically. Through this result, we confirmed that our fusion FGFR will be phosphorylated properly when combined with the targeted antigen.
According to these papers and searched results, we convince that our project’s pathway will work completely as we expected.
|
 "
"